This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor II Dinh Van Loc - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Postural neurosurgery began to gain attention and development after 1914, but it was not until the advent of microsurgery in neurosurgery practice, respiratory anesthetics and muscle relaxants, and current monitoring devices. In modern times, the complexity of the surgery in the sitting position is really partly solved. However, because it is an unusual position in surgery, anesthesia for brain tumor surgery in the sitting position also has certain risks and benefits.
1. What is a brain tumor?
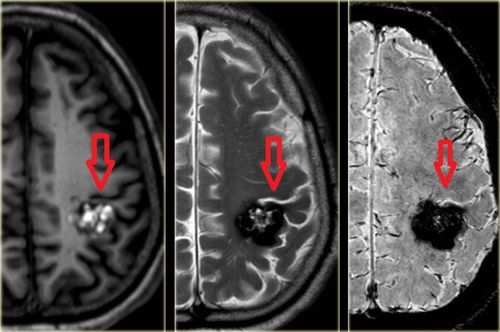
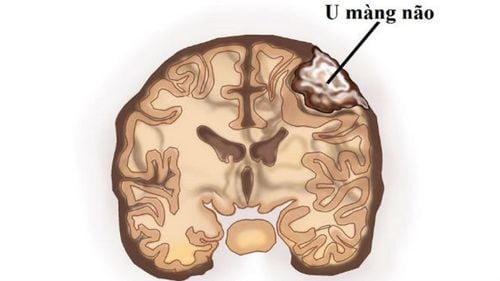
Brain tumor is a conventional name to refer to intracranial tumors because actually tumors in brain tissue account for only about half of intracranial tumors, the rest can be meningioma, tumors of vascular origin.The goal of surgery to treat brain tumors is to remove the tumor and not cause damage to healthy brain tissue. However, this goal is highly dependent on other factors such as tumor location, tumor size, tumor volume, or surgical expertise. There are tumors that cannot be completely removed such as meningioma, brain tumor deep in the medulla, brain stem and large blood vessels, skull base because it is close to the respiratory and cardiovascular centers, difficult to stop bleeding.
2. Matters needing attention when anesthesiology resuscitation in brain tumor surgery sitting position
Each type of brain tumor can cause 3 syndromes, including:Increased intracranial pressure syndrome : Headache, nausea, vomiting, vision disturbances or loss of consciousness Partial or generalized seizures Signs Focal nerves From the perspective of anesthesia, increased intracranial pressure can be obvious or subtle, so it is necessary to monitor intraoperatively. Brain tumor surgery is aimed at treating the cause, which in most cases of preoperative ICP is compensated by CSF volume depletion or hypovolemia due to corticosteroid therapy and diuretic therapy. osmotic. Therefore, the anesthesiologist must avoid all factors that contribute to intracranial decompensation, such as increased CO2, decreased mean arterial pressure, or pain.
Anesthesia The basic method used is general anesthesia with artificial ventilation and the selection of anesthetics that have little effect on intracranial pressure. In the operating room, the anesthesiologist needs to deal with 2 stages of the patient's life: the closed brain phase (controlling intracranial pressure and mean arterial pressure) and the open brain phase (ensures the brain is not damaged). edema to facilitate the surgeon's work)
In addition, the anesthesiologist should also pay attention to the following issues:
Return of the jugular vein: If there is obstruction of venous blood from the brain to return evenly, can be the cause of cerebral edema, incorrect posture or inappropriate breathing mode (the head is always in an upright position to avoid obstructing blood return) PaCO2: Reducing CO2 is the fastest and most effective way to create Cerebral vasoconstriction, reducing cerebral blood flow and blood volume but need to be reduced within a safe range (30-35 mmHg) because below 25 mmHg can cause vasoconstriction leading to cerebral ischemia and cerebral edema Anesthesia: When choosing The ideal anesthetic agent should satisfy three conditions: maintain a constant or slightly increased flow/oxygen consumption ratio, have cerebral vasoconstrictor properties, and maintain a constant PPC above 60-80 mmHg and have a beneficial effect. use on electricity o Infusion: It is necessary to choose infusion based on 2 factors: osmotic pressure and colloidal pressure. Commonly used solutions are NaCl 0.9%, Albumine, Hydroxylethylamidon. Solutions containing glucose should be avoided and be aware that Hydroxylethylamidone can cause clotting disorders
3. Notes on the patient's province after surgery
After the surgery, the anesthesiologist needs to choose for the patient to wake up early or slowly depending on the condition of the patient and the operating room. Each designation will have different advantages and disadvantages.Early awakening: Being awake and extubating right in the operating room
Advantages: Assessing the neurological status and being able to return to surgery in time when needed, assigning necessary tests early , patients have less hypertension and increased catecholamine secretion, easier and simpler transportation of patients to the postoperative room Cons: Patients are at risk of hypoxia and hypercapnia, difficult to monitor and treat in At the time of transportation to the postoperative room, patients who want to wake up soon need to have no preoperative consciousness disorder, uncomplicated surgery, surgery time less than 6 hours, hematocrit above 25%, no risk of complications. due to mixed nerve damage or autonomic nerve center and hemodynamically stable Slow awakening: Wake up and remove the endotracheal tube in the postoperative room after controlling hemodynamic status, cerebral edema,...)
Advantages: To improve the problem of the brain as well as the circulatory and respiratory system for the patient and then let the patient wake up Indicated slow awakening in patients with abnormalities Hemodynamic compromise, hypoxia or hypercapnia, inefficient spontaneous breathing, coagulopathy, muscle relaxation stasis and disturbance of consciousness, intraoperative cerebral edema or convulsions upon awakening
4. Sitting position in brain tumor surgery
The sitting position in brain tumor surgery has many advantages as follows:Allows the surgeon easy access to structures in the midline and pontine-cerebellar angle Helps to drain blood and cerebrospinal fluid, hemispheres the brain is lowered thereby minimizing surgical manipulation. The anesthesiologist can access the patient's airway and monitor with a monitor without much difficulty When resuscitation is needed, the chest wall can be accessed, the diaphragm is free, so ventilation is easier than other positions, the capacity Vitality and functional residual volume are also better. However, the sitting position is often considered dangerous due to potentially life-threatening complications when compared with other positions:
The sitting position can Causes severe hypotension, air embolism, paradoxical air embolism, quadriplegia, and intracranial gas accumulation. Enlarged tongue and peripheral nerve damage occurring at posterior fossa resection are more common in the sitting position than in other positions. Other position Rare but possible bilateral posterior compartment syndrome Semi-lying semi-sitting position with legs at heart level can cause damage to the peroneal nerve by wrapping a bandage at the tip of the fibula or stretching the sciatic nerve Hospital Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in the field of medicine. With the treatment of the disease, patients can completely rest assured that they will be examined and treated for brain tumor surgery at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.