This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Ta Quang Hung - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang.Laryngeal mask anesthesia is a simple technique that does not require a lot of experience, is less stimulating when released from anesthesia, does not cause reflexes, and is very suitable for ophthalmic surgery. In particular, laryngeal mask anesthesia is often indicated for intraocular surgery in functionally lost eyes that are no longer able to treat conservatively.
1. Learn about intraocular surgery and laryngeal mask anesthesia in intraocular surgery
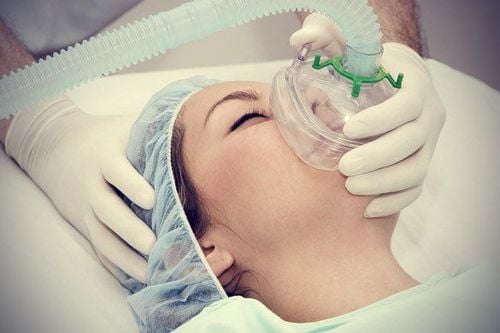
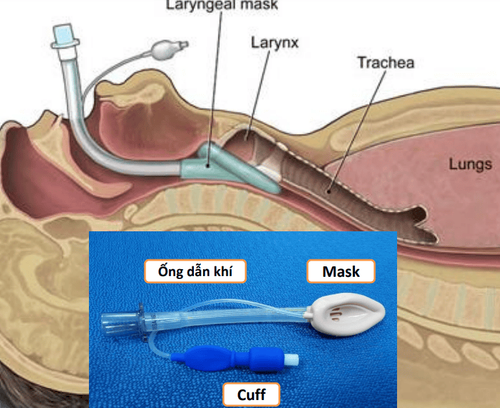
Intraocular laparotomy is surgical removal of all tissues in the eyeball, leaving the sclera, tenon sheath (the fibrous membrane that covers the sclera) and the entire conjunctiva.Indicated in cases of purulent inflammation of the eye, anterior segment injury, rupture of the eyeball that can no longer be preserved, loss of function of the eye that cannot be treated conservatively, pain, irritation, need to install an eye fake... Laryngeal mask anesthesia is a method of general anesthesia with a laryngeal mask placed for the purpose of controlling breathing during surgery. Laryngeal mask anesthesia is indicated in intraocular surgery, with advantages such as:
Easy to perform and control the patient's airway. Especially suitable in case of difficult or impossible prognosis for intubation. The greatest advantage of the laryngeal mask over other supraglottic airway devices is ease of placement, allowing rapid airway control. Laryngeal mask ensures better O2 supply, laryngeal mask causes less cough reflex as often seen in endotracheal use, less sympathetic reflexes (increased blood pressure, increased heart rate) than when placed or during extubation. Laryngeal masking also reduces the need for anesthetic and reduces the incidence of sore throat compared with endotracheal intubation. Laryngeal mask anesthesia in ophthalmic surgery does not require the use of muscle relaxants, so it also avoids the side effects caused by the use of muscle relaxants: residual muscle relaxants, respiratory failure, pneumonia...
2. Indications and contraindications of laryngeal mask anesthesia in intraocular surgery
Indications:Patients with contraindications to anesthesia for ophthalmic surgery. Anesthesia does not guarantee pain control for surgery. Patients with neuromuscular disease cannot use muscle relaxants during endotracheal anesthesia. Patients with indications for endotracheal anesthesia predict difficult intubation, or failed intubation. Contraindications
Insufficient means of resuscitation. The operator has little experience and is not technically proficient. Contraindicated with the use of Laryngeal Mask.

3. Anesthesia procedure for laryngeal mask in intraocular surgery
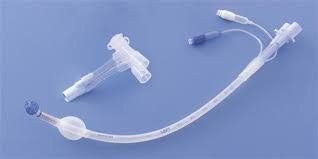
Preparation: Laryngeal masks of various sizes, other airway control devices to prevent laryngeal masks from being placed, splints suitable for masks, bronchial and oral suction catheters, squeeze balloons, suction machines, ventilators .Steps to proceed
Step 1: Vacuum the ball, lubricate the back of the mask.
Step 2: Initiate anesthesia.
Put a masque for the patient to breathe 100% oxygen Most people start with fentanyl, then use sleeping pills (Propofol), muscle relaxants if necessary. Do not use muscle relaxants in patients with neuromuscular disease. Step 3: Place the laryngeal mask.
Have the patient lie on his or her back. Place the laryngeal mask according to the technique of the index finger holding the mask such as holding a pen with the tip of the index finger placed at the junction between the mask and the tube, pushing the mask to slide along the upper wall of the palate towards the back of the pharynx, then slide it to the vestibule of the larynx. Put the mask in place, the laryngeal mask lies face down on the vestibule of the larynx. Step 4: When the mask is in position, pump the cuff. Check that the mask is in place, then secure the tube with two strands of tape.
Step 5: Maintain deep enough anesthesia with evaporative anesthetic, ensure surgery and mechanical ventilation through the anesthetic machine.
Step 6: Get rid of anesthesia after finishing surgery.
4. Accidents and handling
Difficult to place: Do not try to push, check that the head of the laryngeal mask does not roll, lean against the back wall of the pharynx, let the head tilt to the maximum, push the lower jaw forward. Consciousness during surgery: Due to superficial anesthesia, surgery causes pain. Increase anesthesia, add pain reliever. Inhalation of vomit into the lungs: Prophylaxis by telling the patient to fast. Using a double-bore larynx mask, one tube can be inserted into the stomach to aspirate fluids and secretions. Injuries when putting on masks due to too rough movements: Rarely, the technique needs to be done gently. Changes in hemodynamics: increased pulse, increased blood pressure during laryngeal mask placement: Ensure appropriate anesthesia and analgesia during laryngeal mask placement. Master. Doctor Ta Quang Hung has over 10 years of experience in teaching and practicing in the field of Anesthesia and Resuscitation. Currently, working as an Anesthesiologist, General Surgery Department - Vinmec Danang International HospitalPlease dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MORE
Eye surgeries performed at Vinmec hospital Mechanism of sympathetic inflammatory eye disease What do you know about ocular hypertension?