The article was consulted by a gastroenterologist, Department of Internal Medicine, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Anal fissures after childbirth are common among mothers after labor. The condition significantly affects mothers both physically and mentally.
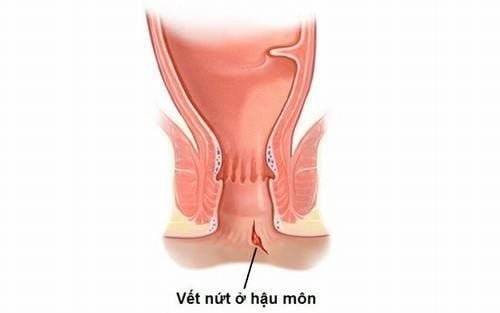
1. What is an Anal Fissure After Childbirth?
An anal fissure after childbirth is a tear in the anal mucosa that causes pain, usually occurring after straining to pass hard stools.
Symptoms of anal fissures after childbirth include severe pain and a burning sensation during and after bowel movements, and bleeding during bowel movements. Anal fissures after childbirth are often mistaken for hemorrhoids because both conditions can cause anal bleeding. However, they are two different issues.
The main cause of anal fissures after childbirth is the sudden contraction of the anus during childbirth and constipation. However, there is no clear cause behind this condition as many patients do not experience constipation. The primary cause of tears or fissures in the anal mucosa is hard stools.
2.What to Do About Anal Fissures After Childbirth?
Treatment for anal fissures after childbirth includes the following methods:
2.1. Non-Surgical Treatment
This is the basic treatment applied to all anal fissures after childbirth to eliminate the causative factors and help increase blood flow to the damaged mucosa. This method can heal up to 90% of acute anal fissures after childbirth.
Preventing constipation or softening stools helps eliminate the causative factors. Patients should drink plenty of water (more than 2 liters/day) and increase fiber intake in their diet, such as vegetables, beans, fruits, etc. Drinking plenty of water is important because it softens the stool, preventing anal damage and recurrence.
Additionally, doctors may prescribe stool softeners to reduce pain and bleeding. Soaking the anus in warm water (40°C) for 10-20 minutes, 3-4 times a day, helps relax the sphincter, increase blood flow, reduce pain, and make patients with anal fissures after childbirth more comfortable. Warm compresses can be applied to the anal area, but care should be taken to avoid skin burns.
Doctors may also prescribe topical ointments from the Nitroglycerin or calcium channel blocker groups to relax the internal sphincter and increase blood flow to the fissure area. This therapy can help heal the condition with a success rate of 65%-90%.
However, side effects of these medications, such as headaches, facial flushing, and hypotension, may prevent patients with anal fissures after childbirth from continuing long-term treatment. Another method is injecting Botox into the internal sphincter to relax it for about 2-3 months. Chronic fissures can heal in 60%-80% of cases, but Botox injections are expensive and often recur.
When lifestyle adjustments and the above treatments do not heal the fissure, acute anal fissures after childbirth can become chronic. At this point, it is necessary to identify other causes of anal fissures after childbirth, such as infections, anal examinations under anesthesia or sedation, and measuring internal sphincter tone to determine hypertonicity. Surgery is the last resort for treating chronic anal fissures after childbirth that do not respond to conservative treatment.
2.2. Surgical Treatment
Medical treatment has advantages such as being repeatable, combining multiple drug groups to increase effectiveness, and having fewer complications. Although surgery can be considered the gold standard, it is applied more than conservative medical treatment due to the risk of complications like fecal incontinence (5%-15%).
Simple surgery involves cutting a part of the internal sphincter (performed under local anesthesia) to reduce pain, relax the muscle, and heal the wound. Patients with anal fissures after childbirth can be discharged the next day, experience pain relief after a few days, and the fissure heals completely after a few weeks. The success rate of surgery is up to 90%. Failure or recurrence may be due to insufficient sphincter cutting, in which case surgery can be repeated on the other side. Excessive sphincter cutting can lead to fecal incontinence.
3.What to Eat for Anal Fissures?

Fiber-rich foods help improve the condition
- Fiber-rich foods: Fiber promotes digestion, softens stools, and helps break down waste in the body for easier elimination. This can prevent constipation, which is beneficial for patients with anal fissures after childbirth. Mothers should eat plenty of green vegetables such as spinach, amaranth, and kale, which are high in fiber to improve the condition.
- Drink plenty of water: Drinking plenty of water aids digestion, softens stools, and reduces constipation, preventing anal fissures after childbirth. Drinking 2 liters of water daily helps detoxify the body, improve digestive function, and prevent constipation.
Additionally, mothers can consume fruit juices such as orange juice, avocado, and almond milk. Fruit juices are rich in vitamins and minerals, providing abundant energy for the body and stimulating the taste buds, creating a sense of appetite.
- Laxative foods: To effectively treat anal fissures after childbirth and prevent recurrence, patients need to address this condition. Mothers should eat laxative foods that stimulate the digestive system to prevent constipation effectively. Some laxative foods to include in meals are sweet potatoes, potatoes, pumpkin, spinach, amaranth, papaya, and black sesame,...
- Iron-rich foods: When experiencing anal fissures after childbirth with bleeding, patients are at risk of blood loss and anemia. Therefore, it is essential to include iron-rich foods in the diet, such as amaranth, chicken liver, and oil-rich seeds (peanuts, sesame, walnuts, almonds).
- Aloe vera: Known as a cooling herb, aloe vera not only has beauty benefits but also treats many diseases. Aloe vera has high antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, reducing pain and preventing infections effectively.
Mothers after childbirth only need to extract the aloe vera gel and apply it around the anus 3 times a day for a month to heal anal fissures. Additionally, aloe vera has cooling properties and detoxifies the body, so it can be combined with daily meals to prevent bloody constipation.
- Olive oil: Olive oil is a natural oil rich in beneficial fats that lubricate the intestines, effectively preventing constipation. Moreover, with anti-inflammatory and moisturizing properties, olive oil helps prevent anal infections and quickly heals wounds, preventing anal fissures after childbirth.
To use olive oil to treat anal fissures after childbirth, mix one tablespoon of olive oil with one tablespoon of honey and one tablespoon of beeswax, then boil. After the mixture cools, apply it to the fissure. Doing this daily will heal the fissure. Additionally, using olive oil as a substitute for daily cooking oil can improve digestion, prevent constipation, and prevent anal fissures after childbirth.
- Coconut oil: Coconut oil contains triglycerides that lubricate the anus, reducing pain during bowel movements. Additionally, coconut oil has antibