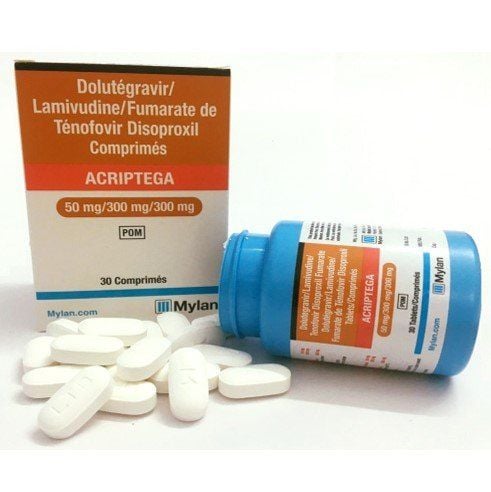
A regular blood test cannot detect the presence of HIV in the body. Only specialized tests, such as antigen and antibody tests, performed at the appropriate time can accurately diagnose HIV.
1. Can HIV Be Detected by a Regular Blood Test?
A general blood test does not include an HIV test. If an HIV test is not specifically requested by a doctor, HIV will not be detected.
The main tests in a general blood test usually include:
Complete Blood Count (CBC): Measures the components of blood such as platelets, red blood cells, white blood cells, and some of their properties like size and hemoglobin levels. This test helps detect basic abnormalities in the blood, leading to further tests for accurate diagnosis of the underlying cause.
Blood Glucose Test: Measures the concentration of glucose in the blood to determine the risk of diabetes. To ensure accurate results, blood samples should be taken after fasting for 8 hours.
Lipid panel: Measures cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood, including total cholesterol, HDL (good cholesterol), and LDL (bad cholesterol). This test helps diagnose high cholesterol levels in the blood. Cholesterol is considered high if it is > 2.50 g/l, and triglycerides are considered high if they are > 2 g/l.
Liver Enzyme Test: Measures the levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALAT or SGPT) and aspartate aminotransferase (ASAT or SGOT) enzymes. These levels help diagnose liver diseases (due to alcohol, viruses, or cancer). Elevated levels of these enzymes can also indicate other conditions such as pancreatitis or myocardial infarction.
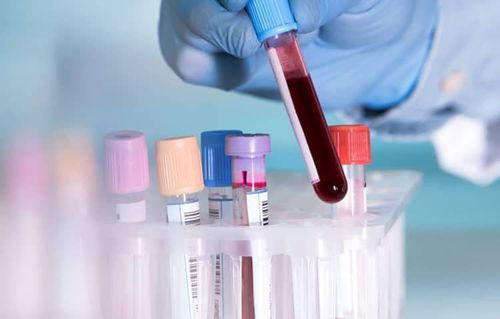
2. How to Test for HIV?
If you suspect you have HIV, you should see a doctor and get tested for HIV or visit preventive health centers and large hospitals for accurate HIV testing.
Antigen Test: This test detects the HIV virus in the blood. It can indicate the amount of virus present in the blood (also known as the HIV viral load test). This test is quite expensive and is not commonly used for individual screening unless you are at high risk of HIV exposure or show early HIV symptoms.
Antibody Test: Most rapid HIV tests or home test kits are antibody tests. This test detects HIV antibodies in the blood or body fluids. For blood tests, you will be asked to provide a blood sample from a vein, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. For body fluid tests, samples are usually taken from the mouth and can be done at home. Screening antibody tests usually provide results quickly (within about 30 minutes).
Combined Antigen and Antibody Test: This test detects both HIV antigens and antibodies in the body. Antibodies are produced by the immune system when the body is exposed to the HIV virus, while antigens are substances that invade the body and activate the natural immune system. When infected with HIV, an antigen called p24 appears about 2-4 weeks after infection.
3. What Do HIV Test Results Mean?
Negative HIV Result: This result does not mean you are completely free from the risk of HIV infection. It means that at the time of testing, your body did not carry the virus or the test did not detect the virus. You may be in the "window period."
The window period lasts from 3 to 6 months, which is the time it takes for the body to produce enough antibodies to fight the virus. Therefore, if you test during the window period, the result may be negative even though you are already infected with HIV. During the window period, you can still transmit HIV to others even if your antibody test result is negative.
If you believe you are at high risk of HIV infection and think you are in the window period, you should get tested again to confirm your HIV status.
Positive HIV Result: This means your body has been infected with the HIV virus. Do not worry; visit a healthcare facility immediately for consultation and early treatment.
4. Benefits of Early HIV Detection and Treatment
Maintaining Health, Prolonging Life, and Living Usefully for Family and Community: You should get tested early if you suspect HIV infection. Do not wait until you feel tired or sick to visit a healthcare facility. By then, your immune system may be weakened, making it difficult to fight off infections, and you will be more susceptible to severe infections. Therefore, visit a healthcare facility as soon as you test positive for HIV to receive consultation and treatment. If your CD4 count is ≤ 350 cells/mm3, you meet the criteria for ARV treatment.
Reducing Medication Costs, Treatment Costs, and Hospitalization Costs: When your immune system is not severely weakened, your body remains healthy, and you will not suffer from opportunistic infections. Therefore, you will not need to spend money on treating severe opportunistic infections (which occur if CD4 < 200 cells/mm3).
Reducing the Risk of Transmitting the Virus to Others: Early treatment helps reduce the risk of transmission to everyone, including your spouse, friends, and children.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.