This is an automatically translated article.
Article by a doctor of Hematology - Blood Transfusion - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
The D-Dimer is evidence for the presence of Fibrin in the circulation. The significance of the d-dimer test is to diagnose thrombotic pathology, detect patients with hypercoagulable state and monitor the progression of thromboembolic disease as well as evaluate treatment effectiveness.
1. What is D-Dimer?
D-Dimer is a degradation product of fibrin fibers during fibrinolysis and under the action of Plasmin. When blood levels of D-Dimer are normal, this indicates the absence of intravascular thrombus. However, high blood levels of D-dimer can be a warning sign of the presence of a blood clot, DIC.
So, D-Dimer means that in the molecule there are 2 D chains linked together. There are 2 types of D-Dimers:
Molecules consisting of 2 D chains A molecule consisting of 2 D chains bonded to E chains.
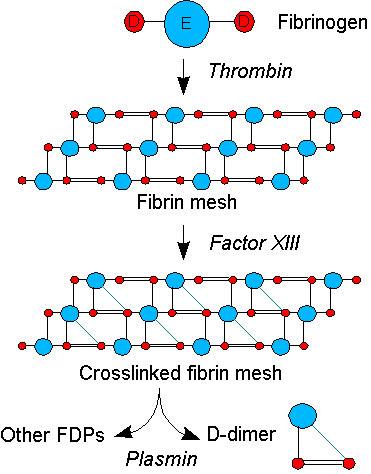
Hình ảnh mô tả quá trình hình thành D-Dimer
Under normal conditions, the process of forming blood clots (fibrin formation) is always in balance with the process of dissolving blood clots (fibrinolysis). All fibrinogen excess activity can lead to thrombosis. All abnormal activation of fibrinolysis can lead to bleeding complications. Specifically:
Process of creating Fibrin: Under the action of Thrombin, circulating fibrinogen will be converted into fibrin in pure form, and then into fibrin polymer under the influence of factor XIII. Fibrinolysis: Under the action of activating the fibrinolytic process, circulating Plasminogen will convert to Plasmin, which destroys factors V, VIII, Fibrinogen as well as Fibrin. Units of D-Dimer include 2 types:
FEU (a unit of Fibrinogen equivalent): 1 FEU reflects the initial amount of Fibrinogen to form D-Dimer type D-E-D. DDU (D-Dimer unit): Reflects the amount of D-Dimer type D-D. The molecular weight of D-D is 195 Kilo-dalton. As for reporting a D-Dimer test as DDU or FEU will depend on the D-Dimer test methods. However, it is possible to convert these 2 units by relying on molecular weight. The weight of FEU is 2 times of DDU.
FEU = 2 DDU or DDU = 1/2 FEU.
Reference range: D-Dimer < 0.5 mg/L FEU, or D-Dimer < 0.25 mg/L DDU.
2. Meaning of d dimer . test
The D-Dimer is evidence for the presence of Fibrin in the circulation. The significance of the d-dimer test is:
Diagnosis of thrombotic diseases: The value of D-Dimer is increased in 90% of cases of deep vein thrombosis, in 95% of cases of pulmonary embolism, and only in 5% of those without thrombosis. Detection of patients with hypercoagulable state: the presence of D-Dimers in a bedridden patient strongly points to the possibility of new thrombus formation and is evidence that requires further investigation. to identify thrombosis and prescribe treatment or prevention of anticoagulation for patients. Monitor thrombotic diseases according to progression and time and to assess treatment efficacy.

Xét nghiệm d dimer chẩn đoán các bệnh lý huyết khối
3. Clinical warnings
Abnormally high levels of D-Dimer test results indicate thrombus formation and fibrinolysis in the body. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct other tests to find the location and cause of the thrombosis. A normal D-Dimer test result means that the patient does not have an acute medical condition that causes blood clots in the body. However, several factors can contribute to altered test results such as:Fibrinolytics False positive results can occur when there is a high rheumatoid factor titer in the supersensitive D-Dimer serum. may be falsely elevated or lowered in the presence of hyperlipidemia or turbid specimens and being treated with a mouse monoclonal antibody.
4. Common causes of increased D-Dimer . levels
Pulmonary embolism Deep vein thrombosis Arterial thrombosis Disseminated intravascular coagulation Myocardial infarction Cirrhosis Postoperative period Veno-peritoneal bypass (Shunt péritonéoveineux) Hypercoagulable state Trauma Infection Malignant pathology Postoperative period After fibrinolysis (Fibrinolysis) Eclampsia The last months of pregnancy. In summary, the D-Dimers are evidence for the presence of fibrin in the circulation. The significance of the d-dimer test is to help diagnose thrombosis, detect patients with hypercoagulability and monitor progression of thrombosis as well as evaluate treatment effectiveness.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.