This is an automatically translated article.
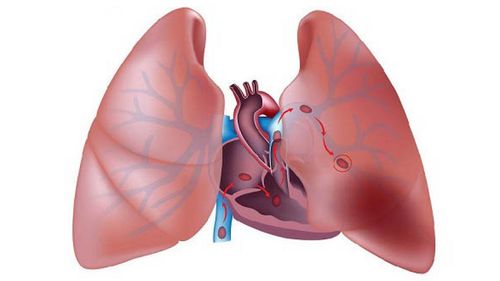
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thuc Vy - Doctor of Diagnostic Imaging - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot becomes lodged in a pulmonary artery and blocks blood flow to the lungs. It is usually caused by a blood clot that originates in the deep veins of the lower extremities or elsewhere in the body.
1. Symptoms of pulmonary embolism
The most common symptoms of pulmonary embolism, which usually have an acute onset, include:Chest pain: The pain is often described as pleuritic, with muscle pain that gets worse or sharp when the person takes a deep breath. Shortness of breath: The person may have difficulty breathing at rest and the shortness of breath may be worse with activity. Hypoxia: Decrease in blood oxygen levels Signs such as: Blood pressure, heart rate, breathing rate, and oxygen saturation can be normal or abnormal, depending on the size of the clot causing the embolism and the extent of the blood clot. effect on lung tissue. The larger the clot, the less stable the vital signs. Abnormal vital signs may include:
Tachycardia Tachypnea Low blood pressure Hypoxia: Decreased SaO2 levels. Oxygen saturation describes how many hemoglobin molecules are carrying oxygen. Normal oxygen levels are usually greater than 92%-93%.
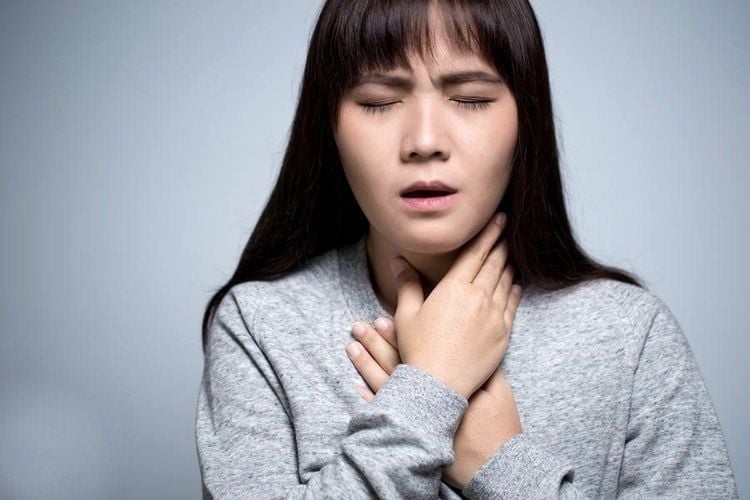

Người bệnh xuất hiện triệu chứng khó thở của thuyên tắc phổi
2. Complications of pulmonary embolism
Because the organs are deprived of the oxygen needed to function, the person suffers from anxiety, fatigue, and dizziness. If the clot is large enough, it can make it harder for the heart to pump blood through the blocked pulmonary arteries, increasing the burden on the heart, increasing pressure inside the heart, and straining the heart muscle. Sudden death is a common complication of pulmonary embolism. The patient collapses, stops breathing, and goes into cardiac arrest without any prior warning symptoms.3. The role of chest X-ray in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism
A chest X-ray is done to create pictures of your heart, lungs, blood vessels, airways, chest bones, and spine. A chest X-ray may also show fluid in or around the lungs or air around the lungs. If you have symptoms of chest pain, chest trauma, or difficulty breathing, you will have a chest X-ray first. Chest X-ray images will help your doctor determine if you have heart problems, collapsed lungs, pneumonia, broken ribs, emphysema, cancer, or any other condition. However, chest x-ray cannot confirm a diagnosis of pulmonary embolism and even chest x-ray may appear normal while patient has pulmonary embolism, but chest x-ray can be helpful. effective in helping doctors rule out certain conditions with symptoms similar to pulmonary embolism.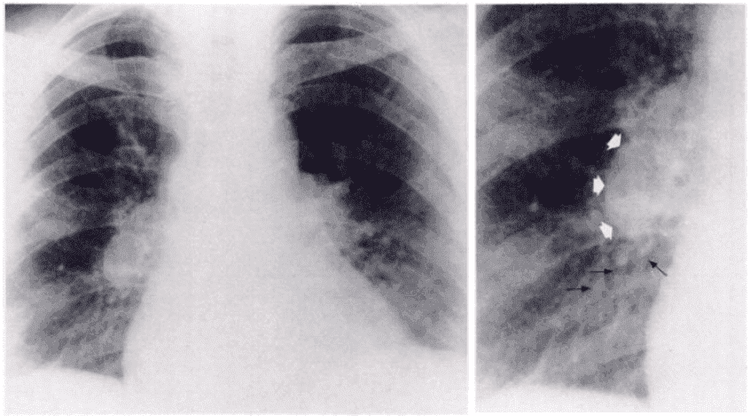
Dấu hiệu thuyên tắc phổi trên X-quang ngực
Blood tests Computed tomography computed tomography scintigraphy, pulmonary perfusion scintigraphy (V/Q scans) Pulmonary angiogram MRI . This may be a good option if you are pregnant or if your doctor is concerned that a diagnostic technique that uses contrast material could be dangerous for the patient. Echocardiography . Although echocardiography does not detect pulmonary embolism, the technique is useful for detecting cardiac overload. Pulmonary embolism can be difficult to diagnose, especially in people with a history of heart or lung disease. For that reason, your doctor will ask about your medical history, do a physical exam, and, especially, will order certain types of tests or imaging techniques such as X-rays, blood tests, etc. CT scan...
Currently, at Vinmec International General Hospital, fibrinolysis is being applied to emergency treatment of patients with pulmonary embolism. With modern imaging equipment, CT perfusion results are available within 7 minutes and performed routinely.
The technique is performed by a team of qualified and experienced medical doctors at Vinmec medical system nationwide.
Master. Doctor Nguyen Thuc Vy has 09 years of experience in Diagnostic Imaging. Dr. Vy has many years of experience working in the Department of Diagnostic Imaging at the University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital in Ho Chi Minh City, trained and attended many courses on specialized imaging at the University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital. Hue Pharmacy, Ho Chi Minh City University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cho Ray Hospital. Currently working at the Diagnostic Imaging Department of Vinmec Nha Trang International Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
MORE:
Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary embolism Tests to help detect chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Symptoms and treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease