This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Master, Doctor Nguyen Ngoc Phu - Department of Intensive Care - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Aspiration pneumothorax is an important technique but not difficult to perform, a requirement that must be understood by emergency physicians in order to free the patient's pleural space from the pressure of the lung. Air by inserting a needle or catheter through the chest wall to drain the air out, restore the integrity of the pleural space, help the lungs expand, and restore breathing.
1. What is an emergency pneumothorax?
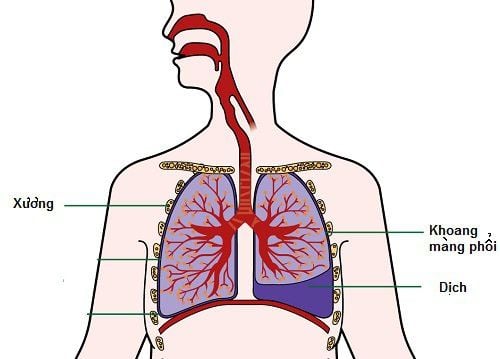
Anatomically, the pleura is made up of 2 pleural leaves: parietal and visceral. The visceral pleura closely encloses the lung parenchyma, and the spleen enters the slits of the lobes and lobes of the lung. The parietal pleura lines the medial surface of the thorax, contiguous with the visceral leaves at the hilum. The pleural space is a virtual space located between the parietal and visceral pleura. Normally your pleural space has a negative pressure (-4 to -7 mmHg). Each side will have 1 pleural cavity.
Pneumothorax is when there is an abnormal amount of air in the pleural space, between the lung and the chest wall. This is a fairly common respiratory disorder that can occur in a variety of clinical settings and can occur at any age.
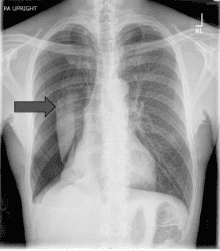
Kỹ thuật chọc hút, dẫn lưu khí màng phổi là 1 kỹ thuật cấp cứu nhằm giải phóng khoang màng phổi khỏi sự đè ép của khí bằng cách chọc kim hoặc catheter qua thành ngực dẫn lưu khí ra ngoài, trả lại sự nguyên vẹn của khoang màng phổi, giúp phổi nở ra, phục hồi lại tình trạng hô hấp. Kỹ thuật này thường thực hiện ở các khoa cấp cứu.
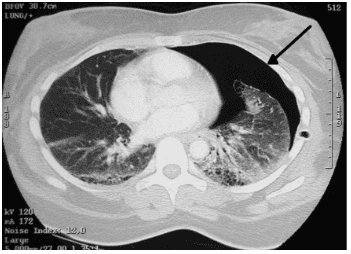
Chọc hút dẫn lưu khí màng phổi là 1 kỹ thuật quan trọng nhưng không phải khó thực hiện, là yêu cầu bắt buộc phải nắm rõ đối với các bác sĩ cấp cứu.
2. When to perform pneumothorax?
Spontaneous pneumothorax : Spontaneous pneumothorax is a condition in which air appears suddenly in the pleural space due to pathological lesions of the pleural lung causing
T tension pneumothorax : Pneumothorax Pneumothorax is air that either enters the pleural space from the lungs or from outside the body, usually due to a lung tear that allows air to escape into the pleural space but not return. Active ventilation is likely to worsen symptoms. Increased pressure in the pleural space pushes the mediastinum to the opposite side and impedes venous return to the heart. This condition leads to circulatory and respiratory instability.
3. When is a pneumothorax not performed?
There are no absolute contraindications.
The doctor may consider not conducting a pneumothorax for the patient when:
Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax: When you have an underlying medical condition such as COPD, bronchial asthma, pulmonary tuberculosis ... often Doctors will conduct emergency pleural drainage opening. - Pneumothorax due to non-pressure trauma. Attention when present: Coagulation disorders: If you have accompanying abnormalities such as thrombocytopenia, blood clotting disorders, the doctor will correct the disorders early if necessary. Skin infection at the intended site of aspiration.
4. How is aspiration aspiration performed?

Trước khi thực hiện chọc hút dẫn lưu khí bệnh nhân cần làm một số kiểm tra như đo huyết áp,đo SpO2, nhịp thở
Step 1: Prepare:
Patient: The patient will be explained about the diagnosis, the condition of the injury, why the procedure is needed, and the benefits and risks. Patients or relatives will have to sign a consent form before the procedure, will have to prepare medical records and do some tests (counting pulse, measuring blood pressure, measuring SpO2, breathing rate) before the procedure. perform the trick. Equipment: Skin antiseptic solution (alcohol, iodine), local anesthetic (lidocaine 2%, needle 25G, syringe 5ml), gloves, hat, shirt, sterile mask, sterile acid, SpO2 monitoring device , pneumothorax needle (usually 16-18G), lead with 3-prong lock, 50ml air suction syringe or suction device, pleural opener (when necessary, open pleural drainage) ). The crew performing the procedure: 01 emergency resuscitation specialist, 01 nurse assistant doctor. Step 2: Steps to perform the procedure
The doctor will put the patient in the Fowler position or recline in a chair. Examine and locate your pneumothorax again and compare with radiographs. The doctor will disinfect the needle puncture site. Usually 2nd intercostal space on the mid-clavicle line or 4th or 5th intercostal space above your midaxillary line. Next, a sterile dressing will be performed and an anesthetic will be injected. The doctor will insert a large needle or catheter perpendicularly through the area under anesthesia, close to the upper border of the lower rib, and maintain continuous vacuum until it enters your pleural space and can see the air coming out easily. . If it is a threaded needle, the iron needle will be removed and connected to a 3-prong lock. In the case of a catheter, the doctor will pull out the metal barrel to leave the plastic sheath, then insert the flexible catheter through the plastic sheath into the pleural cavity and pull out the plastic sheath, pull out the lead in the catheter barrel, connect the catheter to the key 3. fork and fix the catheter. The doctor will suck air with a 50ml syringe until there is no more air and the 3 prongs will be locked. Your doctor will watch you for about 6-8 hours, then take another X-ray. If the gas is gone and the patient's clinical condition is stable, they will be sent home for monitoring. If the air is not exhausted, the doctor will conduct continuous suction and drainage and the patient must be hospitalized for treatment and monitoring. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely rest in peace. examination and treatment center at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.