This is an automatically translated article.
Stunting and rickets in children are two different diseases. There are children who are chubby, eat and sleep well, are not malnourished, but still have rickets (abdominal rickets). On the other hand, there are many children who are stunted and malnourished but never have rickets.1. How to distinguish rickets and stunting
1.1. Manifestations of disease
Stunting: A stunted child is a child who is malnourished, lacking in essential nutrients in the body, affecting the child's life process, activities as well as development. Stunted children have lower measurements of height and weight than normal children, with or without rickets. Symptoms of stunted children are fatigue, inactivity, loss of appetite, fussiness, little sleep, or illness, slow crawling, walking, and teething. Some children have generalized edema, skin pigmentation disorders, pale skin anemia,... Rickets: can be seen even in very plump children due to higher calcium and phosphorus requirements than normal children. often. Children with rickets have symptoms of crying, not sleeping well, or being startled, sweating, hair loss at the nape of the neck, forming a scarf. In addition, children have wide fontanelles, soft fontanelles, and tight fontanelles. If severe rickets, not promptly detected and treated, the child may have chicken breasts, ankles and wrists, bow legs, or constipation, narrow pelvis, slow crawling, crawling, standing, Go,...
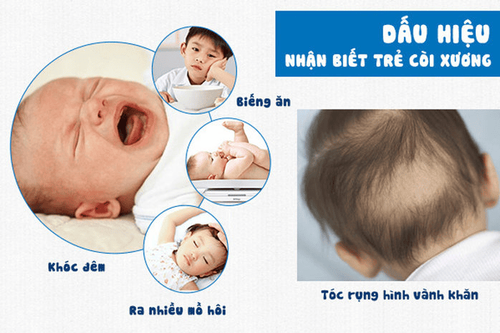
Biểu hiện của trẻ bị còi xương
1.2. The cause to the illness
Stunting: Due to many different reasons: parents lack of knowledge on child rearing, so wean the baby early, give complementary foods too early or too late, food for children is not of good quality,... In addition, children with acute or chronic infections (chronic bronchitis, tuberculosis, measles, diarrhea,...), lack of food due to difficult family conditions, premature babies or other diseases , ... also prone to stunting. Rickets: A condition in which the baby's body is deficient in vitamin D, leading to the inability to absorb and metabolize calcium and phosphorus, which cannot meet the needs of bone development, causing damage to the bones. Rickets can be seen in even very plump babies (abdominal rickets) because the need for calcium and phosphorus is greater than in normal children.
1.3. Complications of the disease
Stunting: The status of stunting and malnutrition in children affects physical development, intelligence, health and increases the risk of diseases for children. In addition, this condition also increases the risk of death in children under 5 years of age. Children are prone to respiratory infections and severe, prolonged diarrhea. In addition, children are also at risk of physical and mental retardation, reduced development of organs, especially the musculoskeletal system, affecting height and ability to work in adulthood.

Trẻ còi cọc dễ bị tiêu chảy nặng kéo dài
Rickets: reducing height, limiting respiratory function, causing slow growth of the child's body, abnormally curved spine, bone deformities, tooth defects, gait changes and adverse effects on fertility fertility in girls due to narrow pelvis. In addition, children are pale, anemic, or have recurrent pneumonia and even epilepsy.
2. How to care and treat children with stunting and rickets
2.1. With stunted children
If the child is stunted, malnourished with moderate and mild severity, it can be treated at home by adjusting and increasing the food intake, finding the cause and eliminating the cause of malnutrition, and treating the diseases. infection (if any). In addition, parents need to monitor their children's weekly and monthly weight and complete immunizations.
For children with severe malnutrition, they need to be treated at the hospital with methods such as rehydration - electrolytes, vitamin and mineral supplements, protein infusion, anti-infection, anemia treatment, anti-hypothermia and anti-hypoglycemia,...
2.2. With children with rickets
To treat this disease, parents need to follow these instructions:
Cho trẻ tắm nắng mỗi ngày để hấp thu đủ lượng vitamin D cơ thể cần
Let children sunbathe daily: expose children's feet, hands, back, belly for 10-15 minutes in the morning (before 9am) to be exposed to the sun. In winter, when there is no sunlight, parents can let their children take electric baths in big hospitals. Under the skin's available provitamin D is 7 dehydrocholesterol, under the influence of sunlight, the provitamin D will be activated and converted into vitamin D to support the body's metabolism and absorption of calcium and phosphorus. Preventive treatment by giving children extra vitamin D as recommended by doctors. Specifically: give the child vitamin D 4000 UI/day for 4-8 weeks. For children with pneumonia, diarrhea, it is necessary to increase the dose from 5000 to 10,000 UI/day for 1 month or inject vitamin D 200,000 UI/time, repeat injection once every 3 months in the first year. For children with rickets, use calcium-containing products such as 1-2 tubes of calcium B1 - B2 - B6 per day. Older children can eat calcium nuggets 1-2 teaspoons/day. Adjust diet: Breastfeeding children, eating calcium-rich foods such as shrimp, crabs, fish, eggs, milk, animal liver, etc. In addition, parents should also add fat to their meals. Daily dose of vitamin D is sufficient for children because vitamin D is fat-soluble, so adding oil helps children absorb vitamin D more easily. In addition, to improve rickets in children, parents should also supplement children with supportive products containing lysine, essential micro-minerals and vitamins such as zinc, chromium, selenium, and B vitamins to help meet meet the nutritional needs of children. At the same time, these essential vitamins also support digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, help improve anorexia, and help children eat well. Parents can also apply dietary supplements and functional foods derived from nature for easy absorption by the baby. The most important thing is that the improvement of the baby's symptoms must take place over the long term. Combining many types of functional foods at the same time or changing many types in a short time can make the baby's digestive system unable to adapt and completely not good. Therefore, parents must be really persistent with their children and regularly visit the website vimec.com to update useful baby care information.