This article has been professionally consulted with Trinh Thi Thanh Huyen M.D M.S- Obstetrician-Gynecologist - Obstetrics and Gynecology Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Oral sex is the use of the mouth, lips, or tongue to stimulate a partner (acting on the genitals, genitals, or anus). Anyone engaging in oral sex with a person who has a sexually transmitted infection is at risk of contracting the disease.
Sexually transmitted diseases that can be transmitted through oral sex
1. Gonorrhea
Symptoms: Not everyone with gonorrhea will have symptoms. Common symptoms include:
- Burning sensation when urinating
- Sore throat
- Abnormal discharge from the vagina, penis, or rectum
- Swollen or painful testicles
- Rectal pain
Transmission: Gonorrhea can be spread through oral sex with someone who has gonorrhea in their mouth, vagina, penis, urethra, or rectum.
Diagnosis and Treatment: Doctors will test a urine sample to diagnose gonorrhea. Samples may also be taken from the:
- Throat
- Rectum
- Urethra in males
- Cervix in females
Gonorrhea can be cured with antibiotics. However, antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea is becoming more common.
If symptoms persist after treatment, seek medical attention.
Complications: If left untreated, complications can include:
- Increased risk of HIV infection
- Infertility in women
- Epididymitis in men
2. Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
Symptoms:
Often, people with chlamydia have no symptoms.
However, if you have chlamydia in your throat, you may have a sore throat.
If you have chlamydia in other parts of your body, such as your rectum, genitals, or urinary tract, you may experience:
- Abnormal discharge, such as bloody discharge, from the vagina, penis, or rectum
- Burning sensation when urinating
- Rectal pain
- Swollen or painful testicles
Transmission: Chlamydia can be spread from an infected person (with chlamydia in their throat, vagina, penis, or rectum) to an uninfected person through oral sex.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Doctors will test a urine sample or a sample of vaginal discharge (for women) for chlamydia.
Chlamydia can be cured with antibiotics. During treatment, avoid sexual contact until you are completely healed.
Complications: Chlamydia can be completely cured with antibiotics, so it's important to get treated as soon as possible to reduce the risk of infecting your sexual partners.
If left untreated, risks include:
- Infertility in women
- Epididymitis in men
- Increased risk of HIV infection
- Transmission to baby during pregnancy
3. Syphilis
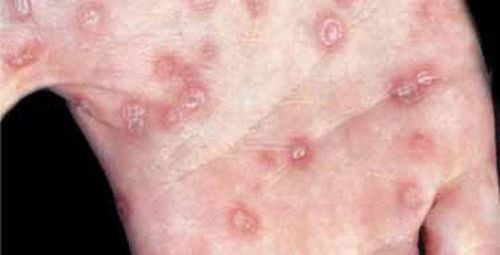
Symptoms: Early symptoms of syphilis are often mild and easily overlooked. Syphilis progresses through four stages, each with distinct symptoms.
Primary Syphilis:
- The hallmark of this stage is a syphilitic chancre (at the site of infection): a painless, firm sore that is usually round or oval.
- The chancre may go away on its own in 3-6 weeks, but this does not mean the infection is gone. The patient needs to be examined and treated by a doctor to be truly cured.
Secondary Syphilis: Symptoms include:
- A rash over the body
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Fever
- Sore throat, genitals, or anus
- Flat, dark-red sores on the palms and soles
- Hair loss
- Headache
- Weight loss
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
Symptoms may disappear on their own, but patients still need treatment to fully recover and prevent the disease from progressing
Latent Syphilis:
- This stage is asymptomatic, and the disease can progress for many years.
Tertiary Syphilis: This stage is now rare, as it can take 10-30 years to develop after the initial infection with the syphilis spirochete left untreated.
Complications of tertiary syphilis include:
- Damage to internal organs
- Vision loss
Neurosyphilis occurs when the disease spreads to the brain and nervous system. Symptoms include:
- Headache
- Difficulty coordinating movements
- Numbness
- Dementia
If left untreated, tertiary syphilis can be fatal.
Transmission:
Can oral sex transmit syphilis? The answer is yes. Syphilis can be transmitted through oral sex with an infected person, especially when there is direct contact with a syphilis sore or rash
Diagnosis and Treatment:
A blood test will be conducted to determine if the patient is infected with syphilis. If the patient has a chancre (the primary sore of syphilis), the fluid from the chancre will be tested.
Syphilis should be treated as soon as possible. Penicillin, administered by injection, is the most commonly used medication for treating syphilis.
Complications:
- Untreated syphilis can lead to serious complications, including:
- Miscarriage or stillbirth
- Increased risk of HIV infection
- Damage to internal organs
- Blindness
- Congenital syphilis (transmission from mother to child)
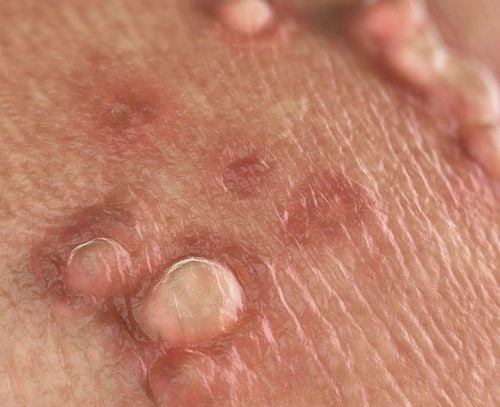
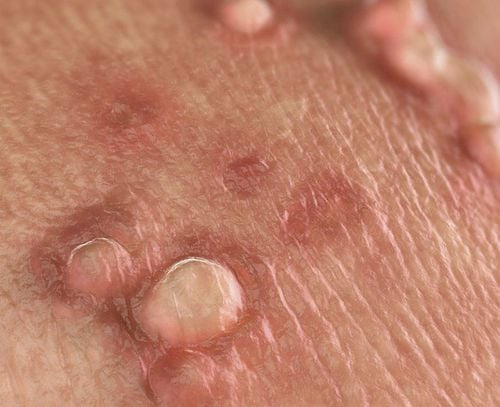
4. Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a very common sexually transmitted infection.
