Liver stones, also known as intrahepatic bile duct stones, are stones of varying sizes or sludge-like formations found in the bile ducts within the liver, the right hepatic duct, and the left hepatic duct. Are liver stones dangerous? What causes them?
1. What Are Liver Stones?
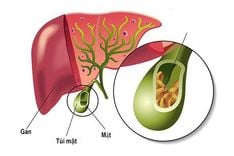
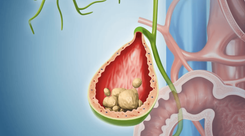
Liver stones, also referred to as intrahepatic bile duct stones, are stones of varying sizes or in the form of bile sludge that appear in the bile ducts within the liver, including the right hepatic duct and left hepatic duct. These stones are primarily composed of bilirubin. Liver stones are relatively common in Asia. In Vietnam, they account for 15–30% of all bile duct stone cases.
2. What Causes Liver Stones?
Liver stones, also known as pigment stones, are primarily composed of bilirubin. They often appear as yellow-green stones, either in clusters or scattered within the bile ducts deep inside the liver tissue. Several factors contribute to the formation of liver stones, including:
- Bile duct infections: This is the most common cause. Parasites such as intestinal worms can migrate to the bile ducts, causing obstruction, altering the solubility of bilirubin in bile, and leading to its accumulation and stone formation.
- Bile stasis in the liver: This may occur in individuals with congenital bile duct atresia or intrahepatic bile duct tumors.
- Hemolytic disorders: Conditions causing red blood cell destruction release large amounts of bilirubin, increasing the risk of bilirubin stone formation in the bile ducts.
- Obesity, metabolic disorders, and sedentary lifestyle: These factors can reduce bile duct motility and lead to bile accumulation.
- Prolonged use of lipid-lowering medications and oral contraceptives.
- Other rare causes: Liver dysfunction disorders such as cirrhosis, viral hepatitis (A, B, C), or drug-induced hepatitis.
3. Symptoms of Liver Stones
The symptoms of liver stones vary depending on their location and size. While gallstones may present with vague symptoms, liver stones often have more distinct clinical signs.
Early stage (small stones): Patients may experience symptoms such as bloating, indigestion after meals, and mild pain in the right upper abdomen. These symptoms are often subtle and can be mistaken for gastric issues.
Advanced stage (stone migration): Symptoms become more noticeable, including:
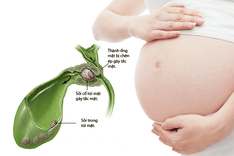
- Severe right upper abdominal pain: The pain usually occurs suddenly after consuming fatty meals or at night, preventing sleep. The pain may radiate to the right shoulder and back.
- Fever with chills: This occurs in cases of bile duct infection. Patients may have a mild, persistent fever or a high fever ranging from 39–40°C.
- Jaundice, yellowing of the eyes, and pale stools: These symptoms are indicative of bile duct obstruction.
Other symptoms include loss of appetite, aversion to fatty foods, and unexplained weight loss. If these symptoms occur, patients should visit a reputable medical facility for prompt examination and treatment.
4. Are Liver Stones Dangerous?
Yes, liver stones can be very dangerous. Early detection and timely treatment are crucial to prevent life-threatening complications. Common complications include:
- Suppurative cholangitis: This is the most common complication. Recurrent infections make treatment challenging, increasing the risk of antibiotic resistance. Chronic inflammation can cause biliary fibrosis, bile duct strictures, liver abscesses, secondary biliary cirrhosis, and, in severe cases, septicemia and liver failure, which can lead to death.
- Bile duct cancer: Liver stones are associated with bile duct cancer in 3–4.3% of cases, particularly in individuals with recurrent stones. Chronic irritation from stones can damage the bile duct lining, leading to abnormal cell growth and cancer.
- Liver damage: Bile stasis caused by stones prevents bile components from being excreted, disrupting liver function. This can result in elevated liver enzymes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer.
5. How Are Liver Stones Treated?
Several treatment options are available for liver stones, depending on the condition's severity:
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): This method is suitable for cases where the bile ducts are not narrowed, and the stones are large enough for removal. During ERCP, the surgeon removes stones from the common bile duct, reducing pressure in the bile ducts.
- Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Lithotripsy: This procedure involves creating a pathway through the skin to the liver. The doctor inserts an endoscope to break the stones, flush them out, or use tools to extract them. This method requires a highly skilled and experienced surgeon to avoid complications like peritonitis or septicemia.
- Open surgery for stone removal: This is used when minimally invasive methods are ineffective. Open surgery may be combined with other procedures to optimize outcomes. The treatment approach depends on the patient's overall health condition.
- Partial hepatectomy: This involves surgical removal of part of the liver when other treatment methods are ineffective. However, partial liver removal may affect bile production, toxin elimination, and glucose metabolism.
All treatments must be performed by highly qualified doctors in well-equipped medical facilities. Patients should strictly follow the treatment plan prescribed by their doctors.
6. How to Prevent Liver Stones?
Liver stones can pose significant risks if not detected and treated promptly. However, adopting preventive measures can minimize the chances of recurrence and related complications. Here are some useful tips:
- Avoid smoking and alcohol: Refrain from tobacco, alcohol, and other stimulants.
Healthy diet:
- Increase intake of green vegetables, fruits, and fiber-rich foods.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Reduce consumption of fatty foods, cholesterol, fried, and processed foods.
- Maintain food hygiene and avoid consuming raw or undercooked food to prevent parasitic infections.
- Regular deworming: Deworm every 6 months to prevent infections from parasites and worms.
- Active lifestyle:
- Engage in daily physical activities such as walking, running, cycling, or yoga.
- Regular exercise (30–45 minutes daily) helps improve bile duct motility and prevent bile stasis.
We hope this information provides a clearer understanding of liver stones. Patients should schedule regular health check-ups every 6 months or annually to screen for risk factors and detect liver stones early for timely treatment.
By following preventive measures and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, individuals can reduce their risk of complications and protect their liver health.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.