This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Tong Diu Huong - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Continuous nosebleeds for a long time will cause severe acute blood loss that is difficult to respond to conventional hemostatic treatments. Interventional embolization of nose bleeding to stop bleeding is an effective treatment method in this case.
1. Why is the need for embolization to treat nosebleeds under the guidance of digital background removal?
Nosebleed is a common phenomenon, due to many causes such as spontaneous, trauma or congenital. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is a common cause of recurrent nosebleeds. Other factors that increase the risk of nosebleeds include smoking, high blood pressure, use of anticoagulants or after radiation therapy, etc.Severe, persistent nosebleeds will cause severe blood loss. Patients present with lethargy, pale mucous membranes, low blood pressure. When conventional hemostatic treatments and nasal mesh inserts (nasal swabs) are not effective, the patient may be indicated for embolization to treat nosebleeds. This is a method of penetrating the blood vessel, blocking the bleeding blood vessel to stop bleeding.
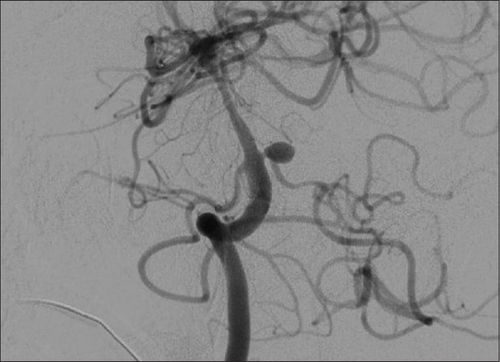
The intervention method of embolization under the guidance of digitized angiogram (DSA) is widely applied because of its safety, high success rate, and less invasiveness. Digital erasure angiography is an endoscopic technique that uses fluorescent light and X-rays to take pictures of blood vessels in the area to be examined before and after contrast is injected into the vessel. The computer will blur the background image, clarify the vascular system, help the surgeon perform the embolization technique more conveniently, and limit the possible risks.
Chảy máu mũi kéo dài gây tụt huyết áp
2. Digital imaging process to erase the background and embolize the nose bleed
Digital angiography erases the background to help clarify the image of blood vessels so that doctors can detect blood vessel abnormalities that cause nosebleeds. Then, the doctor proceeds to occlude the vascular peduncles through endovascular intervention, thereby reducing or stopping the nosebleed.2.1 Indications and contraindications
IndicationsNosebleeds due to tumors located in the nose - jaw region; Nosebleeds due to vascular malformations such as: Arteriovenous catheterization, pseudoaneurysm; Recurrent nosebleeds in case of hypertension; Nosebleeds due to trauma; Malignant tumors invade blood vessels or cause bleeding. Contraindications
There are no absolute contraindications; Relative contraindications for cases of renal failure, coagulation disorders, pregnant women or a history of allergy to iodinated contrast agents.
2.2 Preparation for implementation
Implementation personnel: Specialist doctors, assistant doctors, nurses, anesthesiologists, radiology technicians; Medicines: Local anesthetics or general anesthetics (if indicated), water-soluble iodinated contrast agents, anticoagulants and anticoagulants neutralizers, skin and mucosal antiseptic solutions; Common medical supplies: Syringes, syringes for electric pumps, physiological saline (or distilled water), masks, gloves, gowns, surgical caps, sterile intervention kits (knives, forceps) , scissors, metal bowl, tool tray, bean tray), cotton, gauze, surgical tape, medicine box, first aid kit for an iodine-contrast reaction; Special medical supplies: Y-connector set, 5 - 6F vascular catheter set, 6F guide catheter, 5 - 5F angiography catheter, 1.9 - 3F microcatheter, angiography needle, lead guide standard 0.035 inch, micro-conductor 0.010 - 0.014 inch; Technical means: Dedicated electric pump; background digitizing angiography machine; film, film printers and image storage systems; lead vest, apron, X-ray shielding; Materials that cause embolism: Synthetic plastic beads, bio-glue, bio-foam, metal spirals of all sizes; Patient: The procedure is thoroughly explained; fast, drink 6 hours before the procedure, can drink less than 50ml of water; In the endovascular intervention room, the patient lies on his back, fitted with a device to monitor breathing, blood pressure, pulse, electrocardiogram, SpO2, skin disinfected, covered with a sterile towel with holes; non-remaining patients may be given sedation; Test sheet: The medical record is in accordance with regulations, there is a slip specifying the implementation of endovascular intervention procedures, X-ray films, computed tomography, magnetic resonance if any.2.3 Performing the trick
