This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thuc Vy - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital
Breast implant-associated undifferentiated large cell lymphoma is very rare, with a reported prevalence of 0.3 per 100,000 to 1 in 1,000 women with breast implants. Less than 1000 cases have been reported (as of September 2019).
1. What is breast implant-associated large cell lymphoma?
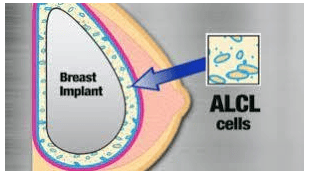
Breast implant-associated undifferentiated large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL), is a very rare form of immune system cancer, mainly associated with textured cosmetic breast augmentation materials (breast implants). textured breast implant: Textured breast implant).
BIA-ALCL is a T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma with 2 subtypes:
Pericapular effusion; Mass around the breast pocket. Breast implant-associated undifferentiated large cell lymphoma is not breast cancer. In general, this is a slow-growing cancer that can often be treated by removing the breast implant and surrounding fibrous tissue.
2. Epidemiology
Breast implant-associated undifferentiated large cell lymphoma is very rare, with a reported incidence of 0.3 per 100,000 to 1 in 1,000 women with implants. Less than 1000 cases have been reported (as of September 2019).
According to statistics, less than 10 patients per year are diagnosed with this form of lymphoma while it is estimated that every year 10 to 11 million women around the world have had breast implants. The majority of cases are related to textured breast implants.

3. Clinical Manifestations
The clinical presentation of breast implant-related undifferentiated large cell lymphoma is that one breast may be larger than the other or have a different shape than the other (asymmetrical). Usually, it takes at least 2 years after surgery for symptoms to appear. However, the average time before symptoms appeared was 8 years.
Symptoms of breast implant-related undifferentiated large cell lymphoma may include:
Swelling or fluid accumulation in the breast or around the implant; Painful, red skin; Palpable lump in the breast; Changes in the shape or size of the breast. Two-thirds of patients had late-onset effusion (more than 1 year after surgery) and one-third of patients had a palpable breast mass.
4. Causes of BIA-ALCL
The exact cause of breast implant-associated undifferentiated large cell lymphoma remains unclear. However, the majority of views suggest that the disease is multifactorial in nature, resulting from a combination of chronic inflammation, long-term allergic reactions, genetic factors, subclinical infections, and biofilm formation. study around the breast pocket. Textured breast implants can cause more inflammation than smooth sheath implants. The end result is thought to be malignant transformation of the T cells, which become undifferentiated lymphoma cells.
5. How is BIA-ALCL diagnosed?
Patients with breast pocket-related undifferentiated large cell lymphoma usually present with pericystic effusion (range 50-1000 mL). Others, less commonly, present with an abnormal mass in the breast, with or without effusion. Mammography is of little value in detecting disease. Ultrasound is the first modality and then breast MRI. Specifically:
Ultrasound: Ultrasound has a high sensitivity (84%) for BI-ALCL. Ultrasound imaging often shows a collection of fluid between the breast sac and surrounding fibrous tissue, often with an internal wall. If a tumor is present, it is usually solid, hypoechoic, and well-defined without vascular proliferation. Complex cystic tumors have also been reported. Inflammation of the breast tissue around the breast pocket may also be seen. Breast MRI: BIA-ALCL-associated tumor and effusion can be well evaluated on MRI. Taking the pill has also been reported in a small number of cases. Needle biopsy: If imaging tests show a mass or fluid collection around the breast, a fine-needle biopsy will be done to diagnose breast pocket-related undifferentiated large cell lymphoma. During the procedure, a small amount of fluid is removed from the breast with a needle. The sample is then sent to a lab for further testing. At least 50 ml of fluid must be aspirated for laboratory and cytology. CD30 immunostaining: A laboratory test is performed on the resulting fluid to detect the presence of CD30, a substance that occurs when T lymphocytes are activated. If CD30 is present, it indicates that BIA-ALCL cannot be ruled out and further testing is required.

6. Treatment and prognosis
If diagnostic tests confirm the presence of BIA-ALCL, the patient is referred to an oncologist. The specialist will determine the stage of the disease and come up with a treatment plan. Treatment will depend on the type and stage of the disease, the patient's general health, age, and other factors. Surgery: In most cases, surgical removal of the breast sac and its surrounding capsule is effective in treating the disease. Removal of some lymph nodes may also be necessary if they contain cancer cells. Chemotherapy: In rare cases of more advanced cancer, patients may need chemotherapy after surgery. Prognosis is very good for patients who are diagnosed at an early stage and treated. The chance of recurrence or death is very low.
7. General recommendations for women with breast implants
All women with breast implants should have regular physical exams and breast MRI as recommended. The FDA (US Food and Drug Administration) recommends that women with breast implants have a breast MRI 3 years after their first breast implant surgery and every 2 years thereafter to verify their integrity. integrity of the breast implant as well as complications if any. Women should also do monthly breast self-exams to detect abnormalities early, if any.
Currently, early cancer screening is considered the perfect measure in the timely detection and treatment of all types of cancer. Reduce the cost of treatment and especially reduce the mortality rate in patients. Vinmec International General Hospital always deploys and introduces to customers the Early Cancer Screening Package at Vinmec - Peace of mind to live well to help with gene testing, imaging, testing of biomarkers to detect tumors you early.
Choosing the Early Cancer Screening Package at Vinmec - Peace of mind at Vinmec, customers will get:
Only one gene test can assess the risk of 16 common cancers in both men and women ( Lung cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, cervical cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer,....) Early detection of early signs of cancer cancer through imaging, endoscopy, and ultrasound. The operation is simple, careful and accurate. A team of well-trained specialists, especially in oncology, are capable of handling cancer cases. With a system of facilities, advanced and modern medical equipment and a team of doctors with deep expertise and experience, it will help the examination and treatment process of patients at Vinmec become faster with High efficiency, save cost and time.
In particular, Vinmec Nha Trang currently has GE's 3.0 Tesla breast magnetic resonance imaging machine with mammography function that can survey and evaluate breast abnormalities in patients with breast implants and evaluate other breast conditions. Complications of breast implant placement.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: My.clevelandclinic.org, radiopaedia.org