Lymph node hyperplasia is a rare disease that few people know or hear about. The article below will help you understand this disease better.
1. What is lymph node hyperplasia?
Lymph node hyperplasia (Castleman disease) is a rare disorder that involves the overproduction of cells in the body's lymph nodes. The most common form of the disease is hyperplasia in only one lymph node, usually in the chest or abdomen.
Multiple lymph node hyperplasia affects lymph nodes throughout the body, and is associated with human herpes virus type 8 (HHV-8) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Treatment and prognosis of lymph node hyperplasia depend on the specific condition. If only one lymph node is hyperplasia, treatment is usually successful after surgery.
2. Symptoms of Lymph Node Hyperplasia
Many patients with only one lymph node hyperplasia often do not experience any signs or symptoms. The discovery of enlarged lymph nodes is often incidental, during a clinical examination or imaging (originally for another medical problem).
However, some patients with single lymph node hyperplasia may also experience signs and symptoms commonly seen in patients with multiple lymph node hyperplasia, including:
- Fever;
- Unintended weight loss;
- Fatigue;
- Night sweats;
- Nausea;
- Enlarged liver or spleen.
In patients with multiple lymph node hyperplasia, enlarged lymph nodes are most commonly found in the neck, collarbone, armpit, and groin areas.

3. When should you see a doctor for lymphadenopathy?
If you notice enlarged lymph nodes in your neck, collarbone, armpit, or groin, see your doctor. Also contact your doctor if you notice any of the following symptoms that persist: a feeling of fullness in your chest or abdomen, fever, fatigue, or unexplained weight loss.
4. Causes of Lymph Node Hyperplasia
The cause of lymph node hyperplasia is unknown. However, infection with human herpes virus type 8 (HHV-8) has been associated with multiple lymph node hyperplasia.
HSV type 8 has also been associated with the development of Kaposi's sarcoma, a malignant tumor that is a complication of HIV and AIDS. Studies have shown that human herpes virus type 8 is present in nearly all cases of HIV-positive lymph node hyperplasia, and in about half of all cases of HIV-negative lymph node hyperplasia.
5. Risk factors for lymph node hyperplasia
Lymph node hyperplasia can occur at any age, but the average age of patients diagnosed with single lymph node hyperplasia is 35. Individuals with disseminated lymphadenopathy are predominantly middle-aged, with a male preponderance
The risk of multiple lymph node hyperplasia is increased in subjects infected with human herpes virus type 8.
6. Complications of Lymph Node Hyperplasia
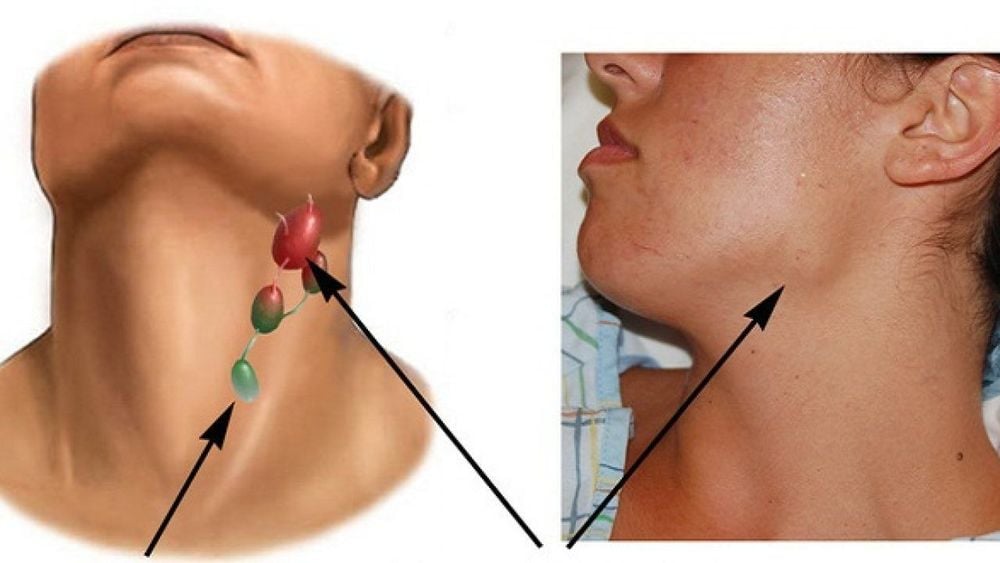
In patients with only one lymph node hyperplasia, the prognosis is good after surgery to remove the affected lymph node. However, in patients with multiple lymph node hyperplasia, the disease can lead to life-threatening infections or organ failure. The prognosis is worst in patients with HIV or AIDS.
Having any form of lymph node hyperplasia increases the risk of lymphoma.
7. Diagnosis of lymphadenopathy
After a clinical examination, the doctor may order some of the following tests
Blood tests, urine tests
To help detect other diseases or infections. These tests also help detect anemia and abnormalities in blood proteins (these conditions are often characteristic of lymphadenopathy)
Imaging techniques
To detect enlargement of the lymph nodes, liver or spleen. Computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the neck, chest, abdomen or pelvis may also be ordered. Positron emission tomography (PET) scan can be used to diagnose and monitor the treatment of lymphadenopathy.
Lymph node biopsy
To differentiate between lymph node hyperplasia and other lymphoid tissue disorders, such as lymphoma. A tissue sample is taken from the abnormally growing lymph node for pathological examination.

8. Treatment of lymph node hyperplasia
8.1 Treatment of single lymph node hyperplasia
Single lymph node hyperplasia can be treated by surgically removing the diseased lymph node. In cases where the diseased lymph node is located in the chest or abdomen (very common), complex surgery may be required.
If the diseased lymph node cannot be removed surgically, medication may be used. Radiotherapy to destroy the diseased lymph node is also an effective method.
After treatment, the patient needs to have a follow-up appointment and perform tests (including imaging) to monitor for recurrence.
8.2 Treatment of multiple lymph node hyperplasia
Treatment of multiple lymph node hyperplasia often requires medications and therapies to control excessive cell growth. Specific treatment depends on the severity of the disease and the status of HIV and human herpes virus type 8 infection.
Treatment of multiple lymph node hyperplasia usually includes:
- Immunotherapy: Drugs such as siltuximab (Sylvant) or rituximab (Rituxan) may be used.
- Chemotherapy: To slow the excessive growth of cells, and is usually indicated when the patient does not respond to immunotherapy or when there is organ failure.
- Corticosteroids: Anti-inflammatory drugs such as prednisone may be used.
- Antiviral drugs: Can block the activity of HIV and human herpes virus type 8.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
Reference source: mayoclinic.org