This is an automatically translated article.
Polyps often appear in the colon and stomach with the number from a few to thousands. This condition is quite common today, but not everyone understands the nature of this damage.1. What are polyps? Are polyps cancerous?
Polyp is a type of lesion that looks like a tumor but is not a tumor, it can be pedunculated or sessile. Polyps formed by mucosal or submucosal tissue proliferate. Most polyps are benign, but some polyps have the potential to turn malignant (cancerous) if left untreated.
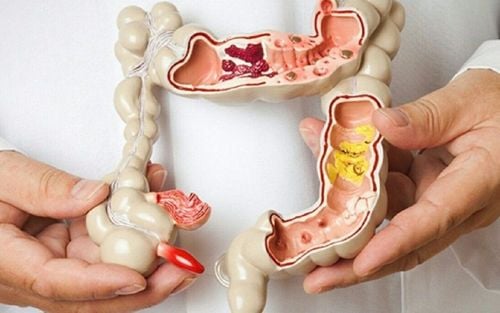
Polyps can appear in one or more places in the body such as the stomach, small intestine, or rectum. Among them, colon polyps have the highest cancer rate. A person with this disease can have dozens, hundreds or even thousands of polyps of different sizes in the colon and may be accompanied by dozens of other polyps in the small intestine and stomach.
2. How do polyps manifest?
Depending on the location of the polyp, the patient will have different symptoms.
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để bảo vệ lá gan khỏe mạnh?
Làm test trắc nghiệm kiểm tra hiểu biết về gan có thể giúp bạn nhận thức rõ vai trò quan trọng của gan, từ đó có các biện pháp bảo vệ gan để phòng ngừa bệnh tật.2.1. Colon polyps
Usually, patients begin to have polyps of various sizes in the colon from puberty, but rarely develop symptoms before the age of 33.
More than two-thirds of all patients with polyps have no symptoms. proof. The rest often have manifestations such as:
Easily diarrhea. Some people have diarrhea alternating with constipation.

Tiêu chảy xen kẽ với táo bón là biểu hiện Polyp đại tràng
Some people have bloody stools. There are a few cases of normal bowel movements but presenting with abdominal cramps along the colonic frame. Some patients have symptoms similar to chronic gastritis with symptoms such as flatulence and dyspepsia. When the number of polyps in the colon is too much, it is necessary to perform surgery to remove the colon with polyps to avoid the risk of turning into colon cancer.
With the number of polyps not too much, from 50 to 60 polyps, it can be thoroughly removed through colonoscopy.
Colon polyps are more common than gastric polyps, with an incidence of about 5 - 6% of the population. Factors that trigger the disease are:
Predisposing factors. Due to heredity. Elderly, over 60 years old. Obese people. Smoke. Drink a lot of alcohol. High fat diet. Lack of fiber. Lack of calcium. Lack of Selenium. There are two common types of colon polyps: hyperplastic polyps and adenomatous polyps.
Hyperplastic polyp : This form is usually small in size. Common in the terminal colon: rectum and sigmoid colon. Hyperplastic polyps rarely become malignant. Adenomatous Polyps: Up to two-thirds of all colon polyps are adenomatous polyps. Most of them do not develop into cancer, although they have this potential. Adenomatous polyps are usually classified according to their size, shape, and histological features by biopsy. The larger the adenoma, the more likely it is to become cancerous. Therefore, large polyps need to be biopsied or completely removed and sent for pathology. It is difficult to distinguish these two polyps based on endoscopic imaging alone, so hyperplastic polyps are still removed. and sent for cytology as an adenomatous polyp.
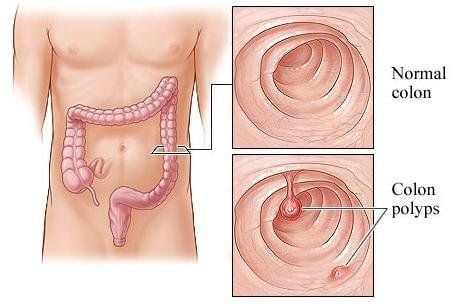
Polyp đại tràng có thể hóa ác tính thành ung thư đại tràng
2.2. Stomach polyps
Gastric polyps are benign tumors, ranging in size from 3-4mm to 2-3cm, growing on the surface of the stomach. The number of stomach polyps can be only 1-2, but sometimes up to 5 - 10 or up to dozens of them. According to statistics, about 1% of the population suffers from this disease.
Common symptoms of stomach polyps are:
Abdominal bloating, indigestion. Pain in the abdomen above the navel. When polyps are large, they will cause bleeding, vomiting, blood or black stools. If this condition is not detected and removed in time, the patient will have chronic anemia with symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, dizziness, paleness, and weight loss.
Endoscopy through the mouth or through the nose is the only method to accurately diagnose this disease. In addition, the doctor will conduct a stomach biopsy to see if stomach polyps have turned into stomach cancer.
Causes of stomach polyps are:
Infection with H. Smoke. Drink beer. Long-term use of high-dose gastric acid-suppressing drugs. Gastric polyps include the following main types:
Hyperplastic polyp : This form forms a chronic inflammatory response in the cells lining the inside of the stomach. This is the most common form in patients with gastritis. There may be an association with HP bacteria. Hyperplastic polyps are unlikely to become gastric cancer. However, with large hyperplastic polyps, more than 2cm in diameter, there is a risk of becoming cancerous. Glandular polyps: Form from glandular cells on the inner lining of the stomach. This form often occurs in people with a rare inherited syndrome called familial adenomatous polyposis. Adenomas are the most common type of gastric polyp. More likely to become stomach cancer.
