This is an automatically translated article.
The article is made by Master, Doctor Bui Thi Hong Khang - Pathologist - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Cytological testing is a form of studying the morphological changes of detached cells obtained from organs in the body by different techniques, with the main goal of screening and diagnosing cancer.
In general, the advantages of cytological diagnostic methods are low cost, fast and relatively accurate results, can be repeated many times without danger to the patient.
1. Collection - Spread - Fixation of cell specimens
Corresponding to 2 parts of cytology, sloughing cytology and aspiration cytology, there are 2 types of cells collected for cytology testing: natural/artificial sloughing cells and aspiration cells. The cells were smeared onto a slide to form a thin layer, fixed immediately in 95% ethanol (wet fixation) or allowed to dry in air (dry fixation), to maintain the same cell morphology as inside. body.
2. Exfoliative cell collection
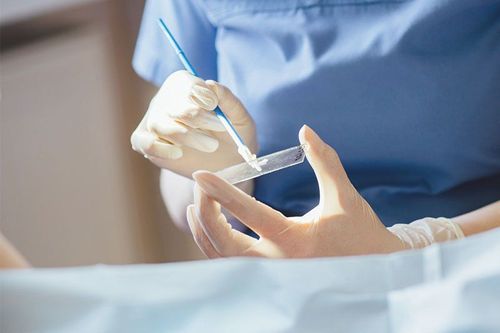
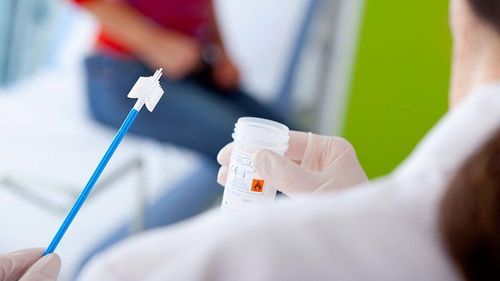
The surface cells of tissues - organs still regularly shed spontaneously during normal physiological activities. When precancerous or cancerous lesions appear, cancer cells with poor adhesion characteristics are even more prone to sloughing off. Therefore, when a tumor in the female genital tract, respiratory tract or body cavity is suspected, it is possible to collect fluid in the sac of the vagina, sputum, peritoneal fluid, pleural fluid, ... to Look for abnormally shaped squamous cells. This method of collection has the disadvantage that the number of natural sloughing cells is usually not much. To increase the number, it is sometimes necessary to use appropriate tools for each organ to sweep, brush, and wash; artificial peeling.Precancerous and cancerous lesions of the cervix usually appear first in the transformation zone. In the routine Papanicolaou (PAP) test, a variety of instruments can be used such as Ayre sticks, combs, brooms; To obtain the correct sloughing cells from this area, spread on the slide in a thin layer and fix (wet or dry).
Hình 1: Que gỗ Ayre (1), que chải (2), chổi quét (3) (A); Dùng que Ayre và que chải để lấy tế bào bong ở vùng chuyển dạng cổ tử cung (B,C); phết tế bào lên lam thành 1 lớp mỏng (D).
3. Body cavity fluids
Body cavities include pleural cavity, peritoneal cavity and pericardial cavity; There may be effusions of varying degrees. Fluid is aspirated with a needle aspiration or drainage tube, for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. The fluid has a different color and cell density depending on the cause of the disease, tumorigenesis or non-tumor.
The primary purpose of cytology of body cavity fluids is to look for sloughing tumor cells. The collected solution must have a volume of more than 20ml, be put into a vial or centrifuge tube (25ml capacity), do not need to be fixed if the smear is carried out within the first 12 hours and the solution can be stored in the refrigerator. at 4 degrees Celsius for 72 hours without fear of affecting cell morphology; If you want to preserve the solution for longer, then fix the solution with 50% ethanol at a ratio of 1:1.

Hình 2: Dịch vàng trong như huyết thanh (1), đục hơn do mật độ tế bào tăng (2), màu đỏ do lẫn máu ít (3) hoặc nhiều (4), dịch mủ màu vàng đục (5), dịch dưỡng trấp màu trắng (6).
Cells in the fluid are collected and smeared on slides according to the following techniques:
Direct smear: Apply to cell-rich fluid samples, use a brush or pipette to transfer cells to the slide and perform the smear. thin. Fix the smear (wet or dry). Centrifugation: Applied to cell-poor samples. Tubes containing 15-20 ml of solution were placed in a centrifuge at 2000 rpm for 10 minutes. Discard the supernatant, use a pipette to aspirate the cell deposits from the bottom of the tube, transfer to a slide for thin smearing. Fix the smear (wet or dry) (Fig. 3C,D).

Hình 3: Nhúng que chải vào mẫu dịch (A), phết lên lam (B); cho mẫu dịch vào ống đem quay ly tâm (C), đổ bỏ phần dịch bên trên, dùng pipét hút cặn lắng ở đáy ống để làm phết tế bào (D).
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.