This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Applications of artificial intelligence have made great progress in medical image recognition. In fact, as early as 2001, neural networks have been used to analyze endoscopic ultrasound images to differentiate pancreatic cancer from focal pancreatitis. A program was designed that could distinguish pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer by extracting pixel features from the images, showing a high accuracy rate of 89%.
1. Overview
Pancreatic cancer is a complex cancer of the gastrointestinal tract. Treatment and diagnosis of pancreatic cancer can be difficult because of the vague initial symptoms, the deep anatomical location of the cancerous tissue, and the high degree of invasiveness of the cancer cells. Prognosis is very poor, the 5-year survival rate of pancreatic cancer patients is less than 1%. However, the application of artificial intelligence in healthcare has a lot of potential. In addition to artificial intelligence-based applications, such as disease data processing, imaging, and pathological image recognition, robotic surgery has revolutionized surgical procedures.Trắc nghiệm: Bạn biết gì về các yếu tố nguy cơ, chẩn đoán và điều trị ung thư tuyến tụy?
Ung thư tuyến tụy phổ biến thứ 10 trong những bệnh ung thư mới và là nguyên nhân thứ 4 gây tử vong do ung thư ở nam, nữ. Bài trắc nghiệm này sẽ kiểm tra kiến thức của bạn về các yếu tố nguy cơ, chẩn đoán và cách điều trị ung thư tuyến tụy.
Bài viết tham khảo nguồn: medicalnewstoday 2019
2. Application of artificial intelligence in pancreatic cancer imaging
Applications of artificial intelligence (especially deep learning algorithms) have made great progress in medical image recognition. Integrated autotransformers and other methods have many applications in this area. In fact, as early as 2001, neural networks have been used to analyze endoscopic ultrasound images to differentiate pancreatic cancer from focal pancreatitis. A program was designed that could distinguish pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer by extracting pixel features from the images, showing a high accuracy rate of 89%.With the development of current diagnostic technology, imaging is relatively simple, but with the help of computer neural networks, differential diagnosis becomes easier and more accurate . Since then, neural network imaging has been used in research to distinguish pancreatic cancer from chronic pancreatitis. This method involves capturing image data into a vector form and then converting it into a color histogram. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of this method in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant pancreatic lesions are 91.4%; 87.9% and 89.7%.
3. Pancreatic cyst lesions are often considered an important sign of pancreatic cancer
Machine learning technology is used to extract the imaging features of this cystic lesion, select and classify those features, and then use them to predict benign or malignant pancreatic cystic lesions. In this process, first, image acquisition is performed uniformly, the edges of the suspect lesion are outlined, and the three-dimensional (3D) shape of the variant is obtained. Then the features of the suspected disease in the images are extracted including structure, density and shape. Artificial intelligence software is used for deep learning, features are screened and analyzed, and visual outputs are obtained. The obtained results, proteomics, and patient data are imported into the machine learning model as input layers to create a predictive model, which can help clinicians differentiate between benign and malignant pancreatic cysts .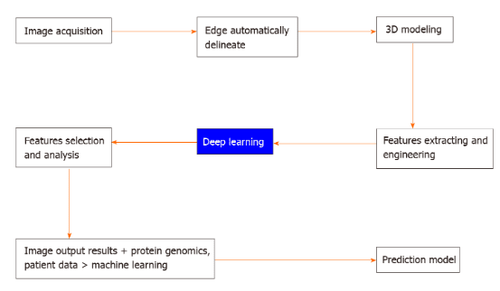
4. How are diagnostic images processed by artificial intelligence?
“Machine learning” technology is used to extract the imaging features of this cystic lesion, select and classify the features, and then use them to predict benign or malignant pancreatic cystic lesions. In this process, first, image acquisition is performed uniformly, the edges of the suspect lesion are delineated, and the three-dimensional shape of the variant is obtained. Then, features of the suspected disease in the image are extracted, including structure, density, and shape. Artificial intelligence software is used for deep learning, features are screened and analyzed, and visual outputs are obtained. The obtained results, proteomics, and patient data are entered into the machine learning model as input layers to create a predictive model, which can help doctors in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant pancreatic cysts. count.5. Limitations of conventional imaging methods
In the past 20 years, with the popularity and development of computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography-CT, medical personnel have been able to collect a lot of imaging data. clearer image. However, because of human limitations, they are subject to errors and the diagnostic efficiency is not high. Furthermore, the training of professional radiologists will be time-consuming. The image itself can only reflect the internal structure of the patient at a certain time and at a certain angle; Therefore, small changes may be difficult to detect with the naked eye. Thus, the application of reliable artificial intelligence can improve the accuracy in diagnostic imaging.As mentioned above, manual diagnosis has disadvantages such as subjective judgment, lack of repeatability and low accuracy.