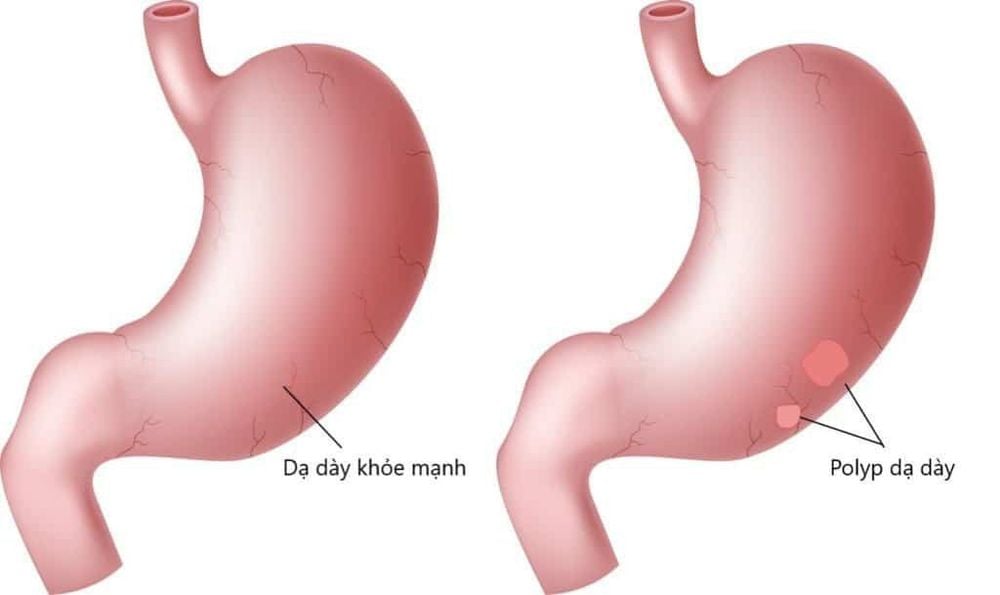
Polyp dạ dày có thể hóa ác tính thành ung thư dạ dày
3. How to treat polyps
The way to treat polyps is generally to remove polyps during colonoscopy, if polyps are found. If polyps are too large to be removed endoscopically, the doctor will treat them with surgery.
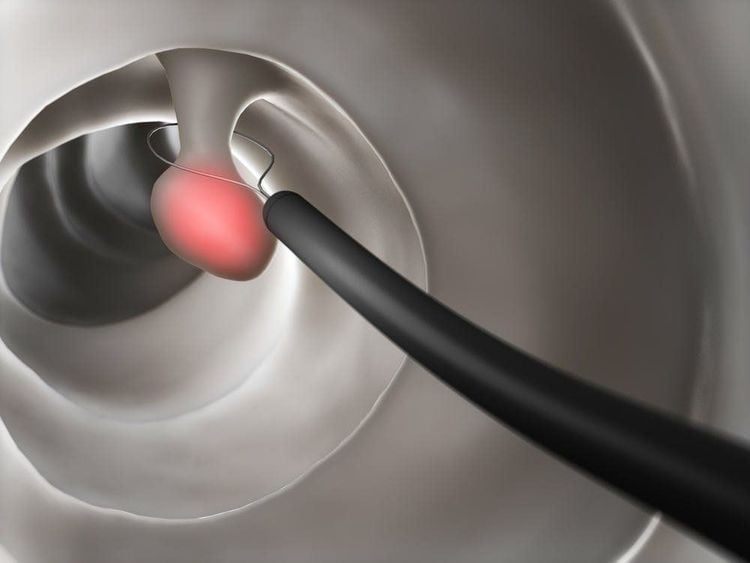
Nội soi vừa có thể chẩn đoán vừa có thể điều trị polyp nếu kích thước không quá lớn
With large polyps in the colon that have turned to early cancer, if the polyps are not too big and have not attached deeply to the wall of the large intestine, the doctor can still cut them. If invasive cancer affects segments of the large intestine, surgical removal of them may be required.
After successful endoscopic polypectomy, the doctor will ask the patient to re-examine the colonoscopy within 3 - 6 months later. If the patient is stable, will continue to monitor and check in the next 1-3 years. During the follow-up, if polyps are detected again, the doctor will proceed to remove the recurrent polyps through endoscopy.
4. How to prevent polyps
Do not smoke. Do not drink alcohol. Increase exercise. Avoid obesity. Eat lots of green vegetables and fruits. Limit your intake of fat and red meat. Get extra calcium from food and milk. As such, polyps are not cancerous and most are benign. However, some cases can turn malignant into cancer, so when detected, polyps need to be treated promptly and monitored to prevent the disease from turning into cancer.
Colon and stomach are the two organs most often polyps appear. Gastroscopy, colonoscopy both help diagnose and treat polyps the best today. In the case of large polyps that cannot be removed through endoscopy, surgery will be required to remove them.
Department of Endoscopy - Gastroenterology is one of the key specialties at Vinmec International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.