This is an automatically translated article.
Post by Master, Doctor Le Thi Minh Huong - Resuscitation - Emergency Doctor - Resuscitation - Emergency Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital
1. ATP Resynthesis
ATP is an energy-rich compound. ATP reserve in a muscle bundle is not much (5mmol/1kg fresh muscle). In order for a muscle to contract for a long time, ATP must always be fully recovered. The energy used to recover ATP is created by breaking down other nutrients such as protein, fat, and sugar. This free energy will incorporate a phosphate group into ADP to produce ATP.
There are 3 energy systems to regenerate ATP to provide direct energy for muscles to work, they are:
Phosphate system Lactic system Oxygen system In which phosphate and lactic systems are anaerobic systems, and oxygen systems are hydrophilic systems. gas. The degree of involvement of the three energy systems in providing energy to regenerate ATP depends on the capacity and duration of muscle contraction, the operating conditions of the muscle, and the level of oxygen supply for body activity.
2. Phosphate energy system
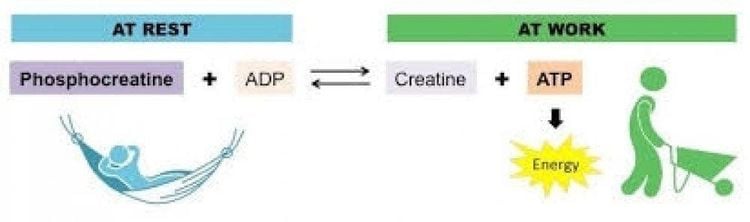
The amount of ATP expended during muscle contraction can be resynthesized by the energy of an energy-rich phosphate compound, CP (creatinphosphate) contained in the muscle. ATP and CP both belong to the phosphate group. Therefore, this energy system is called the phosphate energy system or the ATP-CP system.
This is the first and fastest energy supply system for the body's working muscles, independent of oxygen supply.
The breakdown of CP for energy is fast, with the greatest rate of ATP resynthesis occurring after the second second of muscle contraction. However, the reserve of CP in muscle is not large. CP concentration in skeletal muscle cells is 3-5 times higher than ATP concentration (at rest). The phosphate system has a maximum operating capacity of about 36Kcal/min. However, the amount of CP is small, so it can only be provided to create 5 Kcal, which is enough to resynthesize 0.5 mol ATP (so the operation time is short from the first 5-10 seconds)
Therefore, shoulder Its primary role is to provide energy for activities at maximum capacity (short runs, throws, pushups, jumps, weightlifting). Energy supplied by the CP source for muscle activity for a period of 6-8 seconds.
3. Lactic energy system
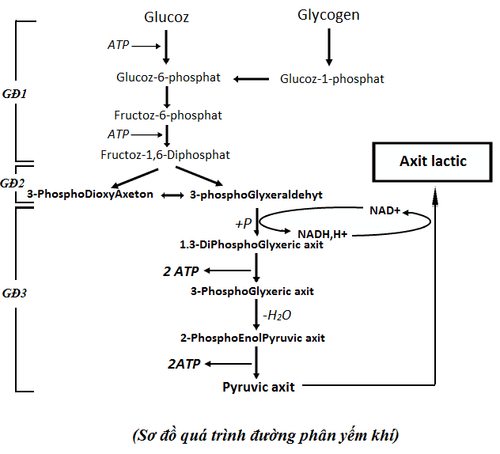
During relatively longer activities, the body uses energy to resynthesize ATP and CP by anaerobic breakdown of glucose. The reaction will produce lactic acid, which is toxic to muscle fatigue. Therefore, this energy system is called the Lactic system, also known as the Glycogen system. The substrate of this energy system is glycogen stored in the muscles, glucose in the blood transported to the muscles, and glucose from the liver transported into the blood.
This energy system has a smaller capacity than the Phosphagen system (3 times smaller than the phosphate system and 1.5 times larger than the oxygen system)
At maximum activity, anaerobic glycogenolysis occurs in no more than 25% of the glycogen. storage. Therefore, the capacity of the lactic energy system is not too large.
Anaerobic glycogenolysis in fact occurs from the very beginning of muscle activity, but the lactic system is at its maximum capacity after 30-40 seconds. Therefore, the lactic system plays a decisive role in providing energy in muscle activity lasting 20 seconds - 2.5 minutes with strong muscle contraction and high speed such as running 400-800m, swimming 50-200m. The increased operating capacity, the shorter the operating time, the higher the role of the lactic energy system.
In muscle activity, where the lactic acid system is responsible for providing energy, the glycogen in the muscles and in the liver is never used to the point of exhaustion. The limited energy of the lactic acid system is not due to low glycogen stores, but because the lactic acid produced inhibits the enzymes that break down glycogen.
The lactic system is an anaerobic system, occurring in activities with sub-maximal capacity, when the oxygen supply is lacking in the first time because the oxygen supply system has not yet developed its capacity and during activities. static force.
4. Oxygen energy system
During muscular activities that are not long-lasting and are supplied with adequate oxygen, that is, in aerobic activity, the body uses oxidative reactions of nutrients such as: sugars, proteins and fats. to provide energy for the body to function. This energy system is called the oxidation system.
In the 3 nutrients providing energy, the role of protid provides very small energy, but mainly glucid and lipid.
This oxidative energy system uses 2 main substances: sugar and fat to provide energy for muscle contraction. These two substances are markedly different in capacity as well as energy capacity. Therefore, they are used in different operating conditions.
Sugar oxidation: occurs like glucose hydrolysis in the lactic system. In this case, due to lack of oxygen, the anaerobic glycolysis of pyruvic acid will convert to lactic acid. Because this process contains oxygen, pyruvic acid does not convert to lactic acid but will continue to be oxidized to the final products, CO2 and H2O.
Complete oxidation of a glucose molecule will regenerate 19 times more ATP than anaerobic glycolysis. The oxygen system is therefore much more energy efficient than the anaerobic lactic system.
To break down glucose or glycogen by aerobic way, the body needs to absorb a certain amount of oxygen and requires a certain amount of time to carry out the oxidation process. Therefore, the capacity of the sugar oxidation system is lower than that of the lactic acid system.
The capacity of the glucose oxidation system depends on the glycogen stores in the muscle and liver, the liver's ability to regenerate glucose from other substances (lactic acid, amino acids, pyruvic acid ...) with a large capacity.
Meanwhile, the aerobic breakdown of fats produces more energy than the oxidation of sugars. Because body fat has a very large reserve (average 10%-30% of body weight), it can be enough energy for the body to operate continuously for dozens of days.
The rate of oxidation of sugars and fats is dependent on the capacity of the aerobic activity. The greater the capacity, the greater the percentage of sugar oxidation that contributes to the energy supply and correspondingly, the smaller the contribution of fat. During light and prolonged muscle activity, most of the energy is supplied by fat oxidation.
In high-capacity operations, energy is mainly supplied by sugar. When operating at maximum capacity and for a short time beyond the aerobic level, the lactic energy system begins to engage in activity.
Follow Vinmec International General Hospital website to get more health, nutrition and beauty information to protect the health of yourself and your loved ones in your family.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
REFERENCEShttps://www.uptodate.com/contents/muscle-examination-in-the-evaluation-of-weakness/abstract/1 Moxley RT 3rd. Evaluation of neuromuscular function in inflammatory myopathy . AU SO Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1994;20(4):827. Dinh Que Chau- Duong Huu Long: "Anatomy - Physiology" Medical Publishing House 2004 Trinh Van Minh: A collection of human anatomy pictures Medical Publishing House 1996.














