This is an automatically translated article.
Post by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Intrahepatic hemangiomas are often misdiagnosed with other liver tumors. Accurate diagnosis of hepatic hemangiomas is an imaging challenge and relies heavily on pathological findings.
1. Overview of imaging diagnosis and treatment of liver hemangiomas
Usually, hemangioma of the liver appears on magnetic resonance imaging (or computed tomography) as a angiogenic solid tumor with areas of fat and washed out, and can be easily diagnosed confused with other liver tumors, especially hepatocellular carcinoma. The therapeutic strategy is not well defined, but surgical resection is indicated for symptomatic patients, for tumors that have an aggressive appearance (i.e., change in size on imaging or operation). high proliferation and an atypical epithelial pattern on liver biopsy), for biopsy-proven large (>5cm) liver hemangiomas, and if still suspicious on imaging or histology. Conservative management may be justified in other conditions, as most cases follow a benign clinical course. In summary, the accurate diagnosis of hepatic hemangiomas is an imaging challenge and relies heavily on pathological findings.
2. Difficulty in diagnosing the nature of liver hemangioma
Angiomyolipoma (AML) is a solid mesenchymal tumor, mainly described in the kidney, and belongs to the group of perivascular epithelial cell tumors (PEComas). Liver localization of Angiomyolipoma, first described in 1976, is rare, as only about 600 cases have been reported after a complete literature search as of 2017. Liver angiomyolipoma poses a challenge A real diagnostic tool from a radiological point of view, especially when the fat content is low, since this type of tumor can appear as a washout-associated hypervascular tumor, mimicking liver tumors. Other, more common vascular hyperplasia, such as hepatocellular carcinoma.
3. Imaging signs of liver hemangioma
The imaging features of hepatic hemangiomas vary widely depending on the large variability of fat, smooth muscle, and vascular factors. Diagnosis can be difficult and depends mainly on the amount of fat present, which is key to diagnosing liver hemangiomas. On sonography, the lesion is often well-defined, strongly echogenic or mixed and, after administration of ultrasound contrast agent, exhibits rapid enhancement in the arterial phase relative to the adjacent liver. In the portal and late stages, hemangiomas may display hypoechoic, isotonic, or hyperechoic. Computed tomography (CT) showed a hypoattenuating tumor with areas of fat within the lesion (density about -50 HU). Classically, this solid tumor is late-stage angiogenesis [CT or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)]. Hepatic hemangiomas with little or no vascularity on histological examination for a prolonged and enhanced portal space in the late stage, whereas hepatic hemangiomas with rich vascular tissue are more likely to show clearance. Tumor signals on MRI are intense in T2-weighted sequences and variable in T1-weighted sequences. MRI is the most sensitive imaging technique for detecting liver fat using a T1 gradient echo sequence in and in the opposite phase. Signals shown in a liver injury on antipulse sequences indicate the presence of fat in the lesion. The imaging features on MRI after contrast injection are similar to those observed on CT scan. When hepatocellular-specific agents (gadoxetic acid or gadobenate dimeglumine) were used, lesions showed decreased signal during hepatobiliary tract.
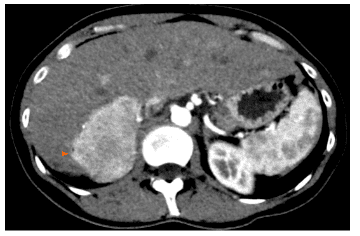
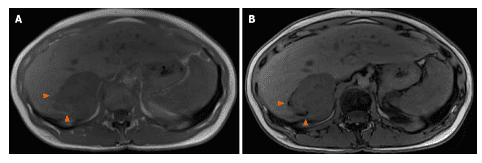
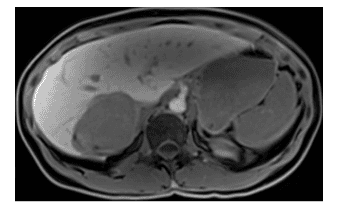
4. Data on evaluation of liver hemangiomas using positron emission tomography
There are limited data on the evaluation of liver hemangiomas using fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18 F-FDG-PET). FDG uptake in hepatic hemangiomas is variable and the value of 18 F-FDG-PET for diagnosis or monitoring of this tumor type is unclear. Given the imaging features of a hepatic hemangioma (a angiogenic lesion with a fatty component in the healthy liver and frequently washed out), the differential diagnoses were a benign hepatocellular tumor (lipoma or adenoma). adenocarcinoma, focal lipomatous hyperplasia) and hepatocellular malignancies (primarily hepatocellular carcinoma). When the diagnosis is difficult, especially with hepatocellular carcinoma, the absence of cysts and venous drainage are two useful radiographic features that can aid in the diagnosis of hemangiomas when they are difficult to diagnose. present.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.