This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Cardiologist - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital
Angina is caused by reduced blood flow to the heart resulting in the heart muscle not receiving enough oxygen. The pain is often triggered by overactivity or stress. There are two types of angina, stable and unstable, of which stable angina, or chronic ischemic heart disease, is more common.
1. Causes of chronic ischemic heart disease
The cause of chronic ischemic heart disease is atherosclerotic plaque that forms in the coronary arteries and causes a partial blockage, blocking the flow of blood in the artery. This partial obstruction allows adequate blood flow to the myocardium, without hypoxia but only during rest, so that at rest the patient does not have angina.
However, a partial blockage also limits the maximum amount of blood that the artery can supply to the heart. So, when the heart muscle needs to work harder, like during physical exertion (running, swimming, climbing stairs, ...) or emotional stress, blood flow cannot increase enough to meet the needs. increasing demand of the myocardium. As a result, the heart muscle is deprived of blood and oxygen, leading to angina pectoris.
Once physical exertion has stopped due to the angina symptoms causing the patient to stop, then the amount of oxygen required by the heart muscle drops to baseline. In a few minutes, the ischemia will clear up and the angina will disappear.

Cơn đau thắt ngực xuất hiện
2. Diagnosis of chronic ischemic heart disease
To diagnose this disease, the doctor will begin a general physical examination and ask about the past symptoms as well as the current symptoms that prompted the patient to see the doctor. In addition, the doctor also asks about risk factors such as whether there is a family history of cardiovascular disease.
To determine the degree of blockage and confirm the diagnosis of chronic ischemic heart disease, the doctor will perform a number of other tests and imaging techniques such as:
2.1 Electrocardiogram (ECG) or EKG) Each beat of the heart is triggered by an electrical impulse produced by special cells in the heart. An electrocardiogram records these electrical signals as they travel through the heart. In an ischemic electrocardiogram, the doctor checks the waves of the heartbeat to see if blood flow through the heart is slowed or interrupted.
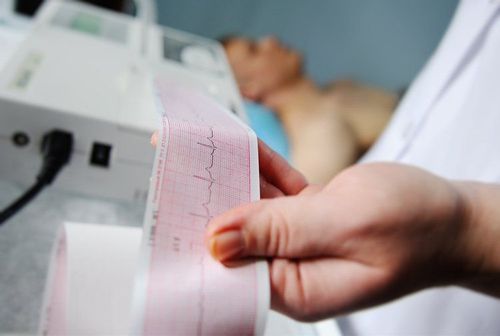
Điện tâm đồ giúp chẩn đoán bệnh
2.2 Stress test Stress test aka cardiac stress test. During the test, the patient will exercise by walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bicycle. During exercise, the patient's blood pressure and electrocardiogram will be monitored. If you can't exercise, you may be given medications that make your heart beat harder to simulate exercise.
2.3 Echocardiogram An echocardiogram uses sound waves to create images of the heart. Doctors use these images to identify areas of heart muscle that have been damaged by poor blood flow.
2.4 Nuclear stress test This test measures blood flow to the heart muscle both at rest and during stress. It's like a normal stress test, but in nuclear stress testing, doctors use an extra radioactive substance that's injected into the patient's bloodstream. This substance when entering the blood will go to the heart of the patient. The doctor will then use a special scanner to capture radioactive substances in the heart and create images of the heart muscle. In the event that blood flow to a certain part of the heart muscle is reduced, not much radioactive material will reach that area.
2.4 Chest X-ray Take a chest X-ray to check a person's heart and lungs. This technique can look for other conditions and check for an enlarged heart.
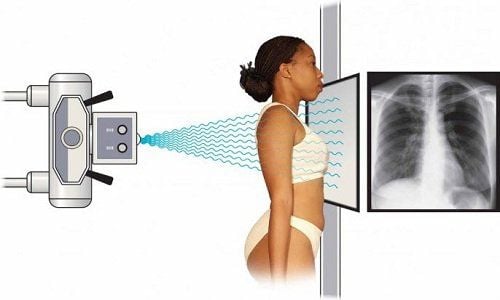
Chụp X-quang ngực chẩn đoán bệnh tim thiếu máu cục bộ mạn tính
2.5 Blood tests Some heart enzymes will slowly leak into the blood if a person's heart is damaged by a heart attack, so a blood test will check for the presence of these enzymes.
2.6 Coronary Angiography Coronary angiography uses X-rays to examine the inside of the heart's blood vessels. During coronary angiography, the patient is injected with a contrast agent that is seen on an X-ray machine. The X-ray machine quickly takes a series of pictures of the coronary arteries, providing a detailed view of the inside of the patient's blood vessels.
3. Treatment of chronic ischemic heart disease
The goals of treatment for chronic ischemic heart disease are (1) to relieve or relieve the symptoms of angina, (2) to prevent further atherosclerotic plaque growth, and (3) to prevent prevent more serious complications such as heart attack, heart failure, and death.
Treatment includes medication, consideration of whether invasive treatment is needed, and lifestyle modifications to prevent complications. Treatment may include one or more medications to relieve angina attacks such as nitrates, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and/or ranolazine (Ranexa).
In a person with chronic ischemic heart disease, invasive therapy (with stents or bypass surgery) may be needed only when medical therapy fails to control symptoms.

Khi sức khỏe có biểu hiện bất thường, người bệnh nên đến gặp bác sĩ
Anyone who has developed complications of coronary heart disease should initiate lifestyle changes and use medications to slow the progression of the disease. Patients should treat or control risk factors for worsening coronary artery disease such as hypertension, diabetes or metabolic syndrome, dyslipidemia, being overweight, sedentary, and smoking.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.