This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Specialist Doctor II Pham Thi Van Hanh - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
The initial manifestations of diphtheria can be confused with some other diseases, this takes away the "golden time" for treatment and raises the danger level for the patient. Therefore, knowing the signs of diphtheria is extremely important.
1 Clinical manifestations of diphtheria
Diphtheria (70%); laryngeal diphtheria (20%); nose 4%; eyes (3-8%), skin: rare
1.1 Diphtheria common form Duration through 4 periods, febrile manifestations are usually mild, early treatment, good prognosis
Incubation period: Lasts about 2 to 5 days: No clinical symptoms and contact with sick people, during the outbreak.
Onset : Average time 2-3 days. Slowly progressing
Mild infection syndrome: Mild fever, sore throat Clear toxic syndrome: Irritability, fatigue, pale skin, runny nose. Red pharyngitis, swelling of one side of the tonsils, corresponding swelling of the neck lymph nodes The liver is slightly enlarged, the heart may be fast or normal. Full outbreak:
Mild infection syndrome: Mild fever, cough, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, pain Toxic syndrome: The intoxication becomes clear, fatigue is severe, bad breath depends on the degree, from unclear to pale green, restlessness, rapid pulse, collapse of the blood vessels Runny nose (one side), blood pus, inflammation of the nasal mucosa. Neck lymph nodes, enlarged jaw angle, and bulging neck create the image of "buffalo neck" Whole body: Tachycardia, myocarditis, nephritis (edema, less urination), subcutaneous hemorrhage.

Bệnh bạch hầu thường diễn biến qua 4 thời kỳ với biểu hiện sốt nhẹ
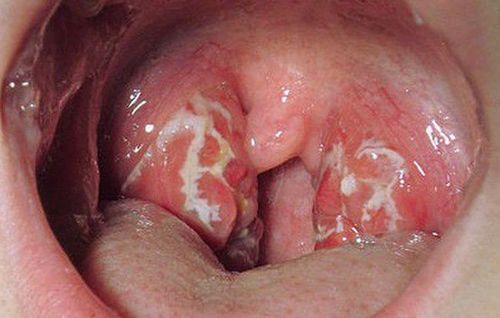
Local: Red throat, with gray-white pseudomembranous, adherent to tonsils, pharynx, spreading rapidly, tough, difficult to peel, causing bleeding, pseudomembranous not dissolving when put in water. Usually occurs in the tonsils, spreading to the pharynx, nasopharynx, uvula, and down the glottis, causing difficulty breathing in the larynx. Depending on the location of the disease, there will be different clinical manifestations.
1.2 Diphtheria Nasal Diphtheria Runny nose, runny nose with pus, mucus, and blood. Examination revealed a white membrane in the nasal septum. Seen in infants, the disease is usually mild. After a period of localization in the nasal septum, nasal tuberculosis, localized pseudomembranous fascia in the back of the nose gradually spread to the pharynx and cause systemic toxicity
1.3 Diphtheria and tonsils The most common form, easily progressing to severe lymphadenopathy laryngopharyngeal, diphtheria malignant, should be detected and treated early. Symptoms include fatigue, sore throat, loss of appetite, low-grade fever, small white spots on the mucous membranes of the tonsils and throat, swollen, painful lymph nodes under the jaw. After 2-3 days, there will be a cluster of necrosis forming a localized pseudomembranous layer on both sides of the tonsils, sometimes spreading to the uvula and covering the oropharynx. Ivory-white or grayish-white pseudomembranous, adherent to the underlying epidermis, tough, difficult to dissect, very easy to bleed, prone to growth, rapidly spreading. There are often swollen lymph nodes under the jaw, lymph nodes in the neck area make the neck swell. In this form of disease, toxins are absorbed into the blood much, causing systemic intoxication, fatigue, lethargy, pale skin, rapid pulse, more lethargy, coma and death within 6-10 days, if not actively treated.
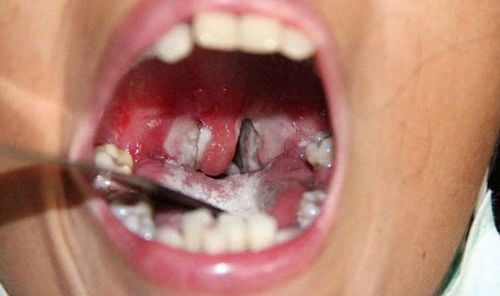
Bạch hầu họng là thể thường gặp nhất và dễ tiến triển nặng
1.4 Laryngeal diphtheria Rapid, severe progression, occurring after oropharyngeal diphtheria due to late diagnosis and treatment, rare primary laryngeal diphtheria. Development through 3 stages:
Hoarseness stage: Low fever, dry cough, hoarseness after resounding cough, old man's cough, loss of voice. On examination, there is pseudomembranous membrane at the larynx or from the pharynx down. If not treated in time, these pseudomembranous membranes will cause airway obstruction. Difficulty breathing stage: Usually at night, difficulty in breathing in the larynx gradually increases, continuously, when breathing in with stridor, cough resounds, and pulls respiratory muscles. respiratory depression, depression above and below the sternum, cyanosis, signs of toxicity, flabby neck, cervical lymphadenopathy, pharyngeal pseudomembranous. Dyspnea is divided into 3 levels: Grade I: Hoarseness, intermittent dyspnea, slow breathing, inspiratory time, increased on stimulation, examination, no indentation or very slight depression, still drinkable. Grade II: Continuous dyspnea, even when quiet, struggling, agitated, hypoventilation, marked chest retraction, signs of toxicity, signs of dehydration, inability to drink, loss of voice - not yet disturbance of consciousness (still awake) Grade III: Signs of upper respiratory tract obstruction, shortness of breath, rapid, shallow, cyanotic, poor gas exchange, severe chest contractions, restlessness (air hunger) – lethargy , coma Stage of asphyxia: Fainting, apnea, cardiac arrest, cyanosis, coma and death 1.5 Malignant diphtheria Primary: 1-2 days, secondary: 10-15 days, delayed: 40 - 50 days.
Rapid progress after 5-6 days: Shortness of breath, diarrhea, hemorrhage, pulse collapse. Causing suffocation, bleeding. There are many complications, high mortality. The disease can have a gradual onset, like diphtheria, but it can also be sudden with high, continuous fever, vomiting, sore throat, severe systemic toxicity, fatigue, and pallor. Pseudomembranous fascia spreads rapidly throughout the nasopharynx, is thick gray, hemorrhagic with many surrounding necrotic tissues. The lymph nodes in the neck are swollen, the neck is tight, the breath is bad, and it's hard to hear. Possible skin bleeding, death pattern, hematemesis, hematuria, hepatomegaly, liver pain, cardiovascular collapse and death.
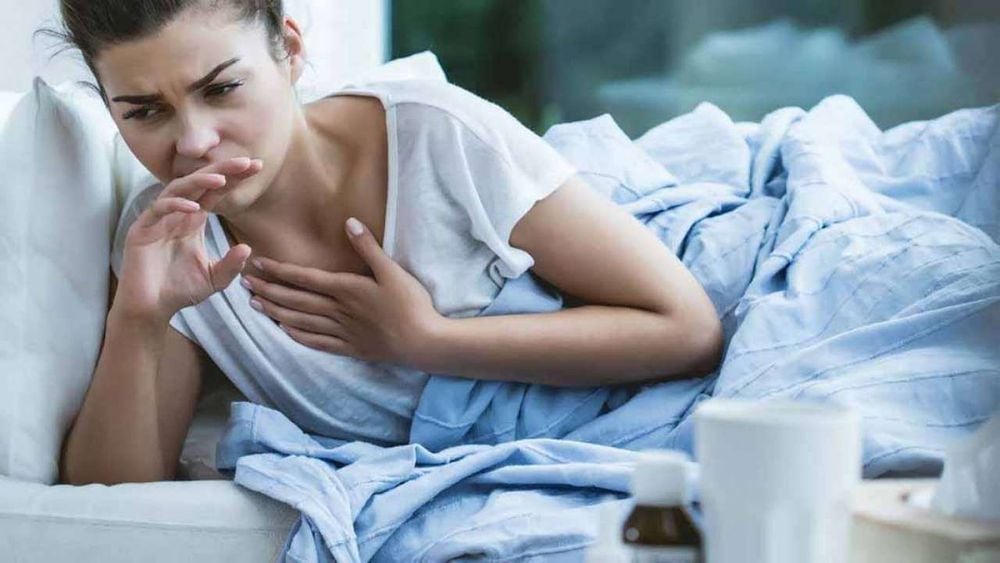

Bạch hầu ác tính thường tiến triển nhanh và có nguy cơ tử vong cao
1.6 Diphtheria skin Bacteriophages penetrate through wounds, burns, often in the lower extremities, including in the perianal area, typical lesions are deep depressions, 0.5-3cm in diameter, ulcers gray-brown, easy to bleed and peel off naturally after 1-3 weeks. Diphtheria skin causes myocarditis (3-5%), causes peripheral nerve damage (20%)
1.7 Diphtheria elsewhere Usually mild (urinary, genital, anal, ear canal mucosa: ulceration: ulceration) , with pseudomembranous membranes, tongue, gums, esophagus, eye conjunctiva).
