This is an automatically translated article.
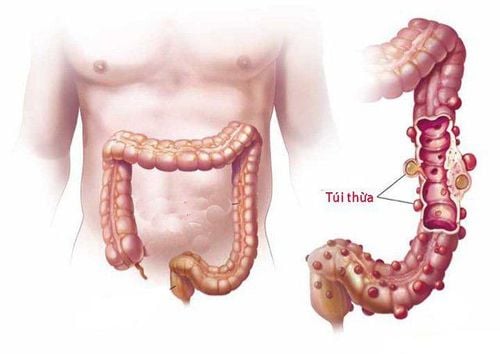
Colon polyps are important because they can become malignant (cancerous). Based on the size, number and histology (histology) of colon polyps can predict the likelihood of developing further polyps and colon cancer.1. What are colon polyps?
Colon polyps are small masses of cells that form on the lining of the colon (large intestine). Most colon polyps are harmless, but over time, some colon polyps can develop into colon cancer, which is fatal when found in its late stages. There may be 1 or more polyps in the colon. Anyone can get colon polyps.Colon polyps usually cause no symptoms. It is important to have regular screenings, such as colonoscopy, because colon polyps found at an early stage can often be completely and safely removed. The best prevention for colon cancer is regular polyp screening.
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để bảo vệ lá gan khỏe mạnh?
Làm test trắc nghiệm kiểm tra hiểu biết về gan có thể giúp bạn nhận thức rõ vai trò quan trọng của gan, từ đó có các biện pháp bảo vệ gan để phòng ngừa bệnh tật.2. What are the symptoms of colon polyps?
Most colon polyps have no symptoms. Your doctor may find it during a routine checkup or trying to diagnose another condition. However, when symptoms appear they may include:Bleeding from the rectum: Blood may get on underwear or toilet paper after a bowel movement. This could be a sign of colon polyps or cancer or other conditions, such as hemorrhoids or anal fissures.
Change in bowel habits: Constipation or diarrhea that persists for more than a week may indicate the presence of a large polyp in the colon. However, a number of other medical conditions can also cause changes in bowel habits.
Change in stool color: Blood can show up as red streaks in stool or make stools black. A change in color can also be caused by foods or medications.
Pain, nausea, or vomiting (rare): A large colon polyp can obstruct your bowels, leading to abdominal cramps, nausea, and vomiting (intestinal obstruction).
Anemia: Bleeding from polyps can happen slowly over time without blood being visible in your stool. Chronic bleeding causes a lack of iron to produce the substance that allows red blood cells to carry oxygen to your body (hemoglobin). The result is iron deficiency anemia, which can make you feel tired and short of breath.

Thay đổi thói quen đại tiện là một trong những triệu chứng của polyp đại tràng
3. When to see a doctor?
See your doctor if you have the following symptoms:Abdominal pain Blood in stools Change in bowel habits that persist for more than a week You should be checked for polyps regularly if:
You are 50 years of age or older. You have risk factors, such as a family history of colon cancer. Some people at high risk should begin regular screening before age 50.
4. What causes colon polyps and who gets polyps?
The cause of polyps is unknown. Healthy cells grow and divide in an orderly manner. Mutations in some genes can cause cells to continue dividing even without new cells. This uncontrolled growth in the colon can form polyps. Polyps can develop anywhere in your large intestine. In general, the larger the polyp, the higher the risk of cancer.5. What are the risk factors for colon polyps?
These risk factors include:Age: Polyps are found in about 15-20% of the adult population. In general, polyps are more common in people over the age of 50, the age at which doctors advise patients to get screened for colon polyps. People with a history of polyps or colon cancer are more likely to develop polyps. You're also more likely to have colon polyps if you had ovarian or uterine cancer before age 50. Smoking and drinking. No exercise, overweight. Inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Family history. You're more likely to get colon polyps or cancer if you have a parent, sibling, or child with the disease. If multiple family members have polyps, your risk is even higher. In some people, this association is not genetic. African-Americans have a higher risk of colon cancer (rare). Type 2 diabetes is not well controlled. Hereditary polyps: A rare disease in which people inherit the genetic mutation that causes colon polyps. If you have one of these genetic mutations, you have a higher risk of developing colorectal cancer. Screening and early detection can help prevent the growth and spread of these cancers.
Tiểu đường type 2 không được kiểm soát tốt có thể là nguyên nhân gây polyp đại tràng
6. What are the complications of polyps?
Some colon polyps can become cancerous. The earlier polyps are removed, the less likely they are to become malignant.7. What if you have a colon polyp?
When a colon polyp is found, the doctor removes it and checks for cancer. Most polyps are removed during a colonoscopy.There are several ways a doctor can find colon polyps including:
Colonoscopy Computerized tomography (CT scan) Contrast X-ray of the colon
8. How are polyps treated?
Your doctor can remove all polyps when found. Methods include:Removal during screening. Most polyps can be removed by biopsy or with a polypectomy.
Minimally invasive surgery . Polyps that are too large or cannot be safely removed during screening are usually removed with minimally invasive surgery (laparoscopic surgery, transrectal TEO).
Resection of colon and rectum . If you have a rare genetic syndrome, like FAP, you may need surgery to remove your colon (total colectomy).
9. What is the risk of polyp removal?
Polyps removed during endoscopy are a routine outpatient procedure. Possible but uncommon complications include bleeding from the resection site and colonic perforation with an incidence of 0.1%. Bleeding from the polypectomy site may occur at the time of resection or several days later, but persistent bleeding is almost always stopped during resection. Perforation usually requires surgery.10. Follow-up care
If you've had an adenomatous polyp or a serrated polyp, you have a higher risk of colon cancer. The degree of risk depends on the size, number, and characteristics of the adenomatous polyps that have been removed.You will need to monitor polyps. Your doctor may recommend a colonoscopy:
In 5 years if you have only one or two small adenomas In 3 years, if you have more than two adenomas, the adenomas are 0.4 inches (about 1 cm) in size or larger, or villous adenomas Within 3 years, if you have more than 10 adenomas Within 6 months, if you have had one very large adenoma or one that had to be removed in several It is important that you prepare your colon thoroughly before your colonoscopy. If stool remains in the bowel that would interfere with the colonoscope's view, you'll probably need a follow-up colonoscopy sooner than specifically directed.
11 How to prevent colon polyps?

Tránh uống rượu và thuốc lá để ngăn ngừa hình thành polyp đại tràng
Avoid alcohol and tobacco Lose weight Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables Avoid fatty foods Eat plenty of calcium (such as milk, cheese, broccoli) Take a low dose of aspirin every day - this can help prevent polyps At Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital (HCMC) new technology is applied in the treatment of Polyps. colon: Robotic surgery with a hand-held robot.
This method has many advantages compared to both classic laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery such as: less invasive, small incision, less pain, low risk of infection, thereby helping customers to lose less blood during surgery. technique, quick recovery; The cost is much lower than robotic surgery.
Patients will be consulted and treated with experienced endoscopic doctors and directly operated by Dr. Do Minh Hung - Head of General Surgery - Vinmec Central Park General Hospital. Dr. Hung has more than 25 years of experience in the field of General Surgery.
>>>> Customers can refer to more information: Day surgery, outpatient surgery
From now until the end of November 20, customers will receive an immediate 20% discount on surgical fees by hand-held robot when treating gastrointestinal diseases; Urology and Gynecology Surgery.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital, please contact Hotline: 0283 6221 166 or register online HERE