This is an automatically translated article.
Muscular dystrophy is an inherited disease. Although not common, the ability to pass it on to the next generation is quite high. How to cure muscular dystrophy is still a question for the scientific community. However, some of the current medical achievements are still being applied to diagnose and treat muscular dystrophy.
1. How is muscular dystrophy diagnosed?
Your doctor will diagnose muscular dystrophy through a physical examination, family history, medical history, and several tests. Diagnostic tests for muscular dystrophy may be:
Muscle biopsy (removing and examining a small sample of muscle tissue)
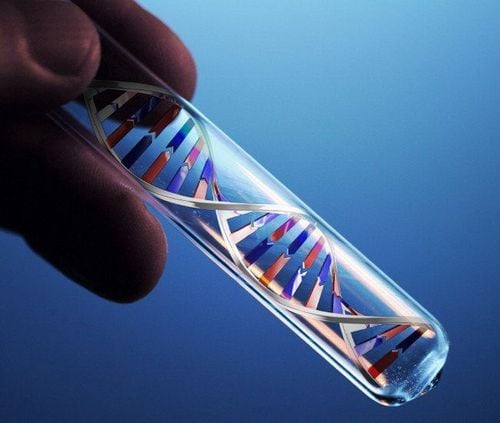
DNA testing (genetics) Electromyography or nerve conduction testing: use electrodes to check muscle and/or nerve function Blood enzyme tests: To look for the presence of creatine kinase (CK), to check for inflammation and death of muscle fibers. Muscle Biopsy: For Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy, a muscle biopsy can show whether dystrophin - a muscle protein that is missing or abnormal. Diagnostic DNA test for muscular dystrophy : Used to analyze the status of related genes.

Xét nghiệm DNA là một phương pháp chẩn đoán bệnh loạn dưỡng cơ
2. What are the treatments for muscular dystrophy?
All types of muscular dystrophy have no cure, but medications and therapies can slow the course of the disease.
Human trials of gene therapy to treat the dystrophin gene are nearing. For example, scientists are studying how to introduce the activated dystrophin gene into the muscles of boys with Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. Two other treatments are Eteplirsen, which increases the protein dystrophin in the muscles, and Ataluren.
Researchers are studying the potential of certain muscle-strengthening drugs to slow or reverse the progression of muscular dystrophy. Several other lines of research are currently looking at the effects of dietary creatine and glutamine supplementation on muscle energy production and storage.

Sử dụng thuốc trong điều trị bệnh loạn dưỡng cơ đem lại hiệu quả cao
3. Conventional medicine for muscular dystrophy
3.1. Treatment through intensive care
Symptoms can often be relieved through exercise, physical therapy, rehabilitation, respiratory care, and surgery:
Exercise and physical therapy can minimize abnormal joint position often or painful and may prevent or delay curvature of the spine. Respiratory care, deep breathing, and cough exercises are often recommended. Assistive wheelchairs and other rehabilitation devices can help people with muscular dystrophy maintain mobility and independence. Surgery can sometimes reduce muscle shortening. In Emery-Dreifuss and myotonic muscular dystrophy, surgical implantation of a pacemaker is often required.
3.2. Drug treatment
In some cases, disease progression may be slowed or symptoms relieved with medication:
In Duchenne muscular dystrophy, corticosteroids can slow down muscle breakdown. The oral corticosteroid drug deflazacort (Emflaza) was approved in 2017 for the treatment of dystrophy. Deflazacort helps patients maintain muscle strength as well as helps them maintain the ability to walk. Common side effects include puffiness, increased appetite, and weight gain. In myotonic muscular dystrophy, the drugs phenytoin and mexiletine (Mexitil) are used to treat slow muscle relaxation. It may also be indicated for the treatment of heart disease associated with muscular dystrophy.
Thuốc corticosteroid deflazacort được FDA phê chuẩn thuốc chữa loạn dưỡng cơ Duchenne
4. Can you prevent muscular dystrophy?
If you have a family history of muscular dystrophy, you should see a genetic counselor before having children. The odds of passing this disease on to your child range from 25% to 50%.
Carriers - often sisters and mothers of people with muscular dystrophy - may not have the disease, but they also have mild symptoms that make it more difficult to recognize. However, these people can still pass the disease on to their children.
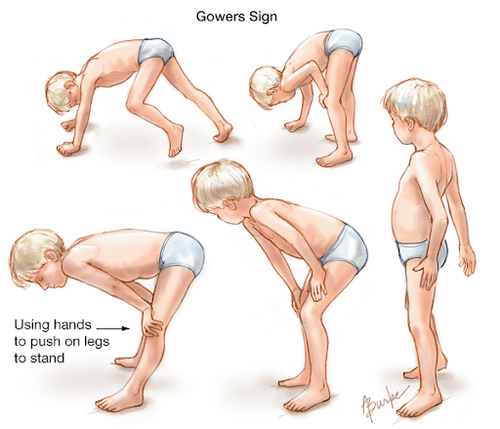
Unlike in girls, muscular dystrophy is almost always evident and affects boys. For Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy, protein and DNA testing helps identify carriers.
DNA exploratory diagnostics can provide prenatal diagnoses. Carrier trials for other forms of muscular dystrophy are also currently under development.

Chứng loạn dưỡng cơ là một bệnh mang tính di truyền
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com