This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Van Sang - Dermatologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. The doctor has 18 years of experience in the field of Dermatology.Hemangiomas are common tumors in young children that form when blood vessels proliferate. Although the majority of hemangiomas are benign and self-destructive, there is also a small percentage of hemangiomas that progress to malignancy, causing many complications for pediatric patients. Therefore, timely treatment of hemangiomas in children will help children develop the best.
1. Overview of hemangiomas in children
Hemangiomas are benign tumors, common in young children, caused by overgrowth of blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries). Hemangiomas in infants usually appear as a bright red nodule, with a strawberry-like surface. This type of tumor can appear anywhere on the body, but the highest rate is in the head, face and neck (60%).Although hemangioma is a benign tumor, it can also cause some serious complications such as:
Ulcer, infection, tumor necrosis; Bleed; Affects aesthetics, causing facial deformity; Heart failure ; Airway obstruction in case of tracheal tumor or large submandibular tumor causing airway compression; interfere with eating, breathing, or vision if the hemangioma grows in the child's mouth, lips, nose, or eyelids; Harmful to health if hemangiomas grow on the genitals, rectum,...; Throat hemangioma, if not handled promptly, will spread and invade deep tissues such as the larynx, causing complications such as difficulty breathing and massive bleeding; Affect patient psychology.
2. How to treat hemangiomas in children?
2.1 Do hemangiomas need treatment? The course of a typical hemangioma is usually: appearing in the baby in the first weeks after birth, developing during the first year. When a child is 6-18 months old, most hemangiomas will gradually improve (called the regressive stage), the hemangioma will reduce red, gradually turn gray, softer and flatter.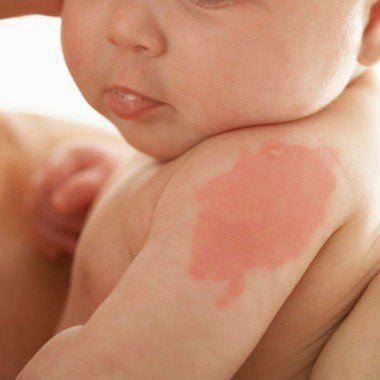
According to doctors, most neonatal hemangiomas do not require treatment because they can regress on their own over time into fatty deposits. However, children with hemangiomas need periodic follow-up by a specialist. Children will have a general assessment, measure the size of the tumor, take pictures of the tumor and periodically evaluate it. During this time, the area of the hemangioma can be bandaged if needed. The follow-up period is usually 5 consecutive years. Then, the decision to have treatment will depend on the child's age, size, location, growth rate, and how it affects the life of the hemangioma.
Accordingly, hemangiomas are often indicated for treatment when:
Hemangiomas affect organ functions, including: Limited vision, impaired hearing or obstructing the airway; Hemangiomas with complications: Ulcer, infection, bleeding; Hemangiomas have the ability to cause skin dilation or scarring, especially in cosmetic locations such as the face and chest because it can affect the child's psyche. 2.2 Treatment methods for hemangiomas There are different methods of treating hemangiomas. Which method to apply depends on each disease type and specific location. The purpose of treatment is to cure the disease, ensure aesthetics and not affect the development of the child's body. The treatment of hemangiomas in children has the following options:
Local treatment:
Topical beta-blockers: Typically Timolol - a drug capable of stopping growth, reducing its size or color of hemangiomas located on the surface of the skin; Topical Steroids: May prevent the growth of small, flat hemangiomas on the skin, but are less commonly used as Timolol because of more side effects; Steroid injection: Can be injected directly into the tumor to slow down the growth, has a good effect on small and localized hemangiomas. Systemic treatment:
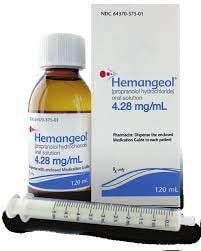
Oral propranolol: Mainly used to treat complicated hemangiomas. This drug is also used to treat high blood pressure. Before treatment is indicated, the child will have liver and kidney function tests, echocardiogram, and pediatric specialist examination. When giving medicine to children, parents need to be especially careful because it can cause low blood sugar if the child does not eat and drink enough. In addition, the drug Propranolol also lowers blood pressure and slows the heart rate. Therefore, the use of the drug should be under the close supervision of the doctor; Oral steroids: It is necessary to have an experienced doctor to treat and monitor the response of the drug because it can cause many complications if used for a long time such as oral thrush, mental retardation,... Methods Other treatment:
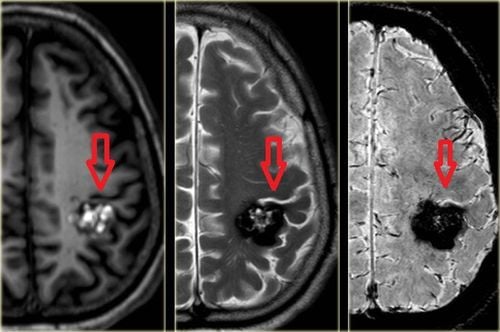
Laser treatment: Laser is a useful method for pediatric patients with flat and shallow hemangiomas, bleeding hemangiomas or wanting to heal ulcerative hemangiomas. This method of treatment also helps to remove the sequelae of the color and shape of hemangiomas on the skin, but has the disadvantage of causing pain to the patient; Surgical treatment: Mainly applied to cases of small ulcerative hemangiomas or located in positions that, when growing, will affect organ functions or affect aesthetics. In addition, surgery is also applied in overcoming cosmetic sequelae such as stretch marks or bad scars; Vascular embolization: Applied in case of vascular malformation tumor. However, after embolization, surgery should be performed immediately to ensure effective treatment of the disease; Injectable scleroderma: Effective for vascular endothelium and vascular malformation with large tumor, unclear boundary, dangerous if surgery is performed; Other methods: Radiation, cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen gas at negative temperature,... The prevention of hemangiomas in children is only applicable to masses acquired after insect bites, trauma, etc. .. In this case, parents need to well control the lesions in the vascular area that are prone to hemangiomas right after the child is injured and promptly and effectively treat it.
Pediatrics department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, pneumonia in children, .... With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.