This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Pham Van Hung - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. The doctor has 30 years of experience in examination and treatment of internal diseases, especially in Cardiology.Venous malformation is a common vascular malformation with an incidence of up to 50%. Treatment of venous malformations has many different methods, but patients should learn as well as consult a specialist to come up with the most appropriate treatment plan.
1. What is a venous malformation?
Vascular malformation is an abnormal development of blood vessels during embryogenesis and will stay with the patient for the rest of his life if left untreated. Vascular malformations according to the classification of the International Association for the Study of Vascular Abnormalities (ISSVA) in 1996 include:High-flow vascular malformations: Arteriovenous malformations, arteriovenous malformations, and vascular malformations Low: Venous malformation, lymphatic malformation, capillary malformation Combined vascular malformation: Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome, Proteus syndrome, Parkes-Weber syndrome, Maffucci syndrome, Venous malformation as a soft mass Easy to press down, the lesion is usually blue-violet, sometimes calcified nodules can be palpated by hand, commonly known as venous stones.
Lesions of venous malformations can be very small or take a long time to develop. Varicose veins can form in many different places on the body and cause many injuries such as:
Varicose veins of the extremities will unbalance the two limbs. Venous malformations in bones cause pathological fractures, bone weakness. Varicose veins in the gastrointestinal tract lead to chronic bleeding and anemia, part of the Blue Rubber Bleb syndrome. Cluster vein malformation (cluster hemangioma). Familial mucocutaneous malformation causes dome-shaped skin lesions.
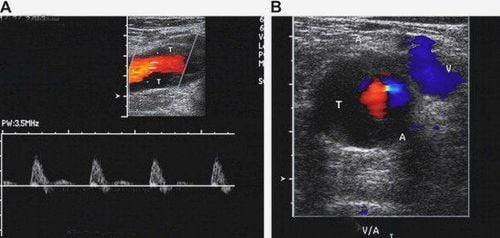
2. Subclinical diagnosis of venous malformation
Usually venous malformations are diagnosed clinically. However, for venous malformations in unspecified locations, it is necessary to rely on the following diagnoses:Doppler ultrasound: This is an ultrasound method of blood vessels, using high-frequency sound waves to simulate the image as well. Like arteriovenous activity, this method is painless for the patient and gives accurate results. Magnetic resonance imaging: This is a way to assess the limits of the lesion, help the doctor diagnose and give the most appropriate treatment. Standard X-ray: This helps detect venous stones.
3. Treatment methods for venous malformations
3.1 Medical treatment
3.1.1 Compression tape
This is a method used for venous malformations of the extremities with the aim of reducing pain and reducing blood clots and preventing chronic ulcers.This method should be used from an early age to create a habit later. The bands are designed by experts and for growing children, they will be resized to accommodate growth. This method is not used for patients with varicose veins because it will cause pain for the patient. This is also an effective support method for the treatment of venous malformations by sclerotherapy.
3.1.2 Anticoagulants
Venous malformations will form a clotting disorder, so the use of anticoagulants is essential. Some anticoagulants used for this disease are low-dose Aspirin combined with anti-inflammatory drugs, Heparin, oral anticoagulants...
3.2 Interventional treatment
In order to treat vascular interventions, it is imperative for the physician to understand the extent and severity of the vascular malformation. At the same time, the risk of thrombosis, bleeding, the possibility of nerve damage, skin, skeletal muscle damage as well as the ability to improve life after treatment must be assessed.Some intervention methods are as follows:
3.2.1 Surgical methods
This is the earliest and only method to completely treat vascular malformations in general and venous malformations in particular. However, this method comes with many risks such as extensive bleeding and recurrence of the disease.This method is chosen to use when the method of sclerotherapy of venous malformations cannot be performed due to the location of the malformation or the lesion is too large. For invasive venous malformations, open surgery removes the deformity in the joint and avoids joint damage.
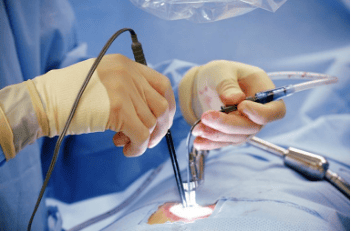
3.2.2 Method of sclerotherapy of venous malformation
This is the first choice in the treatment of venous malformations with the aim of destroying the malformed blood vessels by causing endovascular damage through inflammation and fibrosis leading to destruction of the malformed blood vessels.3.2.3 Laser method
This method is gradually being widely used in the treatment of vascular malformations. This method only works for superficial lesions on the skin or on the mucous membranes of the head and neck.Used preoperatively for large vein malformations to remove the malformation and form a fibrous band for easy resection and reduce bleeding during surgery.
3.2.4 Button method
This method is often used in conjunction with sclerotherapy to help improve the success rate of sclerotherapy. However, this method is not used for venous malformations of large volume and diameter.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website for the best service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE ALSO :
Recognizing the types of vascular malformations on the skin Overview of dynamic - venous malformations Direct sclerotherapy treatment of venous malformations under digital angiography erasing the background