This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Ta Quang Hung - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang. The doctor has more than 10 years of experience in teaching and practicing in the field of Anesthesia.CSF arachnoid cysts are benign tumors, accounting for about 1% of intracranial lesions. Laryngeal mask anesthesia is an anesthetic technique used in endoscopic surgery to break arachnoid cysts of cerebrospinal fluid.
1. What is cerebrospinal fluid arachnoid cyst?
Subarachnoid cysts are cystic lesions containing cerebrospinal fluid, mainly congenital. These are congenital lesions that arise during development.Arachnoid cysts are usually benign and account for about 1% of intracranial lesions. The incidence of CSF arachnoid cysts in men is 2-3 times higher than in women.
With small and asymptomatic arachnoid cysts will be treated conservatively. If there are clinical symptoms that determine the cause from the cyst or the cyst is too large to press heavily on the brain structure, surgical intervention is required.
Some of the currently applied treatment methods are: Fine-needle aspiration cyst, surgically opening the cyst into the normal CSF-containing spaces, shunt draining into the intra-abdominal peritoneal cavity.
2. Laparoscopic surgery to destroy arachnoid cysts with cerebrospinal fluid
2.1 Indications for laparoscopic surgery Indications for laparoscopic surgery for the following types of arachnoid cysts:Arachnoid cysts in the pituitary fossa Arachnoid cysts in the cerebellar pons. ) Paraventricular arachnoid cyst Temporal arachnoid cyst. 2.2 Contraindications for laparoscopic surgery There are no contraindications to endoscopic methods in the treatment of arachnoid cysts. This endoscopic approach will be about 50% successful for temporal arachnoid cysts and 95% successful for pituitary arachnoid cysts.
3. Anesthesia with laryngeal mask endoscopic surgery to destroy arachnoid cysts of cerebrospinal fluid

Indication for laryngeal mask anesthesia in the following cases:
Selected when intubation is difficult, especially difficult to ventilate or cannot be ventilated. Airway and respiratory control in general anesthesia for certain surgeries Temporary airway and respiratory control in the emergency department. Contraindicated in case:
Stomach full. Maxillofacial trauma complicated by trauma or infection Insufficient means of anesthesia and resuscitation.
4. Steps to administer laryngeal mask anesthesia
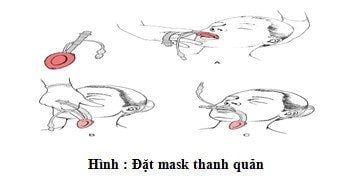
Step 1: Lie on your back, breathe 100% oxygen 3-6 l/min at least 5 minutes before induction of anesthesia.
Step 2: Install the monitor
Step 3: Set up an effective transmission line.
Step 4: Pre-anesthesia (if necessary)
Step 5: Initiating anesthesia
Step 6: Perform the technique of placing a laryngeal mask
Place the patient's head in an intermediate or slightly supine position Hold the laryngeal mask as if holding a pen or finger Place the index finger at the junction between the laryngeal mask and the tube part One hand opens the patient's mouth The other hand brings the laryngeal mask through the dental arches to the base of the tongue, resting the back of the mask on the hard palate, pushing the mask to slide along the hard palate. to enter the hypopharynx Stop on resistance Inflate the cuff according to the volume indicated on the laryngeal mask. Check the tightness of the laryngeal mask (no air leak, easy ventilation) Check the correct position of the laryngeal mask by auscultation and EtCO2 results Fixed with adhesive tape. Step 7: Maintain anesthesia
Maintain anesthesia with intravenous or volatile anesthetics, pain relievers and muscle relaxants (if needed). Control breathing by machine or hand squeeze. Monitoring the depth of anesthesia based on heart rate, blood pressure, sweating, lacrimation (PRST); MAC, BIS and Entropy (if any)... Monitor vital signs: heart rate, blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2, body temperature. Preventing the wrong position, retraction, folding, and obstruction of the laryngeal mask. Criteria for withdrawing laryngeal mask
Patient awake, follow orders. Head elevation for more than 5 seconds, TOF > 0.9 (if muscle relaxants are used). Breathe spontaneously, breathing rate within normal limits. Pulse and blood pressure are stable. Body temperature > 350 C. No complications of anesthesia and surgery.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.