This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
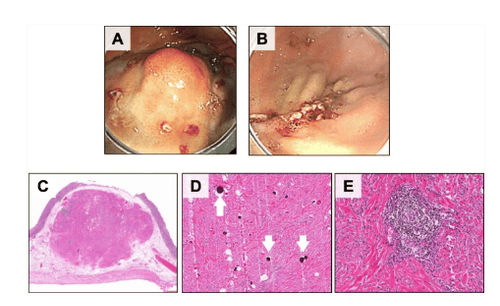
The gastrointestinal tract is a common site of calcified fibrocystic tumors. Calcified fibrous tumors are histologically characterized by rhabdoid cell proliferation with a dense hyalinized stromal, calcification, and variable degree of lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Distinguishing this entity from other gastrointestinal stromal lesions is important because management and prognosis can vary.
The most important entity to consider in the differential diagnosis of calcified fibrosarcoma is GIST, which is significantly more common and can exhibit aggressive behavior. Similarly, IMT generally has a worse prognosis and must be ruled out. Further studies are needed to clarify the pathogenesis of calcified fibrous tumors.
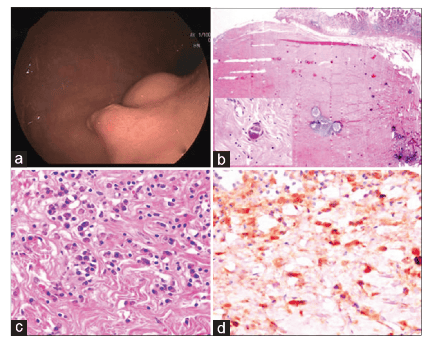
1. Differential diagnosis of calcified fibrous tumor
With pseudocytotic spindle cell proliferation, abundant collagen hyalinization, scattered calcifications, and variable degrees of lymphocytic myositis, lead to a multitude of differential diagnostic considerations for fibrosarcoma calcification.
Differential diagnosis of calcified fibrosarcoma of the gastrointestinal tract includes gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), schwannoma, leiomyoma, solitary fibrous tumor, IMT, plexiform fibroma, fibroma, mesenteric myelitis sclerosis and reactive nodular pseudofibromatosis (RNFP).
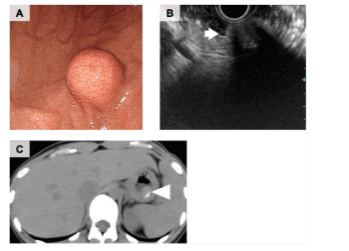
2 Differential diagnosis of calcified fibrosarcoma with GIST
The gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) of spindle cells consists of a uniform population of bland rhabdoid cells arranged in short cells. The GIST scleroderma classification revealed extensive collagen deposition with a relatively low and frequent cellularity, complicating the distinction of this entity from calcified fibrosarcoma.
Features that would favor calcified fibrocystic tumors over sclerotic GISTs include psammomatous calcifications and prominent lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates. Immunohistochemically, the axis cells of the GIST stain were positive for c-kit and DOG1, while these were negative for calcified fibrous tumors. CD34 immunostaining was positive in both entities, however, positivity was variable and localized in diffuse, calcified fibrous tumors in GIST. The c-kit and PDGFRA mutations commonly seen in GIST were not identified in gastric or colonic calcified fibrosarcomas, which could be used to differentiate these 2 entities at the molecular level.
3. Differential diagnosis of calcified fibrous tumors with Schwannomas
The gastrointestinal schwannomas are most commonly found in the stomach, consisting of rhabdoid cells with "wavy" nuclei and tapered ends arranged in a microscopic pattern.
Peripheral lymph node occlusion is characteristic of schwannoma and may be a confounding factor with calcified fibrous tumors. A microscopic pattern and scattered atypical cells help distinguish schwannomas from calcified fibrosarcomas. However, definitive exclusion of schwannoma is best accomplished by S100 staining, which is diffusely positive in schwannoma and negative in calcified fibrous tumors.
4. Differential diagnosis of calcified fibrous tumor with Leiomyomas
Leiomyomas commonly arise in the stomach, sigmoid colon, rectum, and esophagus and are composed of rhabdoid cells with an elongated cigar-shaped nucleus and abundant pinkish-red cytoplasm. Similar to calcified fibroblasts, leukemias may have hyalinizing stromal and, rarely, mitosis and nuclear loss.
Unlike in calcified fibrosarcoma, immunohistochemistry in leukaemia showed positivity for smooth muscle actin and desmin and negative for CD34.
5. Differential diagnosis of calcified fibrous tumor with solitary fibrous tumor
Solitary fibrous tumors (SFTs) consist of rhabdoid cells with thick bands of hyalinized collagen, hemangioma-like vessels (blood stasis) and perivascular hyalinization. Like calcified fibroblasts, solitary fibrous tumors show extensive hyalinization and no mitotic or meiotic patterns. However, SFTs are usually free of lymphocytic inflammation. Isolated fibroids stained positive for CD34 (95%), CD99 (70%), BCL-2, EMA (20%-30%) and had nuclear expression of STAT-6.
