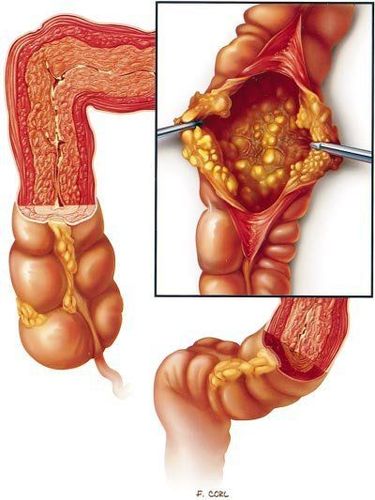
This is an automatically translated article.
The small intestine is part of the digestive tract. Inflammatory bowel disease is a common gastrointestinal disorder. There are many causes and factors that can lead to this condition such as bacteria, fungi or not due to microbiological agents such as chemicals, drugs...1. What is inflammatory bowel disease?
The small intestine is the part of the digestive tube connecting the stomach and the colon, about 7m long, 3cm in diameter. The structure of the small intestine from top to bottom consists of the duodenum lying around and attached to the head of the pancreas; followed by the jejunum and the ileum, which are arranged in many loops of intestine almost parallel to each other and are suspended in the abdomen by the mesentery (a thin membrane, one border attached to the intestine and the other attached to the posterior abdominal wall).The small intestine ensures the following functions:
Absorption of electrolytes, water; Place of digestion and absorption of nutrients glucid, lipid, protid and vitamins; Secretion of intestinal juices, hormones and immunoglobulins; Create peristalsis to push food and waste after being digested to be absorbed into the colon. Inflammatory bowel disease is an inflammation of the small intestine and can cause abnormalities in the digestive system. Inflammation of the small intestine is also one of the causes of small bowel pain, diarrhea... If the inflammation continues, the damaged sites will form ulcers. Affects the function of the small intestine.
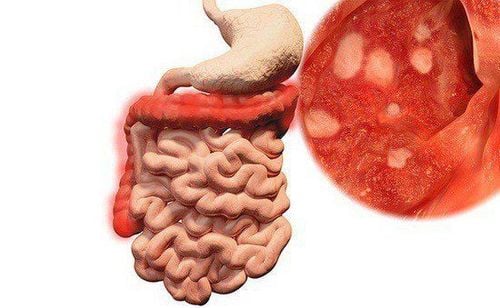
Bệnh viêm ruột non có thể gây ra những dấu hiệu bất thường của cơ quan tiêu hoá
2. What causes small bowel inflammation?
Possible causes of small bowel inflammation include:
Microbial enteritis: But pathogenic microorganisms include bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. This is the main cause of gastrointestinal inflammation in most patients. Microorganisms can affect the lining of the patient's intestines, causing inflammation. Factors that cause infection with pathogenic microorganisms include eating and improperly processing contaminated foods; domestic water sources contaminated with pathogens, especially using untreated lake or stream water; improper body hygiene creates conditions for microorganisms present in a favorable environment to grow and enter the body; do not wash hands with soap often, especially in young children. Crohn's disease: A disease that can affect any part of the digestive tract, but is most common in the jejunum and colon. In which, lesions in the small intestine account for 30-40%. When infected, the patient may present with warning symptoms including abdominal pain, loose stools, unexplained weight loss, which often occurs when the lesion is extensive, fever, complications causing fistula, abscess, bleeding. Tuberculosis Enteritis: Tuberculosis is caused by bacteria. Present with other lesions in the lung, peritoneum or the patient has a history of tuberculosis. Celiac Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An immune-related disease that makes the digestive system unable to tolerate gluten. Thereby causing inflammation of the intestinal mucosa, atrophy of villi, and decreased absorption of nutrients. Symptoms include diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, bloating... Inflammation of the small intestine caused by vasculitis or other autoimmune diseases include: Arteritis nodule, Henoch-Schönlein disease, Behcet's disease, systemic lupus erythematosus ... Inflammation of the small intestine due to bleeding in the small intestine wall: Bleeding can be seen in people with a history of taking anticoagulants, or diseases related to coagulation disorders. Clinical manifestations include abdominal pain around the umbilicus, or pain in an area accompanied by bowel obstruction, abdominal distension... Drug-induced ulcerative colitis: The frequent use of some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is one of the cause inflammation and ulceration of the small intestine. Patients often show symptoms after taking the drug such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, rapid bowel movements... Ischemic Enteritis: Caused by acute mesenteric artery occlusion or chronic. In the acute condition, usually near or complete occlusion of the mesenteric artery causes severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, and bloody stools, requiring early treatment. Chronic occlusion is often not obvious. Lactose intolerance: Patients do not have the enzyme that digests lactose, causing intolerance. If you use foods containing lactose, it will often cause abdominal pain, frequent bowel movements and symptoms that are relieved when lactose is stopped.
