Upper abdominal cramping can occur due to various causes. It is a common symptom that can often be managed with home care or medication. However, in some severe cases, patients should seek medical attention immediately. The following article will help us better understand this condition.
This article was medically reviewed by MSc. Phan Thi Minh Huong, Level II Specialist in Gastroenterology at the Department of General Examination & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Da Nang International Hospital.
1. Causes of Upper Abdominal Cramping
1.1. Intestinal Gas Causing Upper Abdominal Pain
Intestinal gas exists in the human digestive system and may escape through belching or flatulence.
When infections, viruses, diarrhea, or constipation occur, patients may experience intense upper abdominal cramping. Gas accumulation may be the cause if:
- The abdominal pain occurs intermittently.
- The abdomen feels bloated.
- There is a sensation of something moving inside the stomach.
- Belching or flatulence occurs frequently.
- Symptoms of diarrhea or constipation accompany the pain.
To reduce gas, patients should eat more slowly to avoid swallowing air and limit gas-producing foods such as broccoli.
Intestinal gas typically resolves on its own within a few hours without medical intervention. However, if gas-related abdominal pain is accompanied by fever, uncontrollable vomiting, or severe cramping, consult a doctor immediately.
1.2. Indigestion
Indigestion causes discomfort or pain in the upper digestive tract, including the stomach, esophagus, or duodenum. Pain may also be felt originating from the chest. This condition often occurs when there is excessive stomach acid or after consuming highly acidic foods.
In rare cases, indigestion may result from gastric ulcers, acid reflux, or even stomach cancer. Persistent indigestion accompanied by severe pain or unexplained weight loss may signal a more serious health condition.
Treatment: Over-the-counter medications can temporarily relieve indigestion symptoms. Identifying and avoiding trigger foods, along with lifestyle modifications, are essential for managing indigestion effectively.
Those with chronic or severe indigestion should seek medical care to identify underlying causes and receive appropriate treatment.
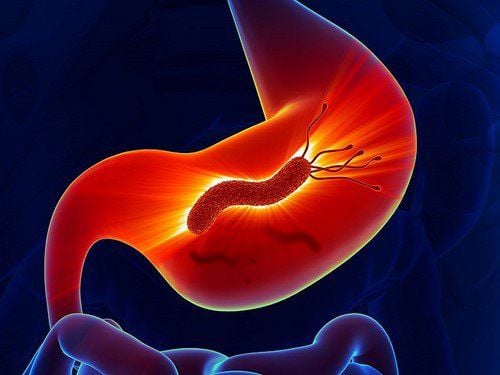
1.3. Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammation of the stomach lining, causing swelling and pain. Acute gastritis develops suddenly and may result from Helicobacter pylori (HP) infection.
Chronic gastritis may be caused by:
- Crohn's disease.
- Autoimmune disorders.
- Sarcoidosis.
- Viral infections, particularly in immunocompromised individuals
Treatment: Antibiotics are often used to treat infections. In chronic gastritis cases, diagnosing and treating the underlying cause is crucial for optimal outcomes.
- Dietary adjustments to reduce stomach acid.
- Pain relievers to alleviate symptoms.
- Medications to protect the stomach lining and prevent worsening symptoms.
1.4. Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, often caused by a virus, results in symptoms such as:
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Diarrhea.
- Pain in the upper abdomen or near the breastbone.
Most symptoms usually resolve on their own within a few days. To ease the symptoms, patients should avoid heavy meals and drink plain water to reduce nausea.
Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial for overall health; therefore, patients should consider drinking electrolyte replacement solutions, such as oral rehydration solution (ORS), until symptoms improve. In some cases, especially for individuals with weakened immune systems, infants, young children, or those with severe illnesses like cancer, medical attention may be required for intravenous fluid administration to prevent severe dehydration.
1.5. Appendicitis
Appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes infected. Without timely treatment, the appendix can rupture, posing severe health risks.
Pain typically starts as a dull ache around the navel and may spread upward. As the infection worsens, the pain often shifts to the lower right abdomen.
Treatment: Surgical removal of the appendix is the primary treatment.
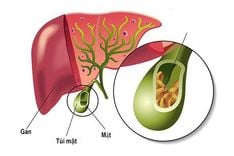
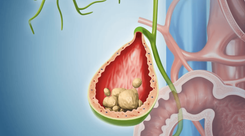
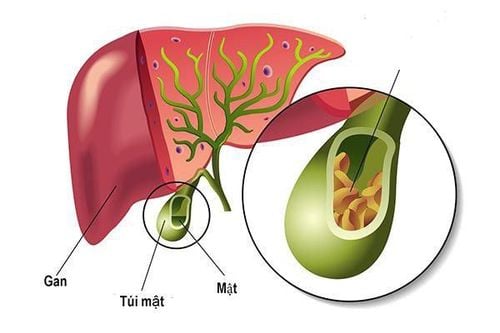
1.6. Gallstones
The gallbladder, located under the liver on the right side of the abdomen, stores bile to aid digestion. Gallstones form due to an imbalance of bile components, such as bile salts, bilirubin, and cholesterol.
