This is an automatically translated article.
Ovarian cyst is a fairly common gynecological disease, often without symptoms, so many patients only know when they are hospitalized because the ovarian cyst has ruptured.1. Why do ovarian cysts rupture?
An ovarian cyst is an enlarged sac containing fluid, solid or mixed tissue and located either on the surface or within the lumen of the ovary. A ruptured ovarian cyst is when the structure of the cyst containing the tumor is no longer intact, and the contents of the tumour escape.The signs and symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst can vary greatly, depending on the features of the previous cyst. However, in most cases, this is considered a gynecological emergency.
Patients will have a high risk of ovarian cyst rupture if they have polycystic ovary syndrome. This is a condition that causes multiple cysts to develop on the ovaries. Having one or more of any of the following can lead to a ruptured ovarian cyst.
The levels of hormones change with the monthly menstrual cycle Pressure is applied to the cyst, from daily activities, exercise, to sex or trauma to the abdomen - pelvis. Pregnancy U has a large size, rapid growth rate or is twisted
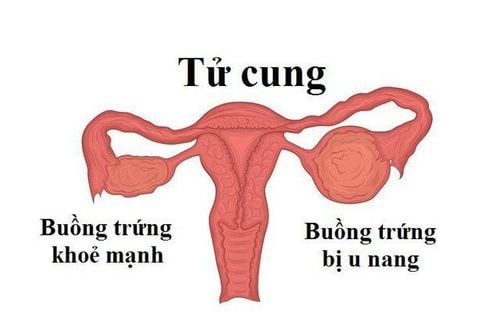
U nang buồng trứng là tình trạng một túi bị phình ra, chứa dịch
2. Signs of a ruptured ovarian cyst
Ovarian cysts can rupture randomly or when there is physical activity, strong force on the tumour. When an ovarian cyst ruptures, the fluid inside leaks out and spreads into the pelvic cavity. At this time, the patient will have the following symptoms:
New dull pain or severe pain on one side of the lower abdomen A vague feeling of fullness or heaviness in the abdomen Bloating Abdominal pain with fever Abdominal pain with sadness Vomiting, vomiting Dizziness, fatigue Rapid breathing Cold, moist skin Vaginal bleeding Depending on the severity of the symptoms in the patient, it is possible to predict the complications of ovarian cysts. A ruptured ovarian cyst can sometimes show no signs, but sometimes it can be life-threatening. Therefore, when one of the above conditions is present, especially when an ovarian cyst is known, a woman needs to be examined early or hospitalized urgently for timely intervention.

Vỡ ung nang buồng chứng khiến người bệnh rất mệt mỏi
3. How is a ruptured ovarian cyst diagnosed?
When a patient is admitted to the hospital because of abdominal pain on one side of the pelvis, accompanied by vaginal bleeding, it will be difficult for the doctor to rule out adnexal diseases through examination alone, the diagnosis of a ruptured ovarian cyst. will be based on test results including:
Blood test: Quantifying beta HCG levels is used to check if the patient is pregnant or not and thereby can predict the gestational age. In addition, blood tests are also needed to know if the patient is likely to have a co-infection. Ultrasound: Ultrasound images can show a cyst on your ovary, the presence of fluid in the sac, and the nature of the fluid. This tool becomes extremely useful when using transvaginal ultrasound, which is inserted and directed towards the uterus to get a closer look at your ovaries.
4. Ovarian cyst treatment?
The treatment of ovarian cysts will depend on the age of the patient, the size of the cyst and the complications associated with it. Accordingly, treatment may become unnecessary if the cyst is small or the patient's body absorbs fluid from the cyst. At this time, the patient can only need the following supportive measures:
Pain relievers: Common pain relievers such as paracetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs do not require a prescription. These drugs not only help relieve pain but also anti-inflammatory, reduce edema of the damaged tissue. Antibiotics: This medicine may be needed to prevent or fight bacterial infections. For surgery, surgical intervention is indicated only to resolve the excessive amount of fluid or blood in the pelvis after the ovarian cyst ruptures, with the risk of causing local infection or spreading to the whole cavity. belly. Even if cyst rupture is accompanied by internal bleeding, necrotic ovarian torsion, surgery will be carried out with appropriate methods for each situation, either aiming to preserve reproductive function or perform radical ablation. .
In summary, ruptured ovarian cyst with warning signs is considered a gynecological emergency, with a risk of life-threatening if delayed management. Therefore, women need to have a habit of periodic reproductive health checks, detect in advance and have a good monitoring plan for ovarian cysts in order to proactively intervene early when indicated, to prevent complications related to ovarian cancer. after.
In order to help customers detect and treat other gynecological diseases early, Vinmec International Hospital has a basic gynecological examination and screening package, helping customers detect early inflammatory diseases Easy, inexpensive treatment. Screening detects gynecological cancer (cervical cancer) early even when there are no symptoms.
Basic gynecological examination and screening package for female customers, has no age limit and may have the following symptoms:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding Having menstrual problems: irregular menstrual cycle, irregular menstrual cycle Irregular vaginal discharge (smell, different color) Vaginal pain and itching Female clients have several risk factors such as poor personal hygiene, Unsafe sex, abortion,... Female customers have other symptoms such as: Abnormal vaginal discharge, itching, pain in the private area, abnormal vaginal bleeding.
If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.