This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Ton That Quang - Head of Anesthesia - Anesthesia Unit - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. The doctor has more than 15 years of experience working in the Anesthesia - Resuscitation industry.Neuroma is an indication for surgical intervention under endotracheal general anesthesia. However, for difficult intubation cases, the alternative sedation is laryngeal mask anesthesia. Accordingly, the laryngeal mask anesthetic method for neurosurgery also achieved certain effects, providing a good outcome similar to the traditional method.
1. What is laryngeal mask anesthesia to cut neuroma?
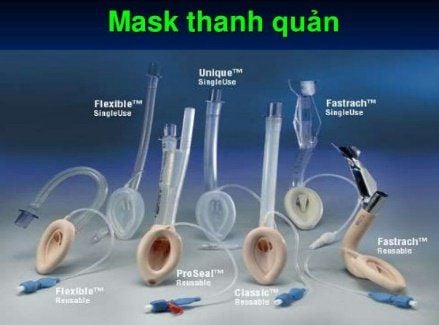
Laryngeal mask anesthesia is a general anesthetic technique. In particular, by using a laryngeal mask, the anesthesiologist can control the respiratory function during the surgery, allowing the surgeon to perform the surgery to remove the nerve tumor. particular or other types of surgery in general.Indications to perform laryngeal mask anesthesia as an alternative to the traditional method of endotracheal anesthesia are previously evaluated cases with the possibility of difficult intubation in the preoperative examination. At the same time, if the initial endotracheal tube intubation with the help of the iron barrel is successful, when the iron is removed, the risk of compression from the adjacent soft tissue mass in the oropharynx will also affect the airflow. difficult to reach or prone to collapsing, no ventilation.
In addition, with cases of cardiac arrest, apnea or respiratory failure with indications for emergency resuscitation intervention, if intubation has failed many times, the laryngeal mask is also an essential and effective tool in Control the airway and assist with ventilation in this setting.

2. Preparation steps for laryngeal mask anesthesia to cut neuromas
About human resourcesDoctors, technicians and/or nurses specializing in anesthesiology and resuscitation have been thoroughly trained in laryngeal mask placement techniques and general anesthesia.
About facilities
100% oxygen source Anesthesia machine system with artificial respiration control function Life function monitor on electrocardiographic parameters, non-invasive blood pressure or invasive arterial blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2, breathing rate, temperature. Emergency resuscitation equipment such as defibrillator, viscous sputum suction machine, suction tube, vasopressor, mask, squeezing balloon, oropharyngeal cannula and prophylactic means of intubation: endotracheal tube: endotracheal tube trachea and laryngoscope
Routine pre-anesthesia examination and intubation assessment are difficult to choose an option appropriate laryngeal mask placement Examination, detection and prevention of risks to anesthesia and surgery, especially medical diseases such as cardiovascular and respiratory function Explain and request consent from the patient and family about the procedure and the surgery, and the risks, complications and possible risks surrounding the surgery. Explain to the patient and cooperate with the medical staff in the preparation for surgery and pre-anesthesia. surgery if necessary when the patient is too nervous, stressed Body hygiene and nutrition according to preoperative procedures Administrative
Medical records are consistent with the indications for anesthesia, laryngeal mask for neurosurgery and not Violation of contraindications Preoperative tests Patient and family consent for surgery
3. Steps in laryngeal mask anesthesia to cut neuromas
Check the complete records as prescribedCheck the patient's correct name and surgical indication
Perform pre-anesthesia technique:
Arrange the patient in the correct position: supine, 100% oxygen breathing 3-6 l /min at least 5 minutes before induction of anesthesia. Install monitoring equipment and devices. Establish an effective infusion line with large needles and physiological solution to keep veins

Sleeping pills: Intravenous anesthetics (propofol, etomidat, thiopental, ketamine...), volatile anesthetics (sevoflurane...). Painkillers: fentanyl, sufentanil, morphine... Muscle relaxants (if needed): (succinylcholine, rocuronium, vecuronium...). Evaluation of the eligibility time to place a laryngeal mask is when the patient sleeps deeply, has enough muscle relaxation, if necessary, medication can be used. the larynx mask is like holding a pen, the index finger is placed at the junction between the laryngeal mask and the tube. One hand opens the patient's mouth with the other hand, the larynx mask is passed through the dental arches to the base of the tongue, resting the back of the mask on the hard palate. Slide the mask along the hard palate to enter the hypopharynx Stops on resistance Pump cuff to correct volume according to instructions on laryngeal mask, can be checked with balloon manometer. Check the tightness of the laryngeal mask by signs of no air leaks and ease of ventilation Check for the correct position of the laryngeal mask by listening for even alveolar murmurs throughout the lung fields on both sides of the lungs. EtCO2 results monitored on the monitor Fixed with adhesive tape Perform anesthesia maintenance techniques:
Maintain anesthesia with intravenous anesthetic or volatile anesthetic depending on the patient's location and comorbidities and coordination with pain relievers and muscle relaxants if needed. Adjust drug dosage according to parameters monitored on monitor and ventilator Monitor breathing by machine or hand squeeze Monitor depth of anesthesia based on heart rate, blood pressure, sweating, lacrimation (PRST) ); MAC, BIS and Entropy (if any)... Monitor vital signs: Heart rate, blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2, body temperature. Prevent the possibility of displacement, retraction, flexion, and obstruction of the laryngeal mask. Criteria to withdraw the laryngeal mask:
The patient is awake and can follow the medical order. Raise the head for more than 5 seconds, TOF > 0.9 in the case of muscle relaxants. Spontaneous breathing, regular rhythm, breathing rate within normal limits. Pulse and blood pressure are stable. Body temperature over 350°C. There were no complications of anesthesia and surgery.
4. Possible complications and how to deal with laryngeal mask anesthesia to cut neuromas
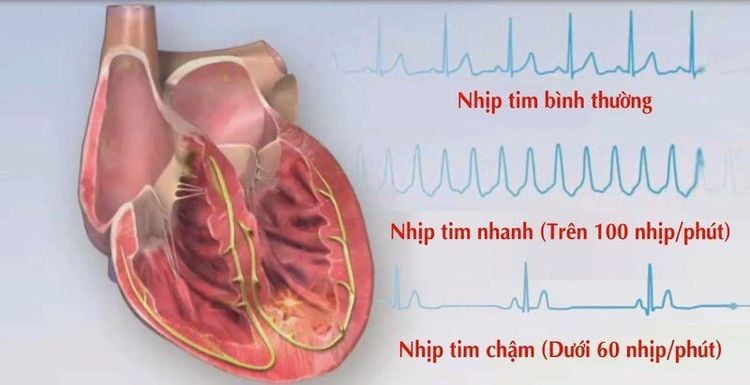
Hemodynamic disorders such as hypotension or hypertension, cardiac arrhythmia: Ability of reflexes during anesthesia and treatment depending on symptoms and causes.
Injuries when putting on a laryngeal mask: The types of damage that can be encountered are bleeding, broken teeth, damage to the vocal cords, falling foreign objects into the airways... and the treatment depends on the type of injury.
Complications can be encountered after removing the laryngeal mask: The most severe is respiratory failure due to reflex airway constriction. Other complications are upper respiratory tract infection, sore throat, hoarseness... which may require treatment or self-remission.
In summary, laryngeal mask anesthesia is a "rescue" measure for difficult intubation cases requiring surgery. With indications for neurosurgery or other surgical interventions, like traditional methods, laryngeal mask anesthesia for neurosurgery still ensures patient safety and efficiency of surgery.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MORE
Anesthesia mask larynx surgery for ear cartilage inflammation, ear malformations Anesthesia mask larynx laparoscopic surgery to treat facial paralysis Anesthesia with laryngeal mask surgery for uterine deformities