This is an automatically translated article.
Acute heart failure (STC) refers to a rapid onset or worsening of the symptoms and/or signs of heart failure, which is life-threatening, often resulting in hospitalization, requiring emergency evaluation and treatment. /emergency. Acute heart failure is a relative term used to describe heart failure that progresses rapidly over hours to days. The clinical feature of STC is the presentation of acute circulatory failure with cardiogenic shock. The pathophysiological feature is total heart failure (both right and left heart failure).Causes of acute heart failure
Acute heart failure can have a variety of causes. The causes of acute heart failure in children are markedly different from those in adults. The main cause of acute myocardial infarction in adults is mainly coronary artery disease, valvular disease, uncontrolled hypertension. The primary cause of acute heart failure in children varies by age, geographic region, and developed and developing countries. In Vietnam, the main cause is acute myocarditis and other diseases causing sudden decrease in heart function.1. Cardiomyopathies Cardiomyopathies: All congenital heart diseases or acquired heart disease when myocardial damage has the potential to cause acute heart failure due to decreased contractility of the myocardium and muscle. the heart is too dilated or the heart muscle does not relax.
Acute myocarditis: is an acute inflammation and necrosis of the interstitial tissue and myocytes of the myocardium, causing myocardial contractility dysfunction in varying degrees of severity. Causes of acute myocarditis are diverse, of which viral myocarditis is the most common. The clinical manifestations of myocarditis are age-dependent, breastfed infants often present from acute to fulminant, older children and adolescents are less acute, with few cases of symptoms being missed. later outcome of dilated cardiomyopathy. The most common viruses that cause acute myocarditis are Coxsackie B and Adenovirus. Endocardial biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosis of acute myocarditis, with high specificity, combined with imaging for accurate results. Dilated cardiomyopathy is the most common primary cardiomyopathy in which the ventricles dilate and contractile function is severely reduced. The cause in most cases in children can be hereditary or a history of viral infection, dilated cardiomyopathy may be a sequelae of previous myocarditis. Active acute myocarditis is identified in 2% to 15% of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. In many cases the disease is familial, with dominant and recessive inheritance, X-linked and mitochondrial inheritance. Diagnosis of the disease is exclusionary after searching for causes, including metabolic disorders and histology, without any pathology. The clinical picture resembles acute, subacute myocarditis or endothelial fibrosis.
Metabolic cardiomyopathy: metabolic disorders that can cause acute heart failure such as hypo/hyperparathyroidism, hypoglycemia, glycogen storage disease (such as Pompe disease), Mucopolysaccharide disease, carnitine deficiency, Fabry disease, fatty acid disorder, metabolic acidosis, hypothermia, hypocalcemia. Adverse drug reactions can cause heart damage causing acute heart failure such as Sulfonamide, Penicillin. The mechanism of cardiac injury of sulfonamides and penicillins is not clear but is often combined in anaphylaxis. Anthracyclines cancer drugs causing acute heart failure have been described in the cancer literature, depending on the dose, the duration of use of the drug, the more the drug accumulates in the blood, the higher the likelihood of heart failure. Anthracyclines cause myocardial toxicity in 2 stages, the acute phase of symptoms is often transient and easy to miss, the late stage presents with the generalized dilated cardiomyopathy. Connective tissue diseases such as Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)... can also damage the myocardium, causing acute heart failure. In particular, heart damage in SLE is one of the severe injuries and one of the causes of death. In SLE, all structures of the heart can be damaged such as pericardium, endocardium, myocardium, intracardiac conduction, leading to various cardiovascular diseases such as pericarditis, endocarditis, myocarditis, coronary artery damage...in which pericarditis is the most common. Neuromuscular disorders that cause cardiomyopathy are often in the late stages of the disease, such as Duchene muscular dystrophy, spinal muscular atrophy, and Friedreich's ataxia.

Trong nhiều trường hợp bệnh có tính chất gia đình, di truyền trội và lặn, liên kết với nhiễm sắc thể giới tính X và di truyền ty thể
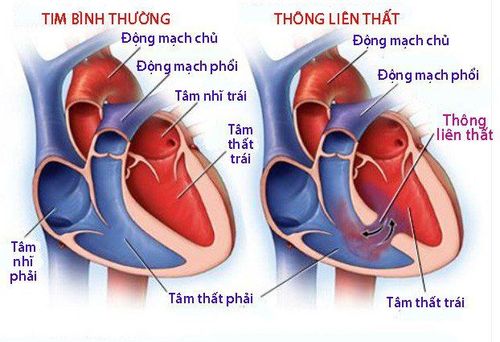
Congenital heart with left → right shunt ventricular septal defect, while the great ductus arteriosus, atrioventricular floor septal defect, arterial root transfer, common trunk, atrial septal defect, aortopulmonary window, left coronary artery exit Abnormally arising from the pulmonary artery ALCAPA... congenital heart diseases with left → right shunt all cause left heart failure except the atrial septal defect which causes right heart failure.
These congenital heart diseases will present with early acute heart failure when pulmonary vascular resistance decreases. With this pathology, the blood will choose the path of least resistance to go, that is the pulmonary artery, so the priority blood flow to the pulmonary artery leads to insufficient cardiac output perfusion for the systemic circulation, also causes pulmonary congestion.
Similarly, in the case of left coronary artery arising abnormally from pulmonary artery, when pulmonary vascular resistance decreases, blood flow to pulmonary artery increases, coronary ischemia increases, resulting in decreased contractility myocardium, reducing cardiac output and possibly causing arrhythmias, eventually causing acute heart failure and possibly cardiogenic shock.
Impaired ejection Left ventricular hypoplasia syndrome, severe coarctation of the aorta, aortic valve stenosis, pulmonary stenosis, mitral stenosis ... These congenital heart types are all ductal dependent; Coronary and systemic perfusion in these diseases depends on the flow of blood from the right heart to the left heart from the pulmonary artery into the aorta via the ductus arteriosus.
Other congenital heart defects: abnormal pulmonary venous return, coronary artery disease, mitral regurgitation, aortic regurgitation....
3.Acquired heart disease Constrictive pericarditis constriction, severe pericardial effusion causing acute tamponade. Acute cardiac tamponade causes bilateral ventricular volume depletion, while systolic function is normal, cardiac output, and ejection volume are reduced.
Infective endocarditis is an inflammatory condition of the endocardium with ulcerative lesions that usually occurs in patients with pre-existing heart damage, acquired or congenital. Congestive heart failure occurs in 30% of cases.
4.Conduction disturbances Persistent arrhythmia, episodes of ventricular, supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation. Low-grade 3rd degree atrial block, especially when the heart rate is less than 50 beats/min.
5.Due to diseases other than the heart

Suy tim cấp có thể do các bệnh nôi tiết như ngộ độc giáp. tăng huyết áp do u tủy thượng thận, tiểu đường,...

Có thể phân loại nguyên nhân suy tim cấp theo các lứa tuổi sau: Thai nhi, Sơ sinh, Trẻ nhỏ và Trẻ lớn
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.