This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor General Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital. The doctor has more than 30 years of experience in the field of internal medicine.
Usually when the body is injured or bleeding, blood clots are the "salvage" factor to help stop the bleeding quickly. However, when these blood clots form abnormally, they can lead to heart attacks or strokes, and even death, if left untreated.
1. What is a blood clot (thrombosis)?
Blood clots are jelly-like masses of blood, usually found mainly in the arteries, or veins in the heart, brain, lungs, abdomen, arms, and legs of the body.
Normally, blood clots will stop bleeding when the body is injured or has cuts. Your body will most likely break down blood clots after your wound has healed. However, in certain cases, the body is unable to deal with these clots. In subsequent visits, they will form inside the blood vessels for no apparent reason. This can lead to serious health problems, such as a heart attack, a heart attack, or a vein blockage.
In addition, blood clots can also take root in the kidneys, intestines and eyes of the body, but this is rare.

2. How are blood clots formed?
The life cycle of blood clots depends on a series of chemical reactions in the body:
Formation of platelet plugs: When a blood vessel is damaged, the release of platelets is triggered. They then gather and stick to the damaged vessel wall, forming a mass that fills the wound and prevents blood from flowing out. Once activated, the platelets will also release chemicals that attract more platelets and other cells to prepare for the next step. Development of blood clots: Proteins in the blood that act as clotting factors signal each other to create a rapid chain reaction that will eventually produce long strands of fibrin, otherwise known as fibrin. . These fibrin fibers combine with the platelet plugs and form a network to "trap" more platelets and cells, thereby forming blood clots at the site of injury. Under the action of platelets and fibrin fibers, these clots will become harder and firmer. Thromboembolism growth inhibition: Other proteins compensate for the proteins (clotting factors) so the clots don't spread more than they should. Thrombolysis: When damaged tissues begin to heal, they no longer need blood clots. Meanwhile, the hard fibrin fibers will gradually dissolve into the blood, and the platelets and cells of the clot will gradually separate from each other.
3. Causes of blood clots
These types of blood clots form when the blood stream comes into contact with substances in the walls of blood vessels or on the skin of the body. This condition is a manifestation of broken blood vessel walls or damaged skin surface, causing blood cells to leak out.
Besides, cholesterol plaques (plaques) form in the arteries, when these plaques fall off, it triggers blood clotting. Most strokes and heart attacks happen when a plaque in the brain or heart suddenly ruptures/sloughs off.
Most of the time, blood clots form because the body's blood flow is abnormal. If they are in the heart or blood vessels, platelets can stick together. Among them, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and atrial fibrillation are two conditions that lead to blood clotting due to slow blood movement.
4. Symptoms of Thrombosis
At first, you may not experience any symptoms, only when the number of blood clots increases more or stops blood flow, the body will have the following signs:
Cold hands or feet Muscle pain or spasms in the affected area Numbness or tingling in the arms and legs Weakness of the affected limbs Changes in skin color in the area of the skin where the blood clot is located.
5. Common types of blood clots
Typically, there are three types of blood clots that form in a vein, including superficial vein thrombosis, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and pulmonary embolism (PE).
5.1 Superficial Venous Thrombosis A blood clot that forms in a vein near the surface of the skin. This condition typically causes the following typical symptoms:
Swelling, pain with inflammation of the skin in the affected vein Feeling stiff in the vein and painful to the touch Red, irritated skin on the affected vein 5.2 Blood Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition in which blood clots form in the deep veins of the body. It usually occurs in the thighs, lower legs, or pelvis. They can also form in other parts of the body, such as the arms, liver, intestines, or kidneys. When suffering from DVT, the patient usually has the following symptoms:
Swelling in one leg, sometimes in both legs Feeling cramping, aching pain in the leg, especially the calf. The pain may get worse when you bend your leg toward the knee. A feeling of heaviness in the leg affected by DVT. Redness of the skin in the affected area DVT is a medical emergency. You should see your doctor immediately if you notice any of these symptoms, including swelling and pain in your feet; shortness of breath and chest pain. If not treated promptly, DVT can turn into pulmonary embolism (pulmonary embolism-PE).
5.3 Pulmonary embolism (PE)
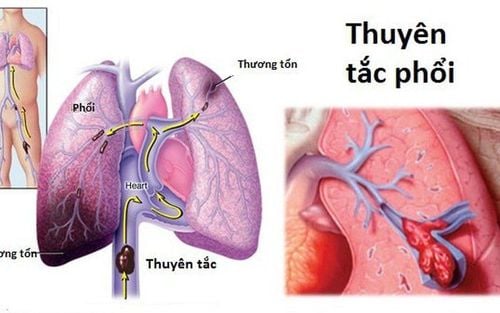
It is a dangerous condition that can even lead to death if not treated promptly. Pulmonary embolism is often a complication of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). When this happens, a blood clot in a deep vein will break off and travel to the lungs, leading to a blockage in the lungs.
6. Certain medications help prevent blood clotting
Certain medications can prevent platelet aggregation, including:
Aspirin Dipyridamole ( Persantine ) Clopidogrel ( Plavix ) Ticagrelor ( Brilinta ) Prasugrel Ticlopidine ( Ticlid ) Certain anticoagulants may be used to prevent blood clotting. blocks blood clotting factors, including:
Dabigatran ( Pradaxa ) Apixaban ( Eliquis ) Heparin Edoxaban ( Savaysa ) Warfarin ( Coumadin ) Rivaroxaban ( Xarelto ) Drugs that dissolve blood clots and activate breaking proteins rupture of fibrin fibrils, including streptokinase, alteplase and tenecteplase. Sometimes, doctors may prescribe these medications to patients for heart attacks and strokes.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com