This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Master, Doctor Hoang Van Lan Duc - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
Recently, a study published in the journal Computer in Biology and Medicine showed that artificial intelligence (AI) can identify kidney stones on CT scans, even when the kidney stones are very small.
Researchers led by Dr. Kadir Yildirim of Turgut Ozal University, Turkey, have developed a deep-learning model to detect and locate kidney stones on non-injection CT films. contrast agent. The algorithm yielded 96.8% accuracy in tests and could be ready for clinical use.
The authors write “this study shows that recently popular methods of artificial intelligence can be used to solve problems and challenges in urology”
To apply AI to diagnosis To diagnose and avoid missing kidney stones on CT scans, the researchers trained and tested a deep learning model from CT images of nearly 500 patients. These cases were divided into two groups, the group of patients with kidney stones and the group without kidney stones were considered as the control group.
All images are obtained from CT without contrast, then reconstructed in the coronal position with 1799 images, including 790 images in patients with kidney stones and 1009 images. images in patients without kidney stones. A radiologist and a urologist will independently evaluate the imaging and label it with or without kidney stones.
Out of 1799 images, 1163 images are used to train the algorithm, 290 images are used for validation, and the remaining 346 images are used for model testing.
On the test images, the algorithm gives the following results: sensitivity (Sensitivity) 95.7%, specificity (Specificity) 97.7% and accuracy (Accuracy) 96.8%.
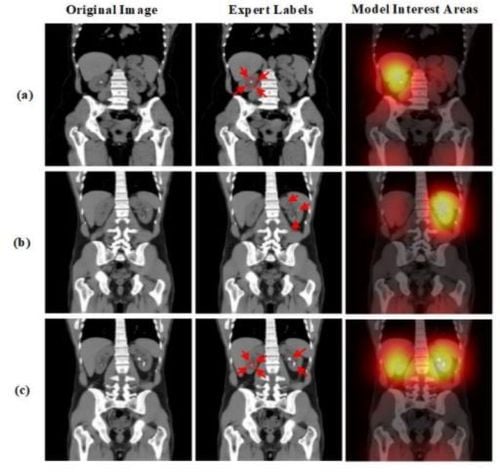
The authors note that this algorithm can identify even small sized pebbles. In addition to determining the presence of kidney stones, it can also be used to evaluate a number of other urinary problems.
They write “Clinically, the algorithmically identified kidney stones were peer reviewed and agreed upon for most imaging. Therefore, our proposed algorithm is accurate and can assist radiologists to detect cases of kidney stones accurately."
Of course, according to the authors, this study still has limitations such as small sample (nearly 500 patients), data collection is limited to only one center, so its universality is not high. The new image evaluation is only based on the reconstructed image in the horizontal plane (coronal), in the near future they will deploy more on other sections such as horizontal (axial), vertical (sagittal). On the other hand, they also wanted to conduct an assessment to see if the size of the kidney stones affected the accuracy of the algorithm.
Currently, Vinmec medical system has applied artificial intelligence in diagnostic imaging, specifically Vinbrain's DrAid software in chest radiology diagnosis. Hopefully in the near future, AI will be researched and applied to many other pathological groups such as identifying kidney stones on CT films.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source : DOI reference code: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104569