6. Diagnosis of calcified fibroblast tumors with IMT . fibroblast proliferation
IMT is fibroblast spindle cell proliferation with a predominantly lymphocyte infiltrate and numerous basal vessels. Inflammatory infiltrates sometimes contain neutrophils, eosinophils and/or foamy histiocytosis.
IMT exhibits variable cytology and often shows a myxoid background. Unlike calcified fibrosarcoma, IMT only rarely contains calcifications. Immunohistochemical stains that are positive for actin and smooth muscle ALK are commonly seen in IMT, but negative in calcified fibrosarcomas.
7. Diagnosis of calcified fibroma with Plexiform fibromyxoma
Plexiform fibromyxoma (also known as plexiform angiomyxoid fibroblastoma) is a benign tumor occurring in the stomach, usually forming a submucosal or transdural mass 0.3 cm to 17 cm in size. cm.
The tumor showed a plexiform multinodular growth pattern with pseudocytosis of bland rhabdoid cells, myxoid stroma, and a prominent microvascular network. Plexiform fibromyxomas are positive for smooth muscle actin and negative for CD34, DOG1, S100, and c-kit.
8. Diagnosis of calcified fibrous tumor with advanced fibrous proliferative neoplasm
Progressive fibromatosis (fibromatosis) often involving the abdominal wall or mesentery, is characterized by layers of transverse rhomboid cells with an infiltrative growth pattern. Desmoid tumors form isolated masses involving the stomach and esophageal junction.
Unlike calcified fibrosarcoma, desmoid tumor is not characterized by prominent lymphocytic inflammation or calcification, it shows strong immunological activity towards nuclear b-catenin.
9. Diagnosis of calcified fibrous tumor with sclerosing mesentery
A subset of sclerosing mesenteritis is currently considered to be expressed by IgG4-RD. This disease involves the mesentery of the small intestine and, similar to calcified fibrosarcomas, is characterized by fibrous, rhabdoid cell proliferation with prominent lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates.
In addition, sclerosing mesenteritis may show variable focal calcifications, although prominent calcifications are not a classic feature. Sclerosing mesenteritis surrounds and encloses fat and is classically associated with fat necrosis, which distinguishes this entity from a calcified fibrous tumor. In addition, the presence of obstructive phlebitis in IgG4-associated sclerosing mesenteritis may help distinguish this entity from a calcified fibrous tumor.
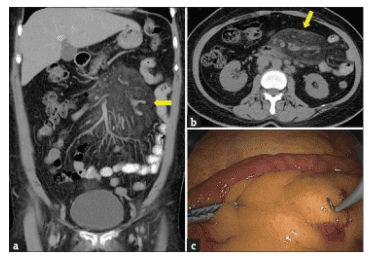
10. Differential diagnosis of calcified fibrous tumor with RNFP . tumor
RNFP is a rare inflammatory fibrous lesion of the gastrointestinal tract, histologically similar to a calcified fibrous tumor. Similar to calcified fibrosarcoma, RNFP consists of fibroblast proliferation in a collagenous hyalinized stroma, associated with a sparse lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate. However, calcified fibroblasts are usually more cellular, with more regular spindle cell tips, and an inflammatory infiltrate consisting of granulosa and plasma cells as well as lymphocytes. The presence of dystrophic or psammomatous calcifications in calcified fibrosarcomas helps distinguish these two entities.
By immunohistochemistry, RNFP showed staining positive for vimentin, smooth muscle actin and desmin, and negative for CD34. In contrast, calcified fibrous tumors were negative for actin and desmin of smooth muscle, but showed CD34-positive staining.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is a prestigious address trusted by many patients in performing diagnostic techniques for digestive diseases, diseases that cause chronic diarrhea or Crohn's disease... In particular, the screening techniques for gastric cancer and gastric polyps at Vinmec were performed using the Olympus CV 190 endoscope, the NBI function (Narrow Banding Imaging - endoscopy with narrow light frequency band) for image results. analyze mucosal pathology more clearly... Thanks to that, the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and give a timely treatment plan. Not only has a modern equipment system, Vinmec is also a place to gather a team of experienced doctors and nurses, especially, with a space designed according to 5-star hotel standards, Vinmec is guaranteed to bring bring the patient comfort, friendliness, peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References
Turbiville D, Zhang X. Calcifying fibrous tumors of the gastrointestinal tract: Clinical pathology review and update. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26 (37): 5597-5605 [PMID: 33071524 DOI: 10.3748 / wjg.v26.i37.5597 ]
Rosenthal NS, Abdul-Karim FW. Childhood fibrous tumor with psammoma bodies. Clinicopathologic features in two cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988;112:798-800. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: 1]
Chorti A, Papavramidis TS, Michalopoulos A. Calcifying Fibrous Tumor: Review of 157 Patients Reported in International Literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:e3690. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: 9] [Cited by in CrossRef: 43] [Article Influence Tracking in F6Publishing: 8.6]














