This article has been professionally reviewed by specialists in Gastroenterology, Department of Outpatient Services & General Medicine, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Gallbladder polyps are a common condition in adults, occurring more frequently in women than in men. In most cases, gallbladder polyps do not present specific symptoms, leaving many patients wondering whether these polyps can resolve on their own and when surgical intervention is required.
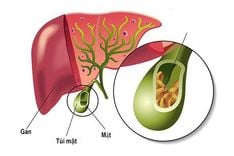
1. What are gallbladder polyps?
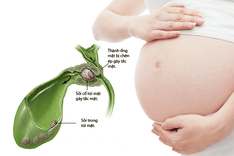
Gallbladder polyps are tumor-like or pseudotumor growths that develop on the surface of the gallbladder mucosa, originating from the gallbladder wall and protruding into the gallbladder lumen. The condition can occur at any age but is most common in adults. Some authors suggest that the condition is more frequent in women aged 30-50 years.
Most cases of gallbladder polyps rarely cause acute symptoms such as pain, fever, or jaundice, which are typically seen in gallstones or biliary tract infections. The symptoms are often similar to those of bile duct stones, chronic gallbladder stones, or gastric-duodenal diseases.
2. Causes
There are many factors believed to be associated with the formation of gallbladder polyps, such as poor liver function, blood sugar disorders, high cholesterol, obesity, irregular eating habits, and viral hepatitis infections. However, no study has definitively identified the exact cause of the condition.
3. Clinical Symptoms
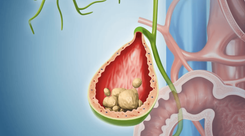
The number and size of biliary polyps can vary significantly, but the most common are single polyps smaller than 10 mm. In some cases, patients may have multiple polyps in the gallbladder or polyps ranging in size from 20-40 mm, and there may even be polyps accompanied by gallstones.
Most cases of gallbladder polyps are asymptomatic and are often discovered incidentally during routine health check-ups or when examining for other reasons. Only about 6-7% of patients with biliary polyps experience symptoms, typically in those with larger polyps. The most common symptoms include pain in the right upper quadrant or epigastric area, with a few cases accompanied by nausea, vomiting, indigestion, and a mild sensation of tightness in the right upper quadrant.

4. Diagnosis of Gallbladder Polyps
To diagnose gallbladder polyps, it is necessary to use various diagnostic and supportive tests (such as liver function tests, biopsy, endoscopic ultrasound, upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, etc.).
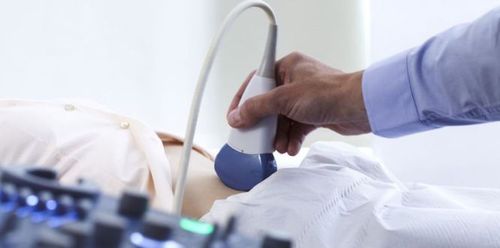
Ultrasound is a highly valuable technique in diagnosing biliary polyps. However, ultrasound cannot differentiate between benign and malignant polyps to determine the need for surgery. Therefore, it is necessary to combine other techniques to assist in diagnosis.
For polyps smaller than 10 mm that do not cause any discomfort, doctors typically recommend periodic ultrasound monitoring every 6 months to 1 year to check if the polyp is growing rapidly.
5. Do gallbladder polyps disappear on their own?
95% of gallbladder polyps are naturally benign (non-cancerous), meaning patients typically do not need to undergo biliary removal. People can live peacefully with gallbladder polyps. However, regular follow-up examinations are necessary to monitor their progression.
For large polyps, those with a broad base, rapid growth, or in significant numbers, it is crucial to follow the doctor's recommendation on whether surgery is necessary. If polyps are not removed, there is a risk of them developing into malignant cancer.
According to domestic and international studies, gallbladder polyps smaller than 10 mm observed on ultrasound are mostly benign. Malignant features include a broad base, irregular shape, and rapid growth. In such cases, surgical removal of the gallbladder is recommended to eliminate the polyps.
In younger individuals, if the polyps are smaller than 1.5 mm and have a low risk of becoming cancerous, doctors may advise monitoring instead of immediate cholecystectomy. However, regular check-ups are essential for health monitoring. So, when is biliary polyp surgery necessary?
6. When is surgery necessary?
Since the exact nature of gallbladder polyps cannot be accurately diagnosed without surgical intervention, doctors have established the following treatment protocol for gallbladder polyps:
- Polyps with a broad base (sessile polyps).
- Polyps larger than 10 mm.
- Small polyps that cluster together inside the gallbladder.
- Polyps that exhibit rapid and abnormal growth, easily spreading or increasing in number and size over a short period.
- Polyps in individuals over 50 years of age.
- Polyps with symptoms that frequently cause cholecystitis.
- Polyps in individuals with primary sclerosing cholangitis or gallstones.
Currently, with the advancement of laparoscopic surgery, laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the gold standard for treating gallbladder polyps or gallstones. This is a minimally invasive procedure that is painless, allows for quick recovery, and has fewer complications when performed by experienced surgeons.
For pseudopolyps, it is sufficient to follow a low-fat diet, limiting fats, animal organs, shrimp, and red meats (such as dog meat, beef, and buffalo). In cases where the gallbladder has been removed, it is important to maintain an easily digestible diet and schedule regular follow-ups for careful health monitoring.
Please call the HOTLINE for more information or to book an appointment HERE. Download the MyVinmec app for quick appointment booking and easy schedule management.