This is an automatically translated article.
Electroconversion cardioversion is a method of using electric current to quell the tachyarrhythmias that are taking over the rhythm of the sinus rhythm, enabling the sinus rhythm to return to its role of the rhythm master. It should be noted that electric shock should not be understood as using an electric current to "excite" the heart to beat.
1. Mechanism of emergency electric shock
Electroconvulsive shock is a treatment used to quickly quell and stabilize most types of arrhythmias.
Electroshock induces depolarization of all cardiomyocytes, to sever re-entry loops or inactivate foci of activity beyond the sinus node by resynchronizing electrical activity in cardiomyocytes.
Normally, sinus rhythm will be re-established after a brief electrical pause that occurs shortly after the shock. The effectiveness of cardioversion will depend on:
The electric shock potential. Organizational resistance. Organizational resistance is influenced by a number of factors, such as patient morphology, coordination status, and patient's thorax. There are two types of emergency electric shocks, including:
Cardioversion: An electrical discharge that is "synchronized" with the patient's QRS complex to convert (usually into an R wave or an S wave, if not present). R waves, to avoid T waves). Defibrillation Shock: Is the discharge of an electric current at any stage of cardiac activity to break the vibration.
2. Indications of cardioversion in emergency
Emergency electric shock is indicated in all cases of tachyarrhythmias causing circulatory arrest, loss of consciousness or severe hemodynamic impairment. Shock should be administered as quickly, as soon as possible, if possible, as soon as the following tachyarrhythmias are noted:
Ventricular fibrillation : This is the most common cause of circulatory arrest . In this case, the sooner the electric shock is given, the more chances it will bring to the patient. The maximum shock energy level is 360J, if the first shock is 200J, the second time 300J is not effective. If electroconvulsive shock is unsuccessful, immediate resuscitation should be performed: chest compressions, artificial ventilation, correction of acid-base balance and electrolyte disturbances, if present. At the same time, it is necessary to monitor the electrocardiogram on the screen continuously, if large wave ventricular fibrillation occurs, then continue to conduct electric shock with the maximum energy level. Ventricular tachycardia: This is the main cause of hemodynamic deterioration. When the patient shows signs of hemodynamic deterioration, an electric shock with an initial energy level of 100 J should be promptly administered. If unsuccessful, the electric shock energy level can be increased to 150J, then 200J. If the ventricular tachycardia is due to digital toxicity, a low-energy electric shock should be indicated. Supraventricular tachyarrhythmias: Atrial flutter, atrial tachycardia, except for atrial fibrillation, the shock energy level is usually between 25-50J. Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome: When a rapid atrial arrhythmia (usually atrial fibrillation) is conduction to the ventricles through the accessory conduction pathway, there is a risk of ventricular fibrillation.
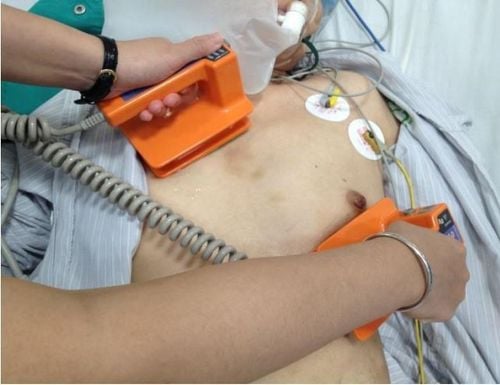
Sốc điện cấp cứu được chỉ định trong tất cả các trường hợp rối loạn nhịp nhanh gây ngừng tuần hoàn
3. Tools and how to conduct emergency electric shock
3. 1. Emergency shock equipment Must always have ready tools to prepare for extrathoracic shock, which can be used immediately in the event of an emergency:
The shock machine works good, all synchronous parts work properly; The two shock arms must be cleaned, have good contact with the patient's chest skin, and must discharge the correct power setting; The machine monitors indicators such as electrocardiogram, breathing rate, SaO2, arterial blood pressure; Instruments and anesthetics; Devices for the patient to breathe oxygen through the nose or through a mask; Canule Malot; Ball Ambit; Intubation equipment; Vaccum; The vehicle containing the first aid kit is fully stocked with drugs and emergency equipment to stop circulation as prescribed. 3.2. How to conduct emergency electric shock Electric shock in the emergency of circulatory arrest due to ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia causing the patient to lose hemodynamics and lose consciousness should be performed immediately when these arrhythmia images are identified on the electrocardiogram. . The steps are as follows:
