This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by MSc, BS. Dang Manh Cuong - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Biliary stenting is a highly advanced technique used to treat obstruction that occurs in the bile duct. Accordingly, the technique of digital angiography erasing the background (DSA scan) uses X-rays to study blood vessels in the body, helping to clearly see the damage before the intervention is indicated.
1. Overview
1.1. Define
Bile is a fluid produced by the liver that helps the body digest fats. Bile is excreted through the bile ducts and stored in the gallbladder. Bile is secreted into the small intestine after a fatty meal. A sphincter (sphincter) named Oddi, located at the junction between the common bile duct and the small intestine (duodenum), is responsible for controlling bile secretion.1.2. Cause of secret rule
Some common causes of biliary obstruction are:Cancer of the head of the pancreas (the most common cause of malignancy); Cancer of the biliary tract or gallbladder; Liver and colon cancer; Metastatic lesions to the liver hilum; Cases of biliary strictures not due to cancer stem from:
Cholecystectomy causing damage to the biliary tree (accounting for 80%); Pancreatitis or primary sclerosing cholangitis; Gallstones ; Patients after radiation therapy or abdominal trauma;

Ung thư gan gây tắc mật
1.3. Treatment of biliary obstruction
A biliary stent is a synthetic plastic or metal tube that is inserted into the lumen of the bile duct to relieve the narrowing of the bile duct. There are two most commonly applied biliary stenting methods: endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography.In addition, surgery is the main alternative to biliary stenting. Doctors usually remove the stricture and create a bridge between the bile duct and the jejunum or between the hepatic duct and the small intestine. Surgical treatment is effective in 85-98% of patients, complications are also rare. But depending on the stage of detection of lesions, there will be patients who are not indicated for radical surgery. In particular, biliary obstruction is often the leading cause of death.
To solve this problem, since the 70s of the twentieth century, experts have carried out percutaneous biliary interventions to release the biliary tract. This is a minimally invasive technique with high efficiency, few complications, and quick recovery time.
2. When is percutaneous biliary stenting required?
2.1. Point
In addition to percutaneous scintigraphy and biliary drainage, percutaneous biliary stenting is also commonly performed to treat malignant biliary obstruction that are no longer viable for surgery. Causes may be due to:Tumor lesions in the late stage; Old age; There are other comorbidities such as diabetes, heart disease, etc.
2.2. Contraindications
Percutaneous biliary stenting should not be performed in the following cases:Severe infection (preferably biliary drainage to stabilize treatment); The diagnosis of malignant biliary atresia is unclear; Possibility of complete surgical resection of the lesion; There is a history of allergy to the iodine in the contrast medium.
3. Prepare
Performers: Specialist doctors (electroradiologists, anesthesiologists, surgeons...), nurses and technicians; Equipment needed: Digital angiography machine to erase the background (DSA capture), ultrasound machine, transducer, film, printer, image storage system, X-ray shielding suit... Medicines: Causes local anesthetic or general anesthesia (depending on indication), water-soluble iodine contrast agent, antiseptic solution... Common medical supplies: Syringe of different sizes, distilled water or aqueous solution Physiological salts, surgical supplies, sterile interventional kits, surgical bandages, accident first aid boxes... Special medical supplies: Kim Chiba cholangiography, intravascular catheters, leads standard, rigid lead, angiographic catheter, pigtail drain, balloon and biliary stent, and finally skin sutures. Patients: Thoroughly explained about the procedure, fasted before 6 hours, lying on the back and fitted with a monitor for vital indicators, disinfecting the skin, covered with a sterile tissue. If there is a blood clotting disorder, they will be treated with vitamin K supplements, intravenously prophylactic antibiotics 6 hours before, given sedatives when they are too excited, do not lie still... Test sheet: Medical record, order sheet, and diagnostic film if available.4. Steps to take
4.1. Percutaneous cholangiography
The technique should be performed under aseptic conditions. Accordingly, doctors often use 22G fine needle (Chiba) to poke the biliary tract under the guidance of ultrasound, digital angiography to erase the background.4.2. Biliary drainage
Performed after cholangiography to evaluate the biliary system. Steps are as follows:Insert a 16-18 F needle into the biliary tract under ultrasound or X-ray guidance; Insert the catheter, then replace it with a guide wire; Insert a catheter to drain the bile ducts out, or bring the tip of the catheter down into the duodenum (called internal-external drainage).
