This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Nguyen Chi Quang, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Ovarian cyst is a common tumor in women. The majority of ovarian cysts are benign, with only a small percentage having cancerous complications. Depending on the size and nature of the patient's tumor, the doctor can choose the appropriate method.
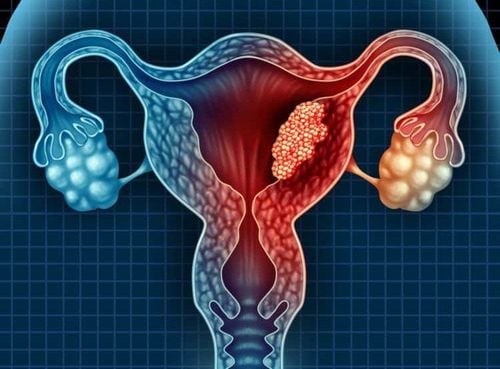
1. What is an ovarian cyst?
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled mass in the ovary. In fact, most ovarian cysts are benign.Some common types of ovarian cysts such as:
Functional cyst: a tumor arising from endocrine dysfunction of the ovaries Ovarian cyst: a mature follicle that does not burst and does not ovulate, this cyst continues Continue to grow, can be over 10cm, secrete oestrogen - the cause of the patient's delay in menstruation. Urgent surgery is required if the cyst ruptures in two and causes heavy intra-abdominal bleeding. Thyroid cysts: common in patients with oviductal carcinoma, trophoblastoma, multiple pregnancy, or infertility. Organic cysts: masses This tumor can change in ovarian histology, so there is a possibility of cancer. Ovarian cyst: this is the most common type of cyst, accounting for 40% of ovarian cysts. This type of tumor is also at risk of becoming cancerous. Ovarian dermoid cyst: accounts for about 25% of ovarian cysts, usually malignant, tumors have similar structure to skin, have stratum corneum, sebaceous glands... Cystic endometriosis : grows right on the surface of the ovary, destroying healthy ovarian tissue. The inside of the cyst is filled with fluid, the capsule shell is thin. Tumors are often painful and can cause infertility if they are attached to the fallopian tubes.
2. Signs of ovarian cysts
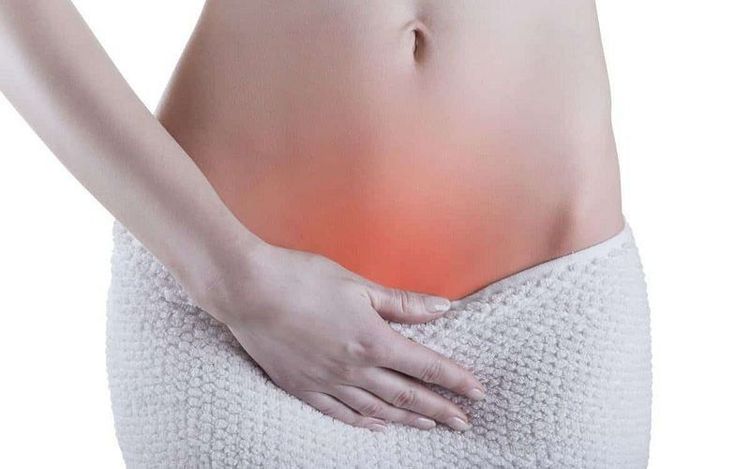
Đau, căng, tức vùng bụng dưới là dấu hiệu u nang buồng trứng
Some signs may appear when you have an ovarian cyst such as:
Pain, pressure, tightness in the lower abdomen Painful pelvic area Low back pain Difficulty urinating and defecating Pain during sex Flowing Abnormal vaginal bleeding Pain during menstrual cycle Tight breasts Frequent urination Dark abdominal pain Discomfort in the vagina Frequent menstrual irregularities Menstrual color turns black Slightly enlarged abdomen Patient may You will experience severe pain if the cyst ruptures.