Apply conductive gel to the two shock plates, then set the power level of the shock machine for the first shock to 200J. The doctor may need to adjust the sync button on the shock machine. Next, two electric shock plates were placed on the patient's chest, one was placed on the right side of the sternum, 1cm from the sternum and 3cm from the clavicles, the other was placed in the apex of the heart. The operator needs to observe the patient and the surrounding, when it is safe for everyone, conduct electric discharge. The emergency department of circulatory arrest needs to maintain the patient's breathing. Once sinus rhythm is restored, the emergency department should continue to inflate the balloon and provide advanced cardiopulmonary arrest. If the electrocardiogram shows still large-wave ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, an electrical shock at an energy level of 300 J should be performed. If there is no result, it is necessary to raise the shock energy level to 360 J and shock until sinus rhythm is established. If the electrocardiogram shows microwave ventricular fibrillation, continued cardiac compressions, balloon compressions, emergency cardiac arrest, injection of adrenaline into the central vein, or endotracheal or direct injection into the heart, is recommended. electrolyte correction... When the electrocardiogram shows large wave ventricular fibrillation, the electric shock continues. The highest energy level specified for the 3rd shock onwards is 360J. Biphasic shock is more effective than single phase, because the current will sweep through the heart once more in the opposite direction after it has passed through the heart for the first time.
In open heart surgery, the doctor can use an electric shock plate placed directly on the heart to shock the rhythm or break the vibration. However, the amount of energy used in this case will be lower than that of the extrathoracic shock.
4. Complications of emergency electric shock
Complications of electric shock may include:
Development of atrial or ventricular extrasystoles Myalgia in the area of the shock plate. However, these complications are usually minor and should not be of concern. In cases where the patient has borderline left ventricular function or when the electrical shock is too repeated, the patient can suffer extensive myocardial damage, sometimes causing electromyography dissociation.
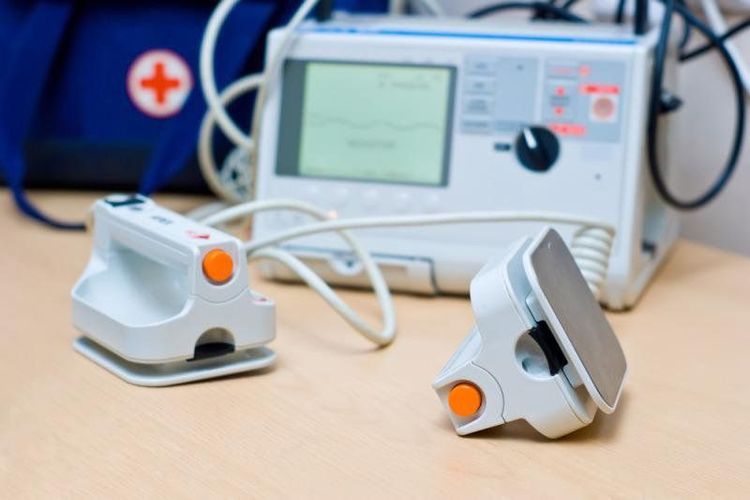
Sau khi tiến hành sốc điện cấp cứu cần theo dõi liên tục nhịp tim, nhịp thở, huyết áp
5. Patient monitoring and treatment after electric shock
Monitoring and management after cardioversion in the emergency room is essential to prevent complications.
After conducting emergency electric shock, it is necessary to continuously monitor heart rate, breathing rate, blood pressure, arterial blood oxygen saturation on the monitor. Follow-up electrocardiogram after electric shock, if arrhythmias are found, they will have to be treated with antiarrhythmic drugs. Note that if ventricular extrasystoles occur after receiving an electric shock to treat ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, it should be treated immediately with intravenous Xylocaine. If atrial extrasystoles occur in patients with atrial fibrillation or Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome who have recently received an electric shock, they should be treated with intravenous amiodarone. Adjust electrolytes and acid-base balance for the patient. After electric shock, the patient may experience ventricular fibrillation or relapse of arrhythmias as before, so in the first 24 hours, it is necessary to closely monitor the patient and find out and treat the causes of these disorders. this beat. In summary, cardioversion in the emergency room is indicated for all cases of tachyarrhythmias causing circulatory arrest, loss of consciousness, or severe hemodynamic compromise. And electric shocks need to be delivered as quickly as possible in the presence of serious arrhythmias.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.