This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Thi Phuong Loan - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General HospitalOvarian cysts are mostly benign, only a small percentage have cancerous and other complications that are life-threatening and affect the ability to perform motherhood. Therefore, when detecting ovarian cysts, it is necessary to diagnose and treat promptly.
1. What is an ovarian cyst?
Ovarian cysts are cysts that form in the ovary, with an outer shell, inside containing fluid, that form during ovulation. The disease can occur in women of any age, but is highest in reproductive age. About 8% of premenopausal women develop large cysts that require treatment. Ovarian cysts are less common in women during and after menopause, with a higher rate of progression to ovarian cancer than other stages.Most ovarian cysts are harmless, with no specific symptoms. As a result, most people don't know they have a cyst - unless the cyst grows large or has many cysts. However, ovarian cyst is a disease that is prone to complications, in some special cases (such as rupture), can cause serious complications (intra-abdominal bleeding, peritonitis). . ). Therefore, a woman needs to have regular health check-ups to promptly detect and receive the best follow-up advice and treatment..
2. Complications occur when ovarian cysts are not treated in time

U nang buồng trứng có thể gây vô sinh nếu không được điều trị kịp thời
Torsion of the cyst: Usually occurs with small-sized, long-stemmed, non-adhesive tumors. This complication can also occur during pregnancy (especially in the first months of pregnancy), or after giving birth. Patients present with sudden, severe abdominal pain, sweating, dizziness, vomiting. In this case, the patient needs to be taken to the hospital for emergency surgery promptly. The doctor will remove the torsion, if the ovary is pink again, then the tumor will be removed to save the ovary. Cyst rupture: Cyst rupture is a rare complication, usually occurs in the case of water cysts due to their thin shell, which will cause severe pain and bleeding. In cases where a cyst is not detected early, it can grow large and rupture or rupture after a severe trauma to the lower abdomen. A ruptured cyst not only causes severe pain, it can also cause life-threatening complications such as ruptured ovarian cyst, bleeding and infection. Patients often present with severe pain around the abdomen, nausea, or vomiting, which is worse when touching the breast. Cyst infection: Bacterial infection occurs when there is cystic volvulus. Manifested by enlarging cyst, sticking to the surrounding viscera. It should be diagnosed and treated early. Pelvic compression: Complications often appear late, when the tumor is large, it is likely to press on the rectum and bladder. Tumor compresses the bladder causing urination, compresses the rectum causes constipation. Enlarged cysts, progressing over many years, occupying the entire abdomen, sometimes compressing the ureters, causing pyelonephritis, compressing the inferior vena cava causing edema, collateral circulation, and ascites. Bleeding in the cyst: This is the most common complication. Bleeding occurs when a blood vessel in the cyst ruptures or becomes twisted. Blood from the blood vessels spills into the cyst and causes the cyst to begin to enlarge. An ovarian cyst is a thin-walled sac filled with fluid that can easily cause bleeding. Not every case of bleeding that occurs requires surgery. In some cases, the cyst will grow for a period of time, then begin to shrink and eventually go away on its own. However, monitoring of a hemorrhagic ovarian cyst is essential to ensure that it is self-limiting and does not pose a danger to the ovaries. Other complications: Infertility, premature birth, miscarriage, difficulty giving birth and the risk of turning into cancer.
3. Complications during pregnancy
Ovarian cysts also often occur during pregnancy, most cases are benign. Ovarian cysts that continue to grow can rupture, or twist, and cause problems during delivery. The most common form of cyst is the corpus luteum or dermoid cyst, rarely malignant cysts. During the time the fetus is over 13 weeks old, the placenta has secreted enough hormones to nourish the fetus, if it is a corpus luteum cyst, it usually decreases in size or does not grow anymore, it may not need surgery and pathological examination. physical. In the case of large growth, in the second trimester of pregnancy, surgery should be performed immediately, unless detected only in the late pregnancy.
An action plan, follow-up - appropriate treatment needs to be in place to protect the health of yourself and your unborn baby.
4. How to detect ovarian cysts?
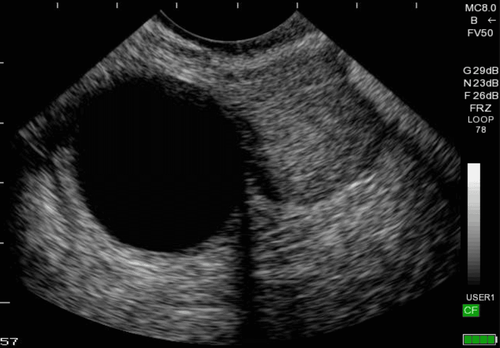
Siêu âm có thể dùng để phát hiện u nang buồng trứng
Diagnostics and tests for ovarian cysts to help diagnose the disease include:
Ultrasound detection of ovarian cysts: Using a transducer placed inside the vagina, ultrasound shows the image and characteristics of the tumor. ovarian cyst in terms of shape, size, position, volume (liquid, solid or mixed). Ultrasound is a modern imaging tool, bringing high accuracy to classify ovarian tumors. However, to get the most accurate ultrasound results, you need to choose a reputable performing facility, modern facilities, and a team of experienced and qualified medical professionals. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital systems have been using modern generations of color ultrasound machines. One of them is GE Healthcare's Logiq E9 ultrasound machine with full options, HD resolution probes for clear images, accurate assessment of lesions.
Pregnancy test to know if the patient is pregnant or not. Test hormone levels. Blood test: For postmenopausal women, the doctor will order an additional test that measures the amount of cancer antigen 125 (CA-125). If you have ovarian cancer, your CA-125 levels are higher than normal. However, in many cases in premenopausal women with certain other conditions cancer (endometriosis, cystic fibrosis, pelvic infection, etc.) can also increase CA levels. -125.
5. Prevent the progression of ovarian cysts
Eat lots of green vegetables and fruits, whole grains. Supplement food sources rich in Vitamin A and Vitamin C. Drink enough from 1.5 liters to 2 liters of water/day. Arrange a reasonable rest time combined with gentle exercises, abdominal and uterine massages. Practice regular gynecological examination to determine the progression of the disease and take timely treatment measures. Limit eating fast food and especially junk food fried through grease and oil many times such as fried spring rolls, sausages, ... Limit the use of alcoholic beverages such as beer, wine, coffee and especially Absolutely avoid smoking. Minimize stress in daily work. When there are signs of ovarian cysts, you should go to reputable medical facilities for timely examination and treatment by an obstetrician and gynecologist, to avoid complications of ovarian cysts that affect reproductive health. produce.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.