Gallstones that block the gallbladder can cause:
- Severe pain in the upper right abdomen.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Fatigue and exhaustion.
If untreated, gallstones can impair liver and pancreatic function, causing jaundice, yellowing of the eyes, or severe pancreatic infections.
Surgical removal of the gallbladder is the most common solution. Medications may be prescribed to dissolve gallstones.
Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and a low-fat diet, can reduce the risk of recurrence.
1.7. Liver or Pancreatic Issues
The liver, pancreas, and gallbladder play critical roles in digestion. Gallstones can obstruct bile flow, leading to pain in the liver or pancreas.
Conditions such as hepatitis, pancreatitis, or, less commonly, liver cancer or pancreatic cancer may cause upper abdominal pain.
Other symptoms include:
- Jaundice.
- Dark urine.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Worsening pain over time.
- Jaundice.
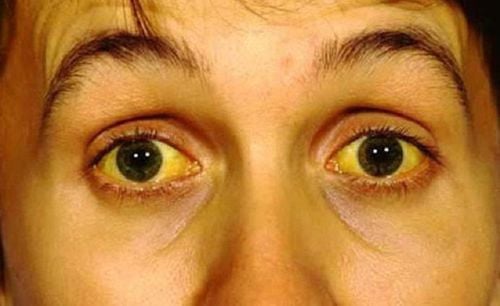
The treatment for liver or pancreatic issues depends on the underlying cause of upper abdominal cramping. Patients with pancreatitis may require hospitalization for intravenous fluids and close monitoring. For liver diseases, treatment may involve medications or liver transplantation in severe cases.
In cases of liver or pancreatic cancer, treatment options may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery. Regardless of the cause, early diagnosis plays a crucial role in improving treatment outcomes and saving patients' lives.
1.8. Bowel Obstruction
Bowel obstruction occurs when the movement of gas and digestive fluids is blocked, causing severe abdominal pain, constipation, and digestion difficulties.
Symptoms include:
- Extreme bloating.
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Constipation or diarrhea.
- Abdominal cramping
- Swelling.
The symptoms of bowel obstruction can vary depending on the location of the blockage. For example, vomiting is often an early sign of small bowel obstruction, whereas this symptom appears later in cases of large bowel obstruction. Partial bowel obstruction may cause diarrhea, while complete obstruction can lead to constipation. Additionally, bowel obstruction can cause a high fever if a part of the intestinal wall becomes perforated.
Bowel obstruction is a medical emergency due to the risk of intestinal perforation or severe infection. Pain relievers, fluids, and other medications are often prescribed; however, in some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the cause of the obstruction.
2. Is Upper Abdominal Cramping Dangerous?
In most cases, upper abdominal cramping due to indigestion can be treated with home remedies or medications.
However, persistent or severe pain may indicate serious conditions such as acute pancreatitis, hepatitis, or stomach ulcers. If symptoms persist, patients should seek medical attention promptly.
3. How to Relieve Upper Abdominal Cramping
To alleviate symptoms, patients can try the following methods:
- Apply a warm compress or a hot water bottle to the painful area.
- Drink warm water or ginger honey tea. Avoid cold drinks.
- Consume water boiled with tangerine peel, fresh ginger, and rice (a traditional remedy).
- Increase intake of fruits and vegetables while avoiding foods that irritate the stomach.
- Rest and avoid strenuous activity.
4. When Should You See a Doctor?
In most cases, patients only need to monitor whether the upper abdominal cramping near the breastbone subsides. If the pain persists or becomes more severe, medical attention should be sought.
Patients should see a doctor within 24 hours if the following conditions occur:
- Vomiting lasting more than 12 hours.
- Fever accompanied by abdominal pain.
- Pain after a physical injury.
- Pain after starting a new medication.
- Symptoms in immunocompromised individuals (e.g., HIV patients, cancer patients, or those on immunosuppressive drugs).
Seek emergency care if you experience:
- Severe upper right abdominal pain.
- Intense stomach pain that is unbearable.
- Pale or white-colored stools.
- Severe abdominal pain in pregnant women.
- Severe dehydration symptoms (e.g., dry lips, dizziness, sunken eyes).
- Persistent vomiting or high fever in infants.
While upper abdominal cramping is often caused by minor issues like indigestion, it may also signal serious conditions like gastritis, appendicitis, or gallstones. For unexplained or severe pain, visit a hospital for an accurate diagnosis and timely treatment.
Vinmec International Hospital is a trusted facility for diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal diseases. Contact the Vinmec Healthcare System for consultations and treatment nationwide.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.