This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Nguyen Chi Quang, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. Dr. Quang has many years of profound professional experience and strength in the treatment of obstetric and gynecological diseases.Ovarian cyst is the most common type of tumor, accounting for about 3.6% of gynecological diseases. There are many types of cysts, of which 90% of ovarian cysts are benign, only 10% are malignant. Not all patients with cysts need surgery.
1. What is an ovarian cyst?
An ovarian cyst is a sac filled with fluid or other tissue that grows abnormally on or inside an ovary. Ovarian cysts are the most common type of tumor, which can develop during childbearing years or after menopause. Most ovarian cysts are benign (not cancerous) and go away on their own without treatment. Rarely, malignant (cancerous) cysts.2. Types of ovarian cysts
There are the following types of ovarian cysts:Functional cyst: This is the most common type of ovarian cyst, usually causes no symptoms for women, and disappears on its own in about 6-8 weeks without treatment. treat.
3. Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Most ovarian cysts have no symptoms, and many cases are discovered during routine examinations or scans for other reasons. Sometimes, ovarian cysts cause pain, dull discomfort, or sharp pain in the abdomen with activity. Large cysts can cause torsion of the ovary, causing a person to experience intermittent or sudden pain on one side of the abdomen. Bleeding or ruptured cysts can also cause sudden, severe pain in the abdomen.4. Diagnosis of ovarian cysts
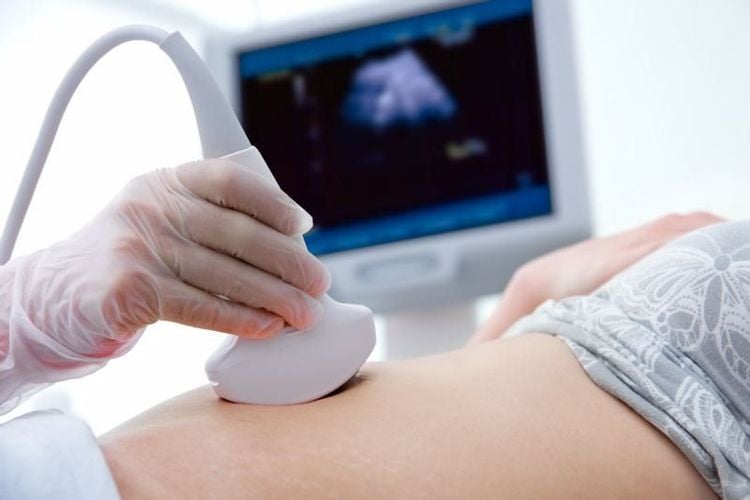
When the patient suspects a cyst, the obstetrician-gynecologist may order some more tests to determine the exactUltrasound: An imaging technique using ultrasound waves (waves) high-frequency sound) to build and reconstruct an image of the internal structure of the body. During an ultrasound, the sonographer places the transducer on the abdomen or through the vagina. Ultrasound shows the shape, size, and location of the cyst, as well as checking whether the inside of the cyst is liquid or solid.
5. Treatment of ovarian cysts
Depending on the type of cyst and a combination of other factors, monitoring or surgery may be possible if the cyst size is large or causes symptoms in the patient.Follow up the cyst by periodic ultrasound to assess the change in size and shape. The doctor will tell the patient how often to have an ultrasound, and how long to follow up with the ultrasound. In many cases, cysts go away on their own after one or two menstrual cycles.
6. When should surgery?
If the cyst is very large or the cyst is causing symptoms in the patient, or if cancer is suspected, surgery may be recommended. The type of surgery depends on several factors, including the size of the cyst, the age of the patient, whether the patient is still planning to have children, and a family history of ovarian or breast cancer. It is possible to surgically remove the cyst from the ovary, or in some cases to remove the ovary.7. The surgical procedure
For benign cysts, laparoscopic surgery (minimally invasive surgery) is recommended, with only laparoscopic instruments and small incisions. Besides laparoscopic surgery, the doctor will conduct open surgery with a longitudinal or transverse incision in the patient's lower abdomen, if cancer is suspected or the cyst size is too large.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Acog.org