Viêm ruột non là bệnh khá thường gặp do nhiều nguyên nhân gây ra
3. Is inflammatory bowel disease dangerous?
Depending on the cause of the small intestine inflammation, there are different health effects for the patient. Some of the effects of small bowel inflammation include:
Causes symptoms that affect the patient's quality of life such as: Abdominal pain, digestive disorders such as nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite. , diarrhea, weight loss... In some cases, acute enteritis can cause abdominal pain, fever, diarrhea and can cause dehydration. If the patient is not treated early, electrolyte disturbances can be life-threatening. When inflammation of the intestinal wall persists, causing ulcers, the small intestine will lose its ability to process food, excrete waste and absorb water, leading to chronic diarrhea. Small scratches that form inside the wall of the small intestine can cause small bowel pain and blood in the stool. In addition, in Crohn's disease other parts of the body can also be affected such as the eyes, skin and joints. People with Crohn's disease can also develop eye inflammation, arthritis, and skin disorders. Not only that, this disease also increases the risk of gastrointestinal cancer. Therefore, it is necessary to be treated and properly to limit the development of the disease, limit the risk of recurrence. The disease often causes the small intestine to reduce the absorption of nutrients, thereby preventing the body from getting enough nutrients. Can cause some diseases related to infection, iron deficiency anemia or B12 deficiency ... In case of enteritis caused by embolism, if not treated, it will cause intestinal necrosis, breaking the intestinal mucosa, releasing bacteria. pathogens outside the abdomen. As such, inflammation of the small intestine can also cause life-threatening complications depending on the cause.
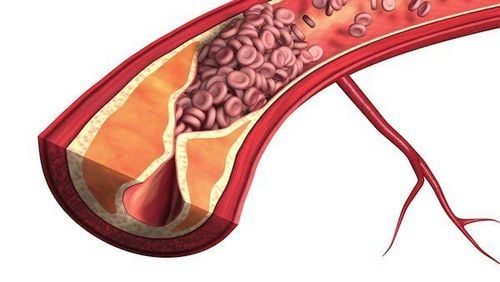
Viêm ruột non do thiếu máu nuôi dưỡng
4. Notes when suffering from small bowel inflammation
People with small bowel inflammation do not always need treatment. Mild cases and inflammation caused by a viral infection are most likely to clear up on their own within a few days. However, in some cases where medical attention is needed, you should go to the hospital immediately if you notice signs including:
Symptoms persist for more than 2 days without improvement or increase; Diarrhea that lasts for 3 to 4 days; Gastrointestinal disorders accompanied by fever higher than 38oC; There are signs of dehydration such as dry mouth, wrinkled skin, sunken eyes, little and dark urine; Young children have symptoms such as diarrhea accompanied by lethargy, fatigue, poor feeding, vomiting a lot; See blood in the stool; Abdominal pain, accompanied by bowel obstruction, vomiting. Inflammatory bowel disease is a fairly common disease with many causes. The key to treatment is finding the cause. If abnormal signs of the digestive system persist or are severe, it is necessary to visit a doctor to know the specific cause and appropriate treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.