This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Huy Nhat - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. Doctor Nguyen Huy Nhat has many years of experience in the field of respiratory disease treatment.Ventilator-associated pneumonia in children is a severe nosocomial infection and is the most common of all nosocomial infections. If not diagnosed and treated promptly, the disease can progress very seriously and cause many serious consequences.
1. What is ventilator-associated pneumonia?
Ventilator-associated pneumonia is pneumonia that occurs 48 hours after the patient is intubated and artificially ventilated. This is the most severe and common nosocomial infection of all the nosocomial infections. Ventilator-associated pneumonia is called early-onset if onset is < 4 days, late onset when onset is 5 days or more.2. Diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia
The American Thoracic Society (ATS) in 2005 approved the diagnostic criteria for ventilator-associated pneumonia:1 - More than 48 hours of mechanical intubation.
2 - Chest radiograph shows new, progressive, or persistent infiltrates.
3 - Temperature ≥ 380C or < 35.50C.
4 - The bronchial fluid is purulent or thick yellow.
5- Peripheral blood leukocytes > 10 G/L or < 4 G/L .
6- Culture of air, bronchi with pathogenic bacteria, blood culture (+).
7- CPIS score ≥ 6.
Confirm the diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia when there are 2 criteria (1), (2) and at least 2 of the criteria (3), (4), (5) , (sixty seven)
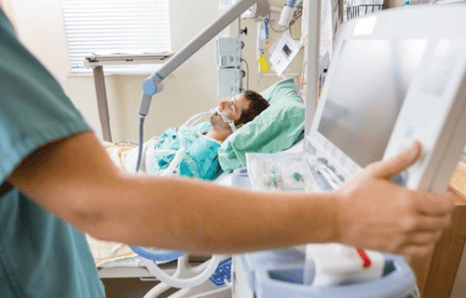
3. Treatment of ventilator-associated pneumonia
General principles of treatment: Use appropriate antibiotics Balance water and electrolytes Ensure nutrition: Nutrition through nasogastric tube and parenteral nutrition to ensure energy supply Have a regimen of care and reasonable ventilator regimen Treatment of underlying disease Antibiotics to treat ventilator-associated pneumonia: Early-onset ventilator-associated pneumonia (<4 days) is usually caused by the following strains of bacteria Enterobacter , Klebsiella, Proteus, E.coli, H.influenzae, S.aureus are not resistant to methicillin. Antibiotics used in this case are usually: 3rd generation Cephalosporin (ceftriaxone) + Quinolone (2nd and 3rd generation), or Ertapenem. Late onset ventilator-associated pneumonia (≥5 days) is usually caused by antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria such as: P.aeruginosa, A. baumannii, methicillin-resistant S.aureus and beta-lactamase-resistant Klebsiella. Risk factors for infection with these resistant strains of bacteria include: Antibiotic use within the previous 90 days, prior 90 day inpatient hospitalization, hospitalization > 5 days, artificial ventilation > 7 days, immunocompromised disease or being treated with immunosuppressive drugs, long-term treatment at dialysis facilities or community health facilities, history of episodes of resistant infections antibiotics in the community or in intensive care units. For these cases, the most commonly used antibiotics are: imipenem or meronem combined with quinolones (2nd and 3rd generation). Cephalosporins against blue pus bacilli (ceftazidim, cefepim) or carbapenem against blue pus bacilli (imipenem – cilastatin). Meropenem or a beta lactamase inhibitor (piperacillin-tazobactam) in combination with vancomycin or linezolid if there is a risk of infection with methicillin-resistant staphylococci. If treatment fails with multiple antibiotics: consider colistin. If ESBL-producing bacteria are used, use carbapenems (imipenem-cilastatin, meronem, doripenem). The pediatric department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, pneumonia in children ,....With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.Articles refer to the source: Ho Chi Minh City Respiratory Association
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.