Anesthesia: Local anesthesia for adults, psychological stability. General anesthesia for children under 5 years of age who cannot control their behavior or adults who are too excited and scared; Select technique and catheter access: Select Seldinger technique, catheter access from femoral artery. If the femoral artery is not accessible, the axillary artery, the main carotid artery, the brachial artery or the radial artery; Diagnostic angiography: Perform antiseptic, anesthetize the puncture site, then insert the needle and insert the tube into the vessel. Next, elective internal carotid angiography, selective external carotid angiography, or selective vertebral artery angiography were performed according to standard techniques. 3D imaging can be performed if indicated; Embolization: Insert the catheter into the gill vessel (usually into the external carotid-internal carotid artery). The microcatheter is then inserted into the malformed blood vessel or artery causing the bleeding. Next, perform embolization (can choose temporary embolization material or permanent embolization material depending on the characteristics and location of the lesion). After satisfactory scan, remove the catheter and insert the lumen, apply pressure directly on the needle puncture site for about 15 minutes to stop bleeding and then apply pressure for 8 hours. The procedure is successful when:The bleeding artery is completely occluded and there is no progressive bleeding; The arteries that supply blood to other organs are normal, not blocked.
Trong khi thực hiện thủ thuật, có thể xảy ra sốc phản vệ
2.4 Some complications and how to handle them
During the procedure:Vasospasm: Depending on the degree of vasospasm, it can be managed by administering a selective vasodilator pump; Due to contrast agents: Including acute reactions such as nausea, urticaria, laryngeal edema, hypotension, bronchospasm; anaphylaxis ; complications due to extravasation of contrast agents. How to handle according to the right protocol depending on each specific case; Due to the procedure: Arterial dissection or laceration causing bleeding. It should be managed by stopping the procedure, applying manual pressure, and re-applying. In case the patient stops bleeding, the procedure can be repeated 1-2 weeks later. After the procedure:
The catheter site has bleeding or hematoma: Treat by applying pressure, keeping the patient immobile until the bleeding stops; Infection after the procedure: Treatment with antibiotics; Suspected arterial occlusion due to thrombosis or arterial embolism due to detachment of atherosclerotic plaques: Should be examined immediately for proper treatment; Arteriovenous bulge or catheterization, catheter or lead rupture: Can be managed with surgical interventions; Other complications: Paralysis, blindness, tooth failure, embolization, pharyngeal necrosis,...: Need specialist consultation to take appropriate measures. Digital imaging techniques to erase the background and embolize blood vessels help treat nosebleeds quickly, effectively, and with few complications. During the procedure, the doctor needs the patient to cooperate to achieve the best treatment effect.
Vinmec International General Hospital has applied digital imaging technology to erase the background in examination and diagnosis of many diseases. Accordingly, the digital background removal technique at Vinmec is carried out methodically and in accordance with the process standards by a team of highly qualified medical professionals and modern machinery, thus giving accurate results, contributing to plays an important role in determining disease and disease stage.
Master. Doctor. Tong Diu Huong has more than 10 years of experience in the field of specialized imaging in diseases on images Ultrasound, X-ray, multi-slice CT, Magnetic resonance in diseases of the nervous system, digestive system , urology, cardiology, musculoskeletal... Besides, there are interventional imaging techniques, fine needle aspiration cells under the guidance of ultrasound and computed tomography.
If you have a need for medical examination by modern and highly effective methods at Vinmec, please register here.
MORE
What is bone tumor? Types of benign tumors in bone Application of digital erasure angiography (DSA) in the field of neurology Digital imaging of background and embolization treatment of uterine fibroids