This is an automatically translated article.
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is a malabsorption condition that occurs when the pancreas fails to produce important digestive enzymes. If the exocrine function of the pancreas prevents the pancreas from making these enzymes, the body will not be able to digest food and absorb nutrients, especially fats. Accordingly, people with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency will not be able to properly digest food or often experience indigestion due to malabsorption.1. Symptoms of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
Initial symptoms of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency can be vague, mild, and similar to other gastrointestinal disorders, and include:Changes in bowel function, including diarrhea and especially foul-smelling, oily, difficult to pass stools due to increased fat secretion Bloating and distention Abdominal pain Abdominal pain Weight loss Besides, other symptoms of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency depend on the exocrine function of the pancreas as follows: as well as the underlying cause of this condition. For example, a person with cystic fibrosis, has both lost pancreatic function and may also have respiratory symptoms.
In addition, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency can also manifest with symptoms of malnutrition due to specific nutrient deficiencies as follows:
Vitamin K deficiency can cause unusual bleeding or bruising Vitamin deficiency D can lead to low bone density, causing osteoporosis Deficiencies of fat-soluble vitamins and electrolytes may manifest as changes in vision (night blindness), neurological symptoms, (depression , memory), muscle or joint involvement (pain and fatigue) and/or skin (rash or swelling) More severe, longer-lasting cases of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency may lead to a more serious condition. If not treated properly, these conditions can lead to kidney failure, neurological disease, severe anemia, convulsions, ascites, infections and delayed wound healing, cardiac arrhythmias and potentially fatal.
2. Causes of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
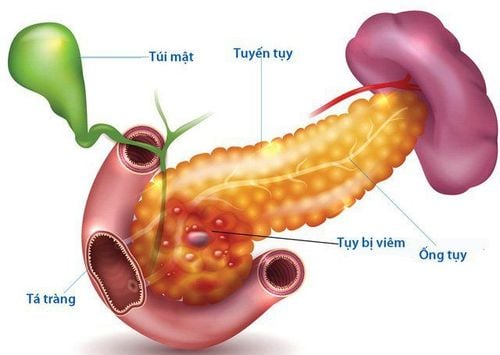
The pancreas is an organ located in the abdomen below the stomach. The role of the pancreas can be divided into exocrine and endocrine functions. Exocrine functions help the body digest food by producing special enzymes while endocrine functions help regulate hormones. Accordingly, to know the causes of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency, it is necessary to know what the exocrine function of the pancreas is.In exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, only the exocrine function of the pancreas is damaged, that is, the part of the cell that secretes enzymes to digest food in the duodenum (the endocrine part of the pancreas that secretes and releases insulin into the pancreas). blood is still normal). Reduced production of three important digestive enzymes - amylase, protease and lipase - results in poor digestion, malabsorption of nutrients and ultimately signs and symptoms of malnutrition.
Chronic pancreatitis is the most common cause of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Inflammation causes the pancreas to become damaged over time, reducing its ability to produce enzymes. In addition, other conditions affect the exocrine function of the pancreas in different ways, including:
Cystic fibrosis Celiac disease Pancreatic cancer Shwachman-Diamond syndrome Hemochromatosis diabetes Zollinger-Ellison syndrome People who have had gastrointestinal surgery, especially bariatric surgery to remove part of the stomach or intestines.
In addition, there may be other reasons that increase the risk of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency such as genetic and lifestyle factors. For example, excessive alcohol use can lead to inflammation of the pancreas, which in turn can make the pancreas less efficient at producing enzymes, eventually leading to true exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.
3. How to diagnose exocrine pancreatic insufficiency?
The exact number of people with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is not known. Furthermore, this condition is rare in the general population but may be due to an underdiagnosed condition. People with mild symptoms who do not receive any treatment should miss the diagnosis. Among those seeking treatment, a re-diagnosis may not be established in the first place until the condition worsens. Especially in the early stages, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency can be misdiagnosed as a functional gastrointestinal disorder such as irritable bowel syndrome.In people who have been diagnosed with another condition of the digestive system, such as Crohn's, the initial symptoms may be due to that condition and treated accordingly. It can take years for the symptoms of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency to be properly diagnosed, when the exocrine function of the pancreas has been so damaged that the body cannot compensate.
Accordingly, the diagnosis of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency will be made after excluding more common causes of gastrointestinal symptoms, starting with questions such as the following:
Symptoms during a meal or bowel movements Lifestyle habits, such as frequency of drinking and smoking Other medical conditions, previous surgeries, and family medical history Current medications, including including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines or any supplements or herbs Diet, Other issues such as exercise, social and work history and mental health After With careful medical history, although there is no specific test to diagnose exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, your doctor may order tests to rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. :
Blood tests: look for nutritional deficiencies, inflammatory responses, blood sugar levels, pancreatic enzymes or specific signs of medical conditions. condition associated with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Stool tests: People with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency often experience bowel symptoms that indicate the intestinal tract cannot properly absorb certain nutrients, especially fats. At this point, a stool sample is needed to check for the presence of unabsorbed fat. If diarrhea persists, the patient's stool will be tested for microorganisms that can cause infection. Imaging tests: CT scans, ultrasounds, and MRIs may be ordered to help the doctor look inside the abdomen and assess whether the pancreas is damaged, blocked, or inflamed. Breath test: Some people with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency will also be found to have a condition called small bowel bacterial overgrowth.
4. How to treat exocrine pancreatic insufficiency?
Cases of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency were treated with pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy and nutritional supplements such as vitamin B12 even before the diagnosis was confirmed. In fact, if symptoms are indeed due to exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, a person will experience rapid remission after starting oral enzymes, such as lipase with meals.In addition, the immediate treatment of patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency focuses on restoring nutritional status and weight. Often, patients can have long-term treatment at home without the need for hospitalization. However, if the person is severely malnourished or unable to absorb food by mouth, the person may need to be hospitalized for enteral nutrition (feeding tube) or intravenous fluids.
Besides, as soon as exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is diagnosed, the doctor may also recommend changes in diet and lifestyle, such as cutting down or quitting smoking or drinking alcohol, because of these problems. This bad habit can promote an inflammatory response.
In summary, patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency often experience a range of symptoms related to specific nutritional deficiencies. When properly diagnosed, these patients can be treated with oral supplementation of enzymes needed for digestion that the exocrine pancreas no longer produces. It is also important that any underlying or associated disease causing exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is diagnosed and treated appropriately. With pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy, dietary and lifestyle modifications, as well as ongoing monitoring for nutritional deficiencies and any additional needs, most people with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency can effectively control the outpatient situation.
References: verywellhealth.com, lluh.org, healthline.com, identifyepi.com
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.