Symptoms: People infected with HPV may not have any outward symptoms. Some possible symptoms include:
- Warts in the genital or anal area
- Warts in the mouth or throat
- If there are warts in the mouth or throat, the patient may experience difficulty breathing or swallowing.
Transmission:
People with HPV in the genital, anal, rectal, mouth, or throat areas can transmit the virus to others through oral sex.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
There is no specific test to detect HPV, especially oral or throat HPV. Some cases of HPV infection are discovered through cervical cancer screening tests (Pap smear). Others may find out when they notice the development of genital warts or other symptoms.
Genital warts can be treated, but there is no way to completely eliminate HPV from the body. Warts may disappear on their own or can be removed by medication or surgery.
Complications:
HPV can go away on its own without treatment.
Even after treatment for genital warts, HPV cannot be eliminated, so the patient can still transmit HPV to others.
Some types of HPV can cause cervical cancer. HPV vaccination can help prevent infection and the consequences caused by HPV.
5. Herpes
Herpes is an infectious disease caused by the herpes simplex virus.
Symptoms: Often, people infected with herpes have no symptoms or very mild ones. The first symptoms usually appear after infection and can include:
- Itching, sores around the genital area, rectum, or mouth
- Headache
- Fever
- Body aches
- Swollen and tender lymph nodes
Transmission:
People infected with herpes in the mouth, genital area, rectum, and anus can transmit the virus to others through oral sex.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Doctors will examine a sample from the sore or perform a blood test.
Although there is no cure for herpes, antiviral medications can reduce symptoms.
Complications:
Whether treated or not, people with herpes can still transmit the virus to sexual partners. However, taking daily medication can help reduce the risk of transmission.
Herpes infection increases the risk of HIV infection. Pregnant women with herpes can transmit the virus to their babies.
6. Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis, or trich for short, is a common infection caused by a parasite.
Symptoms: Common symptoms include:
- Abnormal discharge from the vagina or penis.
- Redness, itching around the vagina.
- Burning sensation when urinating.
Transmission:
People infected with trichomoniasis in the vagina or penis can transmit the infection to others through oral sex. People who are infected can develop trichomoniasis in the throat.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Doctors will perform tests to diagnose trichomoniasis.
Trichomoniasis can be cured with a single dose of antibiotics. To prevent reinfection, it is important to treat all sexual partners.
Complications
Trichomoniasis is very easy to treat, so there are no particular consequences.
7. Hepatitis A Virus

Hepatitis A virus can cause acute hepatitis.
Symptoms: Symptoms of Hepatitis A usually appear about 28 days after exposure to the virus, including:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Nausea, vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Dark urine
- Abdominal discomfort or pain
Transmission
The main transmission mode of the hepatitis A virus is the fecal-oral route. Therefore, oral-anal sex with an infected person can easily lead to transmission.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Blood tests can help detect the disease.
There is no specific treatment for the hepatitis A virus, patients only need to rest for 1-4 weeks and avoid sexual contact with others.
Complications
Although hepatitis A can make patients extremely tired, it usually does not cause any complications.
8. Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B virus is another type of virus that causes liver inflammation.
Symptoms: Hepatitis B often has few or no symptoms. Some common symptoms include:
- Rash
- Joint stiffness
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Nausea, vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Dark urine
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
Transmission
People infected with the hepatitis B virus can transmit it to others through semen or vaginal fluids during oral sex.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Hepatitis B can be detected through a blood test. The time from exposure to the virus until it appears in the blood ranges from 3 weeks to 2 months. Tests can also determine if a person has acute or chronic hepatitis B.
There is currently no specific treatment for hepatitis B. Most people with acute hepatitis B will recover completely after a period of time. For chronic hepatitis B, doctors will prescribe medications to slow the progression of the virus and support the immune system.
Complications
Hepatitis B can become chronic, increasing the risk of cirrhosis, liver cancer, and posing a threat to the patient's life. Vaccination is a method to prevent the disease.
9. HIV
HIV is a virus that weakens the human immune system.
Symptoms: In the early stages of HIV infection, there may be no symptoms. Patients need to be tested to accurately determine if they are infected with HIV.
HIV symptoms vary depending on the stage of the disease. In the early stages, patients may experience flu-like symptoms:
- Fever
- Muscle aches
- Sore throat
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Night sweats
Transmission
The risk of HIV transmission from an infected person to an uninfected person through oral sex is quite low, and the person performing oral sex must have a wound in their mouth to be more easily infected.
If treated according to the correct regimen, people with HIV cannot transmit the disease to others.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
A blood test will accurately determine 1 if you are infected with HIV.
To date, there is no cure for HIV. However, treating HIV patients according to the correct regimen will prevent the virus from developing and prevent transmission.
Complications:
People living with HIV need to adhere to the treatment regimen to reduce the viral load below the detection limit to have a long, healthy life and prevent transmission to others.
How to prevent sexually transmitted infections through oral sex
To prevent sexually transmitted infections during oral sex, the following measures should be taken:
- Use a condom every time you have sex
- Use a dental dam (if available)
- Be faithful to one partner who is not infected with sexually transmitted diseases
- Get regular check-ups
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
References: Medicalnewstoday and NHS.uk