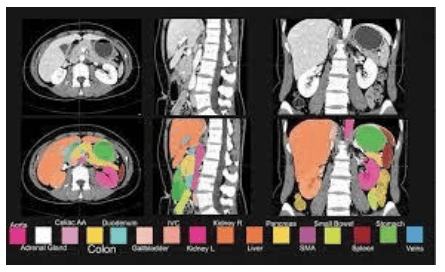
6. Artificial intelligence helps to overcome the shortcomings of current diagnostic techniques
Recent research on using convolutional neural networks for CT recognition in pancreatic cancer diagnosis may provide a way to overcome such shortcomings. An artificial intelligence designed for a related study consists of two parts, namely training and verification.First, a patient data database is established, image data is collected and an image database is established. Then feature extraction, zoning (RPN) and classification and regression networks are established. In the artificial intelligence network, the input image is first converted into a convolutional feature histogram, and the RPN parameters are adjusted through the feature map to generate ROI feature vectors. Then, the RPN parameters are fed into the composite class and a certain model is used for regression and classification. Next, the regression parameters are made into new RPN parameters, and the two RPN parameters are updated only for the unique network layer of the RPN through machine learning.
The RPN parameters are then generated by the regression parameters to refine the single convolutional layer. Using a dedicated verification pool input model, the Secure Global Desktop network is trained by backpropagation and random gradient descent, and the network parameters and weights can be continuously updated and optimized . Finally, the resulting model is an artificial intelligence diagnostic system. The receiver operating characteristic curve of the test results reached 0.9632. The artificial intelligence in that study only needed 20 seconds to identify images, objectively and more efficiently than traditional diagnostic methods. However, it should be noted that this method shows high accuracy in diagnosing pancreatic cancer, which does not mean that the application of artificial intelligence can replace specialists; instead, it provides an auxiliary tool for diagnostics.
7. Some limitations of artificial intelligence in pancreatic cancer diagnosis
Although artificial intelligence has good prospects for diagnostic imaging, it also has limitations and the process of model training cannot be separated with the assistance of artificial diagnostics. In theory, the ultimate goal of diagnostic accuracy is extremely close to the radiographer. Therefore, how to make good use of this to make artificial intelligence more intelligent can be an important problem to be solved in future studies.
In fact, the application of artificial intelligence in photography has been studied by experts and it also requires knowledge from many fields. Such projects create a platform for imaging professionals to communicate with computer professionals. The result is an established medical artificial intelligence system that uses deep learning algorithms to collect and analyze CT images of the pancreas. The experimental group image data and the normal control image data were entered into the program. Through two “matrixes” and the application of a filter, statistics, textures, shapes and other data are obtained. Then, pancreatic carcinomas and normal controls were differentiated by data processing, statistical analysis, and random forest modeling.
Currently, ultrasound of the pancreas is a way to help detect and diagnose some pancreatic diseases quickly and effectively. If you suspect you have pancreatic disease, you can come to Vinmec International General Hospital System, one of the leading prestigious hospitals in the country, Vinmec uses current generations of color ultrasound machines. the most modern in examination and treatment for patients. One of them is GE Healthcarecar's Logig E9 ultrasound machine with full options, HD resolution probes for clear images, accurate assessment of lesions. In addition, a team of experienced doctors and nurses will greatly assist in the diagnosis and early detection of abnormal signs of the body in order to provide timely treatment for pancreatic diseases.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References:Adamska A, Domenichini A, Falasca M. Pancreatic carcinoma: Current and developing therapies. Int J Mol Sci . Year 2017; 18 : 1338. [ PubMed ] [ DOI ] Halbrook CJ , Lyssiotis CA. Using metabolism to improve diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer. Cancer cell . Year 2017; 31 : 5-19. [ PubMed ] [ DOI ] Ngiam KY , Khor IW. Big data and machine learning algorithms for healthcare delivery. Lancet Oncol . Year 2019; 20 : e262-e273. [ PubMed ] [ DOI ]