This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Master, Resident Doctor Tran Duc Tuan - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI is used to evaluate problems with the brain, neck, and spinal cord, or to help doctors evaluate problems in a person's chest, heart, abdomen, joints, or blood vessels. There are several different types of MRI scans and are used depending on the condition for which the patient needs to be examined, treated, and monitored.
1. What is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (English name is Magnetic Resonance Imaging and abbreviated as MRI) is an imaging technique that does not use radiation (X-rays) and is a non-invasive technique. An MRI machine uses a large magnet and a computer to take pictures of the inside of your body. Each photo or "slice" shows only a few layers of body tissue at a time. The images can then be checked on a computer monitor.
Images taken this way can help your doctor find problems in your body more easily. The scan usually takes 15 to 90 minutes, including the scan, the total exam time usually taking between 1.5 and 3 hours.
A contrast material called gadolinium is injected into your vein to help doctors see the image better. The gadolinium gathers around the cancer cells and will show up brighter on the captured images.
2. Types of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2.1 Functional magnetic resonance imaging Functional magnetic resonance imaging (English name functional magnetic resonance imaging and fMRI for short) measures the small changes in blood flow that occur during brain activity. This technique can be used to examine the functional anatomy of the brain, assess the impact of stroke or other disease, or guide treatment of brain diseases. fMRI can detect abnormalities in the brain that cannot be detected by other imaging techniques.
fMRI is becoming the diagnostic method of choice for diagnosing normal, diseased, or traumatized brains, as well as for assessing the potential risks of surgery or other invasive treatments being used. performed on the brain.
Doctors perform fMRI to:
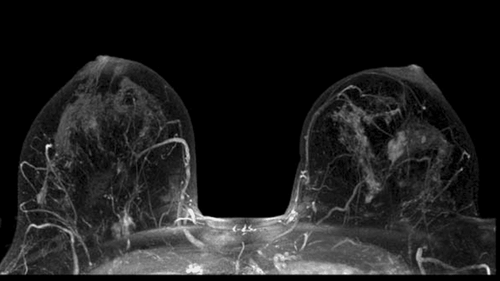
Check the functional anatomy of the brain; Determining which part of the brain is processing important functions such as thinking, speech, movement and sensation, is called brain mapping; Helps assess the effects of stroke, trauma, or degenerative disease (such as Alzheimer's) on brain function; Monitor the growth and function of brain tumors; Guidelines for planning surgery, radiation therapy, or other invasive brain treatments. 2.2 Breast MRI Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (English name is breast MRI) uses a strong magnetic field, radiofrequency pulses, and a computer to create detailed images of breast tissue and any possible abnormalities appear on the breast. A breast MRI does not use ionizing radiation (used in X-rays).
Purposes of a breast MRI scan include:
To help determine the extent of breast cancer : A breast MRI is sometimes used in women who have been diagnosed with breast cancer, to help measure the size of the cancer, to find Look for other tumors in the breast and check for tumors on the opposite breast. But not every woman diagnosed with breast cancer needs a breast MRI. To screen for breast cancer: For some women at high risk for breast cancer, a screening breast MRI is recommended in conjunction with an annual mammogram. MRI is not recommended as a screening test because it can miss some cancers that a mammogram can detect. While an MRI can detect some cancers not seen on mammograms, it is also more likely to find noncancerous cases (known as false positives). . This can lead to unnecessary tests and/or biopsies. This is why MRI is not recommended as a screening technique for women at average risk for breast cancer.
2.3 Magnetic Resonance Angiography Brain Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) uses a strong magnetic field, radio waves, and a computer to evaluate blood vessels and help identify abnormalities. This technique does not use radiation and may require an injection of contrast material. Contrast used for MRA is less likely to cause allergic reactions than contrast used for computed tomography (CT).
Doctors use cerebral angiography to diagnose and treat diseases related to blood vessels. This technique creates images of major blood vessels throughout the body.
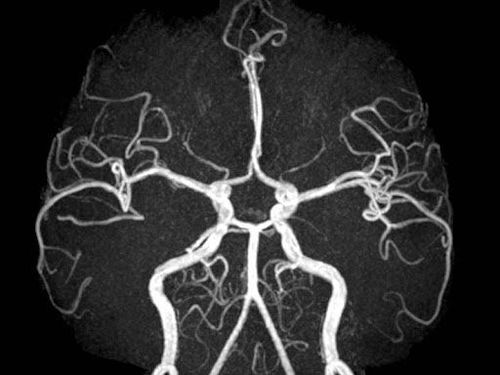
Doctors perform magnetic resonance angiography using:
fluoroscopy to help put a catheter into the blood vessel and inject contrast material to help sketch the image of the blood vessel; Computed tomography (CT) scan; Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). 2.4 Magnetic resonance venography Magnetic resonance venography (English name is magnetic resonance venography and abbreviated MRV) is a highly sensitive imaging technique for the evaluation of deep and superficial venous disease in legs, pelvis, and other areas of the body that cannot be reached by other diagnostic methods. MRV is particularly useful in detecting previously undetected conditions that cause leg pain and swelling.
In general, venous diseases are less common than arterial diseases. In addition, venous disease occurs less frequently, and venous conditions tend to be less severe than arterial diseases.
Therefore, MRV is often used to assess venous blood flow and can detect blood clots or other abnormalities. Some abnormalities in the structure of the veins or problems with blood flow in the brain, abnormalities in the development of veins in young children.
2.5 Cardiac MRI A cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan uses a strong magnetic field, radio waves, and a computer to create detailed images of the structures inside and around the heart. Cardiac MRI is used to detect or monitor heart disease and to evaluate the anatomy and function of the heart in people with heart disease at birth and heart disease that develops after birth. Cardiac MRI does not use ionizing radiation to create images, and it can provide the best picture of the heart in certain conditions.
Cardiac MRI is done to help doctors detect or monitor heart disease by:
Assessing the anatomy and function of the heart chambers, heart valves, size and blood flow through major vessels and structures surrounding as the pericardium; Diagnose cardiovascular (heart and/or blood vessel) disorders such as tumors, infections, and inflammation; Assess the impact of disease on coronary artery disease such as decreased blood flow to the heart muscle and scarring in the heart muscle after a patient has a heart attack; Making treatment plans for patients with cardiovascular disorders; Monitor the progression of certain disorders over time; Evaluate the effectiveness of surgery, especially in patients with congenital heart disease; Evaluation of cardiac and vascular anatomy in children and adults with congenital heart disease. Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the most advanced imaging technologies available today, helping doctors accurately diagnose diseases and offer the most effective treatment regimen.
Vinmec International General Hospital is the first unit to put into use a 3.0 Tesla silent magnetic resonance imaging machine, bringing outstanding advantages. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at Vinmec will have the following outstanding advantages:
High imaging technology, first-class safety by accuracy, non-invasiveness and no radiation. High image quality, allowing doctors to comprehensively evaluate, not miss even the smallest lesions in organs Minimize noise, create the most comfort for patients when taking pictures, reduce stress, this helps better image quality and shortens the maximum scanning time. MRI with Silent technology is especially suitable for the elderly and children, people with weak health, and patients undergoing surgery. .. MRI scan at Vinmec can take 3D vascular reconstruction without injection of magnetic contrast, can reconstruct and handle motion disturbances of the patient Master, Doctor Tran Duc Tuan is trained. methodically in the country and many centers with prestigious medical background in the world such as: Australia, Singapore, Thailand... The doctor has many years of experience in the field of imaging diagnosis and interventional and endovascular interventions. blood. Currently, the doctor is working at the Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Interventional Vascular Unit - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: stanfordhealthcare.org