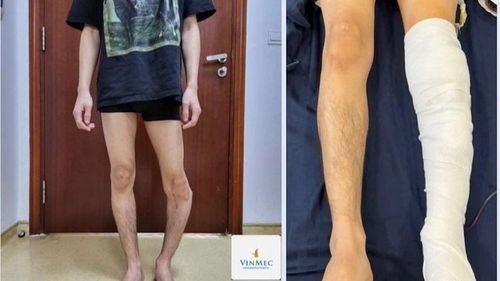
Nội dung bạn đang tìm kiếm không có phiên bản tiếng Việt.
Vui lòng chọn tiếp tục để xem nội dung tiếng Anh hoặc đi đến trang chủ Tiếng Việt.
Rất xin lỗi về sự bất tiện này.

Home
Tag Complications of chickenpox
Articles in Complications of chickenpox
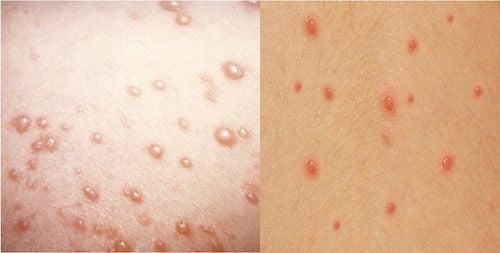
Distinguishing between chickenpox and hand, foot and mouth disease in children
Chickenpox is an acute infectious disease that can break out into an epidemic. This disease occurs in both adults and children, but children are the main ones and it is highly contagious. In hospitals, the number of chickenpox cases shows signs of increasing with many cases of dangerous complications.
In clinical practice, children with chickenpox and children with hand, foot and mouth disease have many symptoms that are easily confused, so here are some signs that parents can help distinguish the disease.
Xem thêm
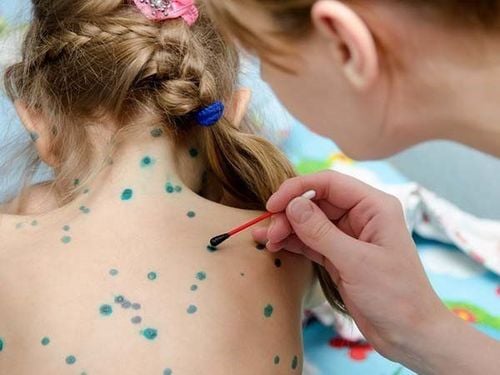
What should people with chickenpox avoid to recover quickly?
Chickenpox is a dangerous infectious disease that causes many complications for the infected person. So what should people with chickenpox avoid to recover quickly?
Xem thêm