There are many causes of arrhythmias, such as stress, anxiety, the use of certain medications, anemia, fever, dehydration, and low potassium levels in the blood. Additionally, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is also a factor that affects heart function.
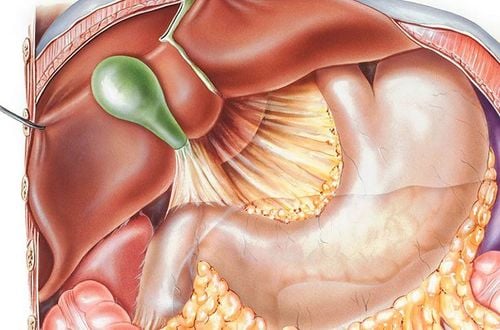
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD is a condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, occurring occasionally or frequently. The causes of GERD include delayed stomach emptying, sudden increases in abdominal pressure, stress, tension, and unhealthy eating habits.
GERD causes several symptoms such as:
Belching, acid reflux, heartburn: These symptoms increase after eating, drinking water, or when feeling bloated and indigested, or when bending forward, lying down, or sleeping at night.
Nausea and vomiting: Patients may feel pressure and tightness in the chest, radiating to the back and arms. This is why GERD is often mistaken for heart disease. The pain is felt in the esophagus running through the chest. Stomach acid reflux stimulates the nerve endings on the surface of the esophageal lining, causing pain similar to chest pain.
Difficulty swallowing: As GERD worsens, the frequency and amount of stomach acid reflux increase, causing swelling and inflammation of the esophageal lining, leading to difficulty swallowing and a sensation of something stuck in the throat
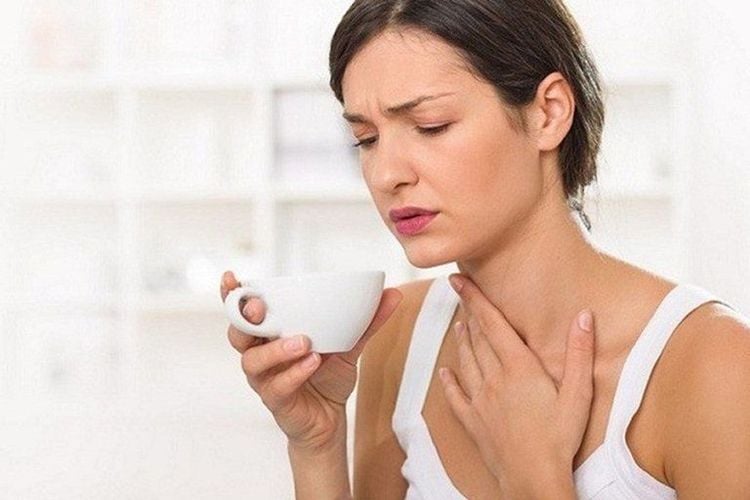

Hoarseness and coughing: Acid reflux can irritate the vocal cords, causing hoarseness and persistent coughing.
Increased saliva production: This is a natural reflex when experiencing acid reflux, as saliva is produced to neutralize the acid.
Bitter taste in the mouth: Refluxed stomach acid mixed with bile causes a bitter taste in the mouth. This indicates a disturbance in the stomach's nervous system, causing the pyloric valve to open excessively and bile to reflux.
2. What is Arrhythmia?
An arrhythmia is an abnormal heart rhythm, which can be too fast or too slow. It can occur at any age and at any time. Arrhythmias can cause symptoms such as:
-Palpitations
-Pounding in the chest
-Chest tightness
-Shortness of breath
Normal heart rhythm originates from the sinus node and conducts to cause atrial depolarization, then conducts through the atrioventricular node-His bundle and Purkinje network to cause ventricular depolarization, helping the ventricles. This activity occurs rhythmically and relatively regularly. Therefore, the normal heart rate ranges from 60-100 beats per minute.
There are many causes of arrhythmias, such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, heart failure, diabetes, or the use of stimulants like tobacco and alcohol. Additionally, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is also one of the causes of arrhythmias.
3. GERD Causes Arrhythmias
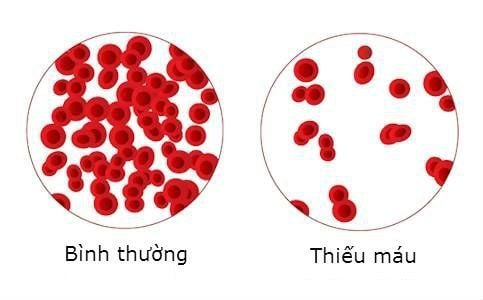
Anemia can be a cause of GERD leading to arrhythmias.
GERD causes stomach acid to reflux and stimulate the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve regulates heart rate and stomach acid secretion. When stimulated, it can cause symptoms like rapid heart rate, shortness of breath, and palpitations.
Additionally, some causes of GERD are also causes of arrhythmias, such as:
-Use of stimulants: alcohol, beer, tobacco
-Stress
-Hormonal changes
-Fever
-Anemia
-Hyperthyroidism
Side effects of medications like cough, cold, flu, and asthma medications
4. Diagnosing Arrhythmias
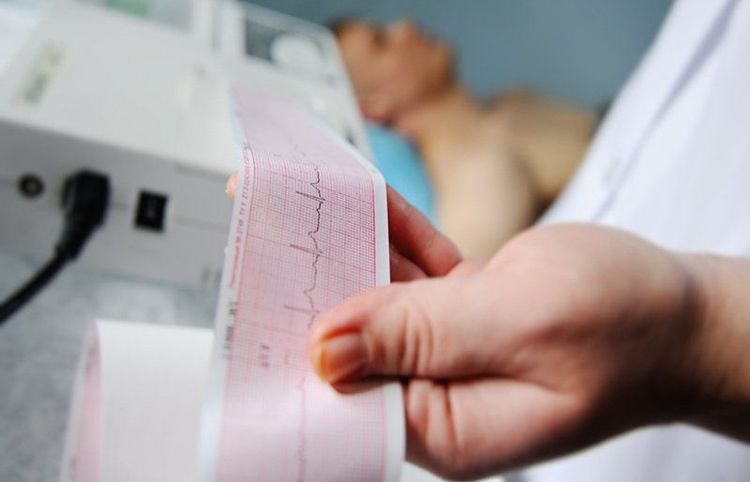
Some methods to diagnose arrhythmias include:
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Records the electrical impulses from the heart and monitors heart rate. It can be performed at rest or during exercise.
Holter monitor: A medical device that records the heart's electrical activity. The Holter monitor can record up to 7 days, allowing for the diagnosis of arrhythmias throughout the day.
Heart rate monitor: Records heart rate information, allowing patients to monitor their condition when arrhythmias occur.
Echocardiogram: An important method to check for heart abnormalities. The echocardiogram results help assess the structure and function of the heart.
5. Treating Arrhythmias Caused by GERD
To treat arrhythmias caused by GERD, it is essential to control GERD and limit acid reflux. Additionally, patients should adopt a healthy lifestyle to reduce arrhythmia symptoms, such as:
Practicing meditation, yoga, and light exercise to increase endorphins and reduce stress
Deep breathing exercises
Limiting and avoiding activities that cause anxiety
In summary, GERD causes acid reflux that stimulates the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve regulates heart rate and stomach acid secretion. Therefore, GERD can cause arrhythmias. If arrhythmia symptoms worsen, such as palpitations, shortness of breath, or chest pain, patients should seek medical attention immediately.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.