4.3. Percutaneous biliary stenting
This technique is similar to that of biliary drainage, specifically:Insertion of rigid wire into the biliary system; Carrying out paving the way in; Place a stent with a diameter of 8-10 mm in the narrow site. Depending on the intervention process, there is biliary hemorrhage or not, a backup catheter can be placed into the biliary system. Note, this drainage catheter will be clamped after 24 hours. If there are no complications, the patient has no pain or fever, the prophylactic catheter can be removed after 48 hours.
5. Evaluation of results
The percutaneous biliary stenting technique is considered successful when:The drain tube and the stent are located in the biliary tree in a safe location, right where the injury is; Bile fluid flows naturally through the drain; There is no accumulation of fluid or blood under the liver, as well as in the abdomen; Reduce obstruction and help bile flow better after stenting.
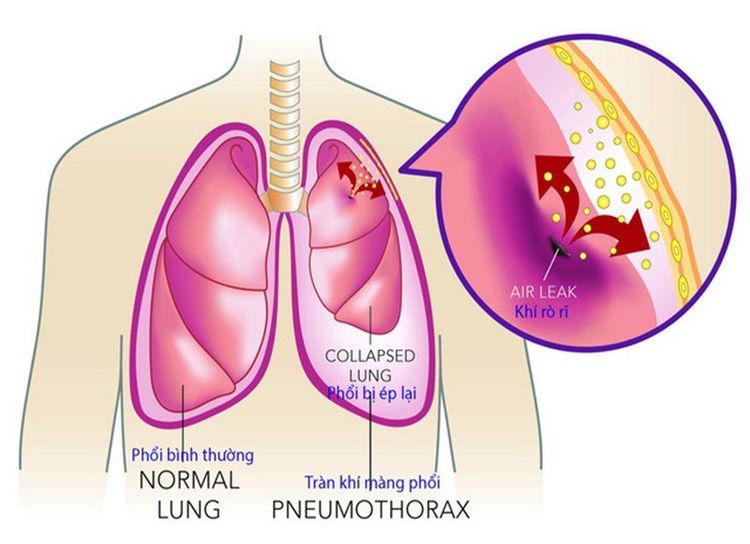
Sau khi đặt stent đường mật qua da có thể xảy ra biến chứng tràn phổi
6. Complications and treatment
Some possible complications include:Septic shock; Peritonitis ; Bleeding in the abdomen; Pneumothorax ; Leakage of contrast material into the abdomen; Sepsis or at the injection site; The stent moves out of place, obstructing, and causing bowel perforation. Depending on each specific complication, the medical team will consult with specialists, thereby giving a treatment direction according to a specific regimen.
After the procedure of percutaneous biliary stenting, the patient should be closely monitored to quickly detect complications if any. Patients should be instructed to lie on their right side for at least 6 hours to reduce the risk of bleeding at the injection site. To make sure the stent is working properly, your doctor should have regular follow-up visits to detect early signs of recurrent biliary obstruction.
Percutaneous biliary stenting is a technique that requires a high level of experience of the doctor and the patient's perfect coordination. In addition, in order to achieve high diagnostic efficiency, patients need to choose reputable sites with digital background scanners, this helps to clearly see the lesions before indicating intervention.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a hospital with a full convergence of general and specialized doctors to perform, examine, operate, diagnose and treat diseases of the biliary tract and digestive tract. In particular, at Vinmec, we also perform stenting techniques to treat many different diseases and bring optimal treatment results to customers.
Before taking a job at Vinmec Central Park International Hospital from December 2017, Doctor Dang Manh Cuong has over 18 years of experience in the field of ultrasound - diagnostic imaging in Transport Hospitals. Hai Phong, MRI Department of Nguyen Tri Phuong Hospital and Diagnostic Imaging Department of Becamex International Hospital.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.