This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Ton Nu Tra My - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Breast density is a measure of the proportions of glandular, connective tissue, and fat in a woman's breasts. It is usually identified using mammography. Women with dense breast tissue is not an unusual condition. Although, the exact relationship between breast density and breast cancer has not been clearly established, people with dense breast tissue may have an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
1. Solid breast tissue
Breasts are made up of glandular, connective and fatty tissues. On the mammogram, adipose tissue appears dark gray and glandular and connective tissues appear grayish-white (opaque). If the breast tissue is predominantly glandular and connective tissue, the whiter the mammogram, the condition is described as “dense breast tissue”.The glandular tissue includes the lobules (which produce milk during lactation) and the ducts that carry milk from the lobes to the nipple during breastfeeding. Connective tissue (also called fibrous tissue), which supports and holds glandular tissue in place. Fat tissue gives breasts a specific size and shape.
Currently, there is still no scientific evidence to show why some women have dense breast tissue while others do not. In general, young women tend to have denser breast tissue than other age groups, and conversely some postmenopausal women may lose breast tissue density due to hormonal changes experienced during pregnancy. menopause. However, some younger women may also have fatty breast tissue while some older women have dense breast tissue. The majority of breast density women have is due to genetics. In addition, dietary changes, nutrition, weight gain or loss, and hormonal factors will all be factors that affect a woman's breast density. About 50% of all women over 40 have dense breast tissue, and that's normal.
The exact relationship between breast density and breast cancer is still being studied with many unknowns. On mammograms, latent cancer can be easily detected in women with predominantly fatty breast tissue, but latent cancer can be difficult to detect in dense breast tissue women.
2. Diagnosis of dense breast tissue
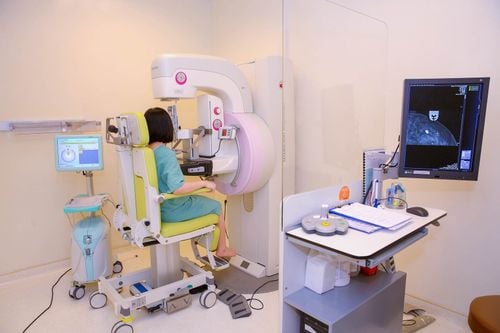
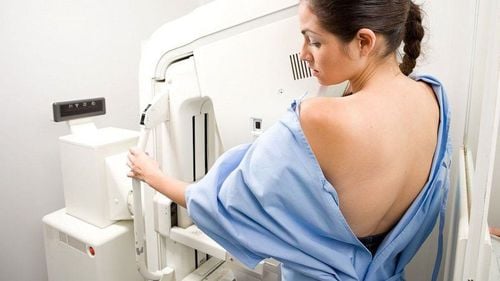
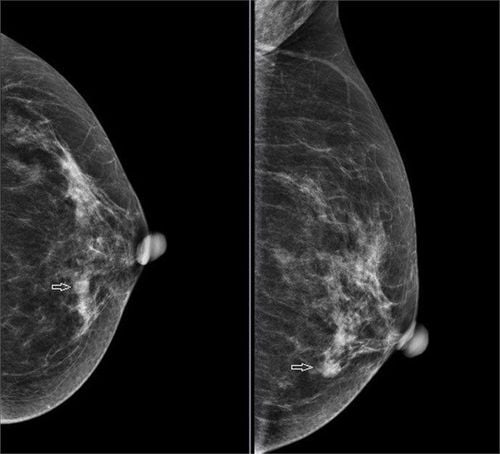
Mammography is most commonly used to determine if a woman has dense breast tissue. This is a diagnostic test that uses low-dose X-rays to evaluate the breasts.Based on the ratio between fibrous tissue, glandular tissue (white on mammogram) and adipose tissue (black on mammogram) breast density will be divided into four levels as follows:
Almost completely fat (type A) ): Breast is almost entirely composed of adipose tissue, the proportion of adipose tissue accounts for more than 75%. Scattered fibrous density (class B): Most of the breast is adipose tissue along with some scattered areas of dense breast tissue. The percentage of adipose tissue accounts for > 50%. Inhomogeneous density of dense breast tissue (type C): Most of the breast is dense glandular and fibrous tissue with some areas of less dense fatty tissue. The percentage of adipose tissue accounts for <50%. Extremely dense breast tissue (type D): The breast consists of almost all dense glandular and fibrous tissue. The percentage of adipose tissue accounted for < 25%. The majority of women (about 8 out of 10) have breast tissue types B and C. Only a very small number of women have breast tissue types A and D.
Density of breast tissue types C and D is considered dense breast tissue. Some countries have enacted legislation requiring the disclosure of mammogram results of breast density in women with dense breast tissue. At that time, these women should talk to their doctors about other imaging tests to help screen for breast cancer.
Additional tests: Additional imaging tests in breast cancer screening in women with dense breast tissue include ultrasound, breast magnetic resonance.
3D mammography (Tomosynthesis), is a method now increasingly widely used in breast cancer screening. Tomosynthesis creates multiple images of the breast from different angles and reconstructs or "composites" into a set of three-dimensional images. Large population studies have shown that Tomosynthesis screening results in improved breast cancer detection results and reduced "callback" rates compared with conventional 2D mammography. Early studies suggest that this method may be beneficial in women with dense breast tissue.

The Diagnostic Imaging Department of Vinmec International Hospital now has a full range of medical machines such as 3D breast ultrasound machines and new generation MRIs with a team of experienced and skilled doctors. Well done will bring accurate results and advice on effective treatment regimens. In addition, to improve service quality, now, Vinmec also provides customers with breast cancer screening packages with methods of breast ultrasound on both sides, mammograms to check and screen. disease since the disease has no symptoms.
The Diagnostic Imaging Department of Vinmec International Hospital now has a full range of medical machines such as 3D breast ultrasound machines and new generation MRIs with a team of experienced and skilled doctors. Well done will bring accurate results and advice on effective treatment regimens. In addition, to improve service quality, now, Vinmec also provides customers with breast cancer screening packages with methods of breast ultrasound on both sides, mammograms to check and screen. disease since the disease has no symptoms.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: mayoclinic.org, radiologyinfo.org