This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Tran Thi Diem Trang - Respiratory Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Pneumothorax is a disease in the pleural cavity where air accumulates, causing the lungs to collapse passively, affecting the respiratory function of the body. Pneumothorax has many different causes as well as diagnosis and treatment, depending on whether spontaneous pneumothorax or recurrent pneumothorax.
1. What is pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax refers to a collapse of one or both lungs due to the release of air into the pleural space. The pleural space is the space between the pleura, the two membranes that surround your lungs. Clinically, spontaneous pneumothorax and recurrent pneumothorax may occur.1.1 Spontaneous pneumothorax
Spontaneous pneumothorax is a phenomenon where air from the lung parenchyma escapes and accumulates in the pleural space, thereby damaging the alveoli.The cause of spontaneous pneumothorax is not due to external trauma or trauma. In a normal state, the pleural cavity does not contain air and the pressure will be negative, making it easy for the lungs to exchange gas, whereas when spontaneous pneumothorax occurs, the lung will collapse, making it impossible to perform. Gas exchange is now possible.
Spontaneous pneumothorax is a disease that occurs in normal people before, usually young men (ages 15 to 34). The mechanism is due to the rupture of air bubbles on the surface of the lung, which can be congenital or bronchiolitis. These cases often occur in thinner and taller people because their pulmonary peak pressure is low, so it is easy to cause air bubbles to burst.
Smoking tobacco and/or marijuana significantly increases the risk of spontaneous pneumothorax occurring, as well as increasing the chance of a second atelectasis.
There is also a form of spontaneous pneumothorax called cyclic pneumothorax, which can occur in women of childbearing age. Symptoms are very similar to spontaneous pneumothorax, but are cyclical and associated with menstrual periods. The disease form is thought to involve a small amount of uterine tissue migrating and implanting in the pleura.
Spontaneous pneumothorax has a 30% chance of recurrence.
1.2 Recurrent pneumothorax
As pneumothorax disease occurring in a patient with pre-existing lung disease, this case will have a worse prognosis than spontaneous pneumothorax. Recurrent pneumothorax is common in people over 30 years of age.
Diseases that can leave complications of recurrent pneumothorax are tuberculosis, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ...
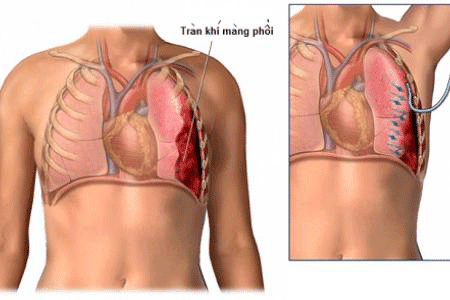
2. Causes of pneumothorax
Pneumothorax has a number of causes such as trauma, procedures... In which, there are causes of spontaneous pneumothorax such as:
Young age, about 20 to 40 years old. The person is tall and thin. People with a history of smoking. Broken air bubbles around lobules of the lung. For secondary pneumothorax, there are causes such as:
Older people, 40 to 75 years old. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pulmonary tuberculosis. Asthma . Primary or metastatic lung cancer. Pulmonary fibrosis . Air cyst. Gas burst. Diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. Pulmonary disease.
3. Diagnosis of pneumothorax
How is pleural ventilation diagnosed? Pneumothorax is usually diagnosed by chest x-ray alone, but your health care professional can also tell you have a pneumothorax by listening to your lungs. In some cases you may be offered a computed tomography (CT scan) scan if the healthcare professional needs more detailed pictures of your lungs. Conditions for diagnosing a pneumothorax include signs and symptoms. Signs of respiratory function and systemic signs are as follows:
3.1 Clinical Manifestations
Functional symptoms such as:Sudden chest pain is the most common symptom in patients when pleural ventilation occurs. Sometimes the pain increases with breathing. Some patients, but not all, have difficulty breathing. Some patients also have a cough, some have shoulder pain, or a sharp pain between the shoulder blades. In the majority of patients, these symptoms do not last long and very rarely get worse. The patient may experience shock (pale, sweating, rapid, shallow pulse, low blood pressure, cold hands and feet, sweating, mental panic, anxiety). In addition, the patient feels short of breath, the patient is often in a state of shock. If pneumothorax is not treated in time, it can lead to serious consequences due to atelectasis, respiratory failure. Physical symptoms such as:
Chest is not symmetrical, the side with pneumothorax will often be enlarged and less mobile than the other side. When palpating the lungs, the vibration may be absent. In the area of air with pneumothorax, percussion sounds echo, there may be low areas where effusion appears, blood may sound cloudy. Alveolar murmur may be reduced or even completely eliminated. These symptoms often have a sudden, intense onset, appear after strenuous exercise, worsen when the patient is at rest, and shortness of breath will gradually increase if the pneumothorax increases. However, in some cases of pneumothorax, the clinical manifestations are very few, not aggressive with signs that can be easily missed such as chest tightness, mild shortness of breath, less cough, sometimes fatigue.
3.2 Subclinical manifestations
Valuable laboratory tests in the diagnosis of pneumothorax are:
chest X-ray. Chest computed tomography. Blood tests. BK talk. Making arterial blood gas. Electrocardiogram measurement. Lung examination.
3.3 Differential diagnosis
Pneumothorax, if generalized, is usually very typical on radiographs. As for the case of localized pneumothorax, X-ray images should be differentiated from the following pathologies:
Enlarged air cysts in the lungs. Gastric air bubbles above the thorax, which may be the result of a traumatic diaphragmatic hernia, diaphragmatic effusion, or diaphragmatic paralysis. Diseases causing difficulty breathing such as COPD, ARDS, pleural effusion, pneumonia. Pneumothorax is a fairly common medical condition today with many causes, depending on whether it is spontaneous pneumothorax or recurrent pneumothorax. In order to be able to have the right and reasonable treatment for the patient, it is necessary to have methods to diagnose the disease accurately and distinguish it from other diseases to clarify the diagnosis.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.