This is an automatically translated article.
Many people often confuse hemangiomas in the liver with liver cancer because of the presence of a tumor. So are liver hemangiomas dangerous, what drugs are used to treat hemangiomas in the liver?
1. What is a hemangioma in the liver?
Intrahepatic hemangioma is a condition in which the network of blood vessels in the liver or on the surface of the liver is tangled, there may be one or more tumors, with the size usually very small (<5cm), however, some cases The tumor can still grow larger.
This is a benign tumor in the liver, often without symptoms and there is no evidence that the tumor will progress to cancer. When the tumor is large, it is likely to cause some symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting. Hemangiomas in the liver can occur in healthy people.
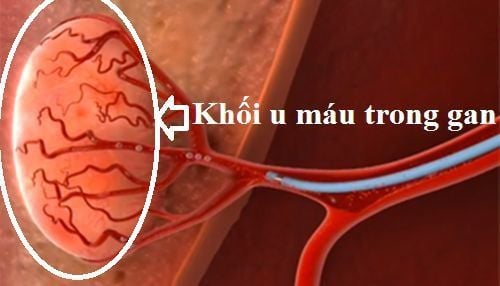
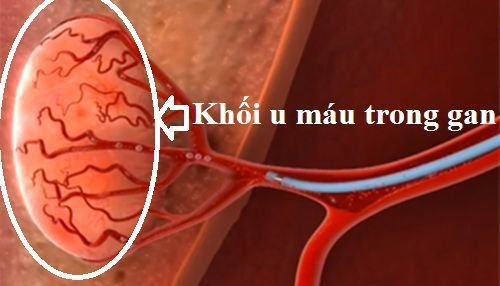
U máu trong gan là tình trạng mạng lưới các mạch máu ở trong gan hoặc trên bề mặt gan bị rối, có thể có một hoặc nhiều khối u
2. Causes of hemangiomas in the liver
At present, the cause of hemangioma in the liver is still unknown. However, the appearance of hemangiomas in the liver can be caused by:
Heredity; Birth defects; Increased blood estrogen levels during pregnancy, or hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women.
3. Are liver hemangiomas dangerous?
Liver hemangiomas are usually benign and asymptomatic, except in rare cases where the tumor is large (>4cm), or the tumor is located near the liver capsule causing compression, or there is an internal thrombus tumor and cause symptoms such as: pain in the upper right part of the abdomen, bloating after eating, vomiting, nausea, loss of appetite, anorexia, feeling full despite eating less.
With large liver hemangiomas, they can rupture and bleed in the abdomen, causing severe pain. Rarely, however, the tumor ruptures on its own and is usually caused by a fall or trauma to the liver. At this time, tumor rupture can affect the patient's life.
In addition, complications of hemangiomas in the liver are rare. However, in cases where women are pregnant or taking hormone therapy (including using birth control pills) or have liver disease, the tumor has the potential to cause complications such as: spreading hemangioma, liver damage and pain.
4. Diagnosis and treatment of liver hemangiomas
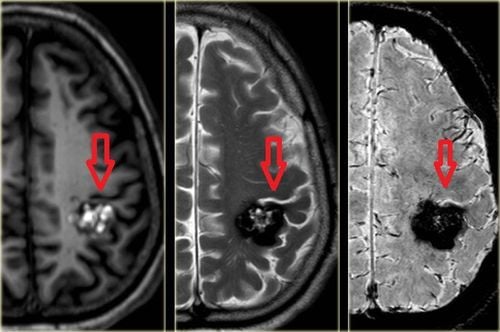
Chụp cắt lớp (chụp CT) ổ bụng giúp quan sát các chi tiết phức tạp của gan
4.1 Diagnosing Hemangiomas in the Liver When a hemangioma in the liver is too large and causing symptoms, the doctor will perform some imaging tests to be able to see the intricate details of the liver. as well as surrounding structures to detect liver problems. Diagnostic methods include:
Liver ultrasound; Computed tomography (CT scan) of the abdomen; Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen. For cases with no symptoms, hemangiomas in the liver are only discovered when the patient has a periodical general health check-up or when examining for other diseases.
4.2 Treatment of liver hemangiomas Currently, there are no drugs that can treat or reduce the size of hemangiomas in the liver.
Most hemangiomas in the liver do not require treatment because they are benign, rarely malignant and cancerous. Treatment of liver hemangiomas is mainly to treat large and symptomatic tumors. Treatment is based on the location, size, and number of tumors. Methods when indicated for treatment include:
Blocking blood supply to the tumor: When the blood flow to the tumor is high and accumulates, it will cause the blood tumor in the liver to grow rapidly. At this time, the doctor will perform a ligation of the artery that supplies blood to the tumor, to stop the tumor from growing. This procedure is called selective hepatic artery embolization or hepatic artery ligation. This procedure does not affect the area around the liver because it still receives blood from another artery and remains healthy; Surgery to remove the tumor: If the liver hemangioma is too large, causing pain or causing significant liver damage, the doctor will decide to surgically remove the entire damaged part; Liver transplant : This is an extremely rare case, only occurs when the tumor size is too large or the number of tumors is too much, and the above measures do not work. Most cases of hemangiomas in the liver are not dangerous and do not cause long-term health problems. Only very rare cases will require a liver transplant and the patient must take lifelong medication to keep the body from rejecting the transplanted liver.
Patients with hemangiomas in the liver can go to Vinmec International General Hospital for examination and treatment. There is a team of well-trained, professional and experienced doctors; system of modern equipment, meeting international standards; professional service quality, helping the diagnosis and treatment process to be highly effective.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.