2. Subclinical manifestations
Microbiological test: Take throat fluid, pseudomembranous tissue in the throat, nose, skin lesions for Gram staining, fresh look for Gram (+) rod-shaped bacilli and culture of bacteria. Blood tests: WBC usually increased, mainly polymorphonuclear BC Electrocardiogram: Detect arrhythmias, (early, many times to monitor)
Thực hiện các xét nghiệm cận lâm sàng để phát hiện và điều trị bệnh bạch hầu kịp thời
3. Diphtheria complications
3.1. Complications due to widespread pseudomembranous obstruction of the airways Pseudomembranous spread to the larynx, trachea, bronchial obstruction, airway obstruction + infection, severe toxicity, bronchopneumonia, esophagitis, Cardia. When lung damage is reduced, sloughing off pseudomembranous membranes can cause sudden airway obstruction (tachypnea, restlessness, malaise, respiratory muscle contraction, respiratory failure and death).
3.2. Complications due to diphtheria toxin Myocarditis, arrhythmia, impaired myocardial contractility, heart failure:
Common (about 2/3 cases), but only 10-25% have clinical manifestations obvious, causing mortality up to 50-60%. Usually appears on days 6-14 of illness or through weeks 3, when symptoms have improved, or very late at weeks 5-6 when the disease has recovered. Manifestations:
Functions: Fatigue, anxiety, irritability, irritability, anorexia, vomiting, epigastric pain. Physical: Tachycardia (maybe slow, irregular), low blood pressure, faint, irregular heart sound, galloping rhythm, murmur, hepatomegaly. Causes acute heart failure, sudden death Electrocardiogram: prolonged PR, T wave change, atrioventricular block - first degree, II, III degree and other arrhythmias (Atrial fibrillation, ventricular rhythm, complete bundle branch block) 90%) Peripheral neuritis caused by diphtheria toxin:
Paralysis of the nasopharynx and posterior pharynx, appearing early in the first 2-3 days, 10% after 2 to 6 weeks, causing damage to the III and IV cords. , VI, VII, IX, X. paralysis of pharyngeal membrane, paralysis of eyes, paralysis of accommodation, nasal voice, difficulty swallowing. and death. Possibly polyradiculopathy and peripheral neuropathy (Guillain – Bare) Damage caused by peripheral neuritis in diphtheria may be reversible but late - (after weeks, months).
Độc tố bạch hầu có thể gây ra tổn thương và làm liệt dây thần kinh ngoại vi
Other complications:
Nephritis: Hematuria, Proteinuria Embolism due to atrial fibrillation causing hemiplegia Superinfection pneumonia Pneumonia subcutaneous hemorrhage due to thrombocytopenia Measlesic rash Current, Vinmec International General Hospital offers a wide range of diphtheria vaccination services for children and adults with 5 combinations, including:
6-in-1 vaccine Infanrix Hexa from GSK (Belgium) 6-in-1 vaccine Hexaxim of Sanofi (France) 5-in-1 vaccine Pentaxim of Sanofi (France) Adacel 0.5 ml of Sanofi - France Tetraxim 0.5 ml of Sanofi - France To ensure vaccination effectiveness and safety, before injecting, Customers will be examined by specialist doctors, fully screened for physical and health problems, advised on preventive vaccines and injection regimens, how to monitor and care after vaccination before Indications for vaccination according to the latest recommendations of the Ministry of Health & World Health Organization.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.