This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by MSc.BSCKII Phan Thi Minh Huong - Gastroenterologist, Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the HBV virus, which, if not treated and controlled well, can cause dangerous complications such as cirrhosis, liver cancer, etc. provide information on hepatitis B treatment regimens under the guidance of the Ministry of Health.
1. Diagnosis of Hepatitis B
Symptoms Hepatitis B often progresses silently, with very faint symptoms. Patients are sometimes subjective and ignore the signs of the disease, by the time the disease is detected, the disease has progressed to a worse stage. Some of the following symptoms will help you recognize hepatitis B early:
Mild fever Loss of appetite Nausea, vomiting Fatigue, lethargy, lack of concentration Jaundice Discolored stools Diagnostic tests for hepatitis B Based on clinical symptoms alone, it is difficult to determine whether a patient has hepatitis B or not. The following tests are important indicators to help accurately diagnose this dangerous disease:
HBsAg test : HBsAg is the surface antigen of the hepatitis B virus. If the result is HBsAg (+), it means the body is infected with hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs test: This is a test to check the body's immunity to hepatitis B virus. If a person has been vaccinated against hepatitis B or has been infected with the hepatitis B virus and recovers from the disease, the body will make antibodies against the virus and the anti-HBs test will be positive. Anti-HBs concentration >10mUI/ml is considered to protect the body from hepatitis B virus. The above are 2 types of tests needed to diagnose hepatitis B and assess the body's immunity to this virus. Besides, the doctor may order other tests including AST, ALT liver enzymes, HBeAg, Anti-HBe, Anti-HBc tests,... to assess liver function, viral load, ability ability of the virus to multiply .., thereby giving an appropriate treatment direction.
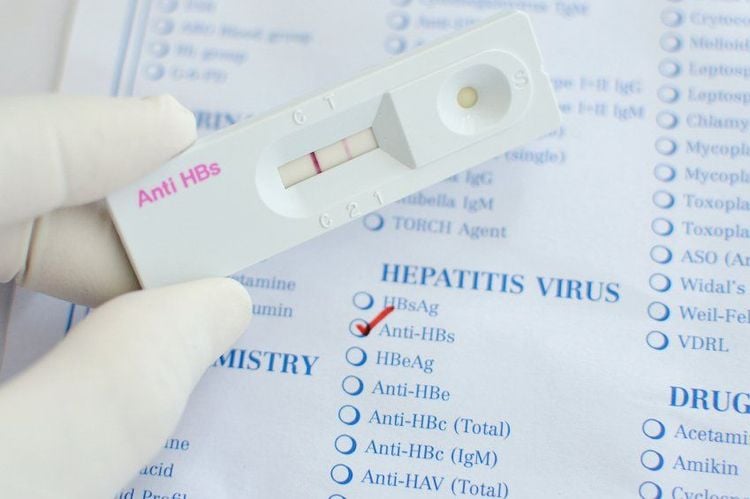
Xét nghiệm Anti-HB
2. Distinguishing acute hepatitis B from chronic hepatitis B
Acute hepatitis B When the hepatitis B virus only exists in the human body for a short time, less than 6 months, and especially can be treated completely. Acute hepatitis B infection can lead to one of the following three situations:
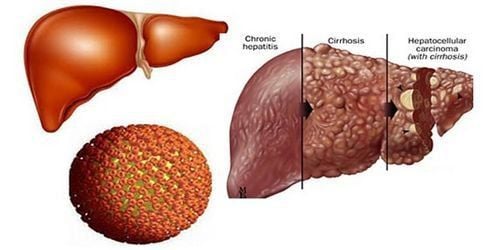
The disease progresses to fulminant hepatitis: Many liver cells are severely damaged leading to acute liver failure and possibly death. This case occurs only in a rather small percentage (1%). Recovery and Immune Response: The hepatitis B virus is cleared after a few months and the body builds up a lifelong immune response. Progression to chronic hepatitis B: The hepatitis B virus is not eliminated leading to lifelong chronic hepatitis B. Currently, there are antiviral drugs for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. However, patients still need to monitor and screen for liver cancer periodically to detect liver damage early. Chronic hepatitis B is defined when the hepatitis B virus persists in the body for more than 6 months. Once diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B, it means that the patient will have to live with the virus for the rest of his life because the disease cannot be completely cured. The symptoms of chronic hepatitis B are very faint, but if you pay attention, you can detect the disease early. Here are a few signs to recognize chronic hepatitis B:
Digestive disorders Jaundice, yellow eyes, mild fever, unexplained fatigue

Cơ thể mệt mỏi không rõ nguyên nhân là một trong những triệu chứng của viêm gan B mạn tính
3. Treatment of acute and chronic hepatitis B according to Decision No. 5448/QD-BYT issued by the Ministry of Health on December 30, 2014
Treatment of acute hepatitis B is mainly supportive
Acute hepatitis B does not need to be treated with drugs, patients only need to be monitored and examined regularly as directed by the doctor. The patient needs to rest absolutely during the period of clinical symptoms. Adequate nutrition, increased intake of green vegetables and fresh fruits to supplement necessary vitamins and minerals. Limit fat, reduce salt, abstain from alcohol and avoid drugs metabolized by the liver Drink lots of water to enhance metabolism and filter out toxic substances. When recovering from acute hepatitis B, the patient still needs to maintain a moderate diet and activity to protect the liver Treating chronic hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus replication inhibitor (orally): Antiretroviral therapy is a long-term treatment process, patients must strictly follow drug instructions to avoid creating drug-resistant virus strains.
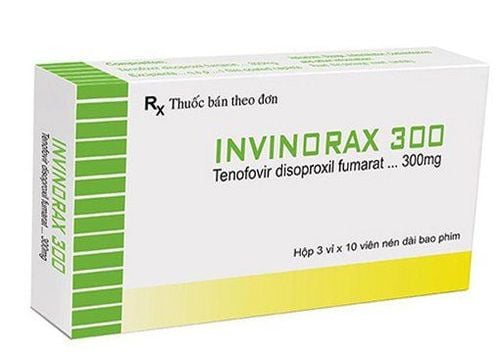
Tenofovir (TDF) 300mg/day or entecavir (ETV) 0.5mg/day Lamivudin (LAM) 100mg/day for patients with decompensated cirrhosis or pregnant women. Adefovir (ADV) is used in combination with lamivudine when there is drug resistance Interferon injection: The drug works to stimulate the body's immune system to destroy viruses and infected cells. Currently, there are 2 types of injection:
Interferon alpha injected under the skin 3-5 times a week Peg-interferon alpha injected under the skin once a week The treatment course lasts from 6-12 months. Patients need to closely monitor the side effects of the drug for timely treatment. Interferon injection is preferred in women who want to have children, have concomitant hepatitis D virus infection, are intolerant or have failed treatment with oral viral replication inhibitors.
Side effects
Oral antivirals usually have few side effects. Adefovir and Tenofovir can cause nephrotoxicity, but very rarely. Interferon injections often have more side effects, the most common are fatigue, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, flu-like symptoms...and can cause allergies, hair loss, and leukopenia.
Treatment of chronic hepatitis B for some special cases Chronic hepatitis B in children
ETV for children 2 years and ≥ 10 kg with a dose varying by weight In case of LAM resistance, increase the dose of ETV double
LAM for once-daily use ADV is used for children 12 years of age TDF is used for children 12 years of age and 35 kg of Interferon alpha is used for children over 12 months of age Pregnant women:
Cases Pregnant women found to have chronic hepatitis B: If treatment can be delayed, it should be delayed in combination with close monitoring of clinical symptoms and laboratory tests.
If you have to treat: Take TDF
In case women are being treated for chronic hepatitis B and want to get pregnant: If you are taking ETV, stop taking ETV 2 months before pregnancy and switch to TDF. In case women are being treated for chronic hepatitis B and are pregnant: Using TDF in the last 3 months of pregnancy can use TDF or LAM drugs. Concomitant infection with hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C
Treatment according to the standard regimen of hepatitis C.
4. How to prevent hepatitis B?
Biện pháp phòng bệnh hiệu quả nhất hiện nay là tiêm vắc xin ngừa viêm gan B
The most effective way to prevent the disease today is to get the hepatitis B vaccine. Vaccinate your baby within 24 hours of birth and follow-up shots at 2, 3 and 4 months old. People who are not yet infected with HBV should be tested for HBsAg and anti-HBs before vaccination. Do not share needles or other equipment that may have come into contact with blood or body fluids. Safe sex. Immediately bandage scratches, open wounds, avoid contact with blood and secretions of patients infected with HBV. Practice sports to improve health and improve physical fitness. Eat healthy, full of nutrients. Abstain from alcohol, beer, tobacco. Due to the problem of alcohol abuse, eating toxic foods, the incidence of hepatobiliary disease in Vietnam is increasing, especially hepatitis B. To meet the demand for medical examination and treatment. Liver - Bile - Pancreas, Vinmec has launched standard liver - bile screening packages, comprehensive liver - bile screening packages and advanced liver - bile screening packages to help assess hepatobiliary function through testing, subclinical; the risk of affecting the liver and early screening for hepatobiliary cancer.
Besides, the Hepatobiliary-pancreatic Center is one of the key centers invested and developed by Vinmec. This is the center of the first private hospital to successfully perform a liver transplant from a living donor. At Vinmec, you will be assured of being examined and treated by a team of experienced doctors and hepatobiliary specialists from abroad.
Hope that the above article has helped readers have an overview of hepatitis B as well as ways to prevent and treat this dangerous disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Source: Department of Medical Examination and Treatment, Ministry of Health