This is an automatically translated article.
Cardiovascular complications in diabetic patients are largely due to the consequences of lipid metabolism disorders, increasing Glucose combined with other factors such as: environment, genetics, comorbidities such as hypertension, disorders. cholesterol1. Microvascular complications in diabetic patients
Microvascular complications, including eye, kidney, and neurological complications, are associated with high blood sugar and can be prevented with tight blood sugar control.1.1 Eye complications: retinopathy of the eye Retinopathy of the eye is the leading cause of blindness in patients with diabetes. Most patients do not detect retinal complications early because there are no clinical symptoms, only when the damage is advanced.
Early detection by regular monitoring and prompt treatment will help prevent and delay the development of complications.
1.2 Neurological complications Neuropathy is a common complication in diabetic patients with many different manifestations. In which, peripheral nerve complications and autonomic neuropathy are the most common, in about 50% of people with type 2 diabetes. Other complications such as cranial nerve palsies, muscle atrophy are less common. .
This complication can be prevented and treated with tight blood sugar control, avoidance of hypotensive factors, and symptomatic treatment.
Complications of auto-digestive nerves
Symptoms: choking, slow digestion, bloating, heartburn, nausea, heat or pain in the epigastrium, vomiting.
Lower gastrointestinal tract neuropathy causing constipation or diarrhea.
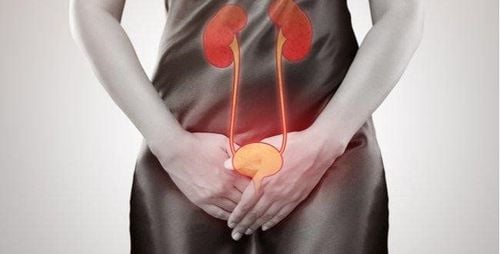
Biến chứng thần kinh tự động tiết niệu – sinh dục
Complications causing decreased or increased bladder activity, genitourinary neuropathy. Men have erectile dysfunction, impotence, women have menstrual disorders, amenorrhea, vaginal dryness, decreased sensation in the groin area, loss of sexual arousal.
Vasomotor neuropathy
Increased sweating of the face and body, usually at the start of meals, at night or during exercise.
Reduces sweating in the distal lower extremities: dry skin, itching, scaling, hair loss, cracks, increased calluses and nail dystrophy.
Peripheral nerve complications
Symptoms:
- Decreased or lost sensation of skin contact, sensation of heat.
- Feeling of crawling, numbness or burning of the toes and fingers.
- Loss of sensation in the hands and feet.
- Dull or paroxysmal pain, increasing pain in the legs, arms and abdomen at night.
1.3 Kidney complications Diabetic kidney complications account for up to 50% of cases of end-stage renal failure, which is also the leading cause of death for diabetic patients.
Can be treated to prevent complications by:
Reduce protein intake: reduce protein intake from 0.8 - 1.0 g/kg/day in early stage and <0.8 g/kg/day in late stage, improve function kidney.
Control blood pressure: blood pressure <140/80 mmHg
Control blood glucose HbA1c < 7%: reduce, slow down the progression of proteinuria.
Treatment of blood lipids: use blood lipid-lowering drugs to prevent cardiovascular events.
2. Macrovascular complications in diabetic patients
The major vascular complication of diabetes is atherosclerosis and its consequences.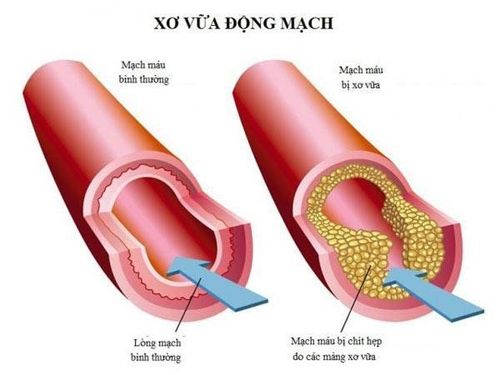
Xơ vữa động mạch ở bệnh nhân tiểu đường
The link between diabetes and atherosclerosis is not completely understood. Diabetes-induced conditions all contribute to atherosclerosis, cardiovascular complications, and leading causes of death.
Atherosclerosis can cause the following consequences:
In cerebrovascular: stroke due to cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral palsy, patients sometimes have transient ischemic attack. In the heart: ischemic cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris In the peripheral blood vessels: thrombosis of the extremities, limb necrosis. Atherosclerosis also contributes to erectile dysfunction, leg ulcers and some other rarer complications such as aortic aneurysm, mesenteric embolism....
3. Prevention of cardiovascular complications in diabetics
Many studies have demonstrated that diabetic patients who control blood glucose are reduced cardiovascular complications.
Kiểm soát được glucose huyết
The study in type 1 diabetes patients also showed similar results, the group of patients on intensive blood glucose lowering treatment had less microvascular complications than the less active blood glucose lowering group.
Thus, cardiovascular complications on diabetic patients are very dangerous, threatening the patient's health and life. But active treatment, especially good blood glucose reduction, will help prevent complications.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.