3. Complications of ovarian cysts
Patients with ovarian cysts, if not examined and treated promptly, will very easily cause extremely serious complications.Torsion of the cyst: patients with torsion of the cyst will have severe abdominal pain, persistent nausea and vomiting, tachycardia, decreased blood pressure, abdominal distension, pain in the lower abdomen and 2 pelvises. It can be seen that the tumor is very tight, less mobile, sharp pain when pressed on vaginal examination. Cyst rupture: the patient feels sudden and continuous abdominal pain. In some cases, rupture of a cyst can cause internal bleeding, which can cause a person to be shocked due to blood loss. Usually after rupture of the cyst, the patient has an infection syndrome, abdominal distention. Vaginal examination revealed a sticky, less mobile, painful lump when pressed. Compression of surrounding organs: This complication often occurs late when the tumor has grown for a long time and has a large size. Large tumor, compressing the bladder causing urinary incontinence, compressing the rectum causing constipation and possibly causing pyelonephritis when compressing the ureter, even large ovarian tumors can compress the inferior vena cava causing collateral circulation, 2 lower extremities edema, ascites. Water cysts may be at risk of cancerous growths.
4. Treatment of Ovarian Cysts
If the patient has a functional cyst usually does not need treatment, it will disappear on its own after a few menstrual cycles. Sometimes functional cysts also have complications such as cyst torsion, cyst rupture... that requires prompt surgery, but these cases are very rare.If the patient has a physical cyst, surgery should be performed as soon as possible. Unlike uterine fibroids, which are benign, ovarian cysts are always at risk of malignancy. And the only way to know the exact nature of the tumor (benign or cancerous) is to surgically remove the tumor for a biopsy. Depending on the size and nature of the patient's tumor, the doctor will choose the appropriate surgical method such as laparoscopic surgery to remove the entire tumor and the affected ovary or just dissect the tumor and leave it alone. benign tumor. It is possible to perform laparoscopic removal of an ovarian tumor or perform a surgical removal of an ovarian cyst.
Currently, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital is applying the method of removing ovarian cysts with a robotic arm. This is a modern surgical method with low risk of infection, short hospital stay and quick recovery time. Under the direction and implementation of Doctor Nguyen Chi Quang - 12 years of experience in laparoscopic surgery with a team of experienced and qualified medical staff and doctors, patients with uterine prolapse - bladder will be operated on. with high safety and efficiency.
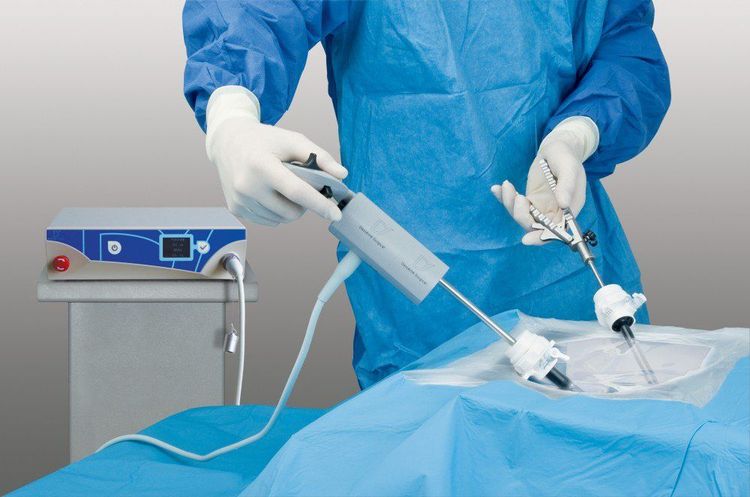
Phẫu thuật ít xâm lấn bằng robot cầm tay
For more detailed advice on the Gynecological surgery incentive program and to book an appointment for examination and treatment at Central Park International General Hospital, please contact Hotline: 0283 6221 166 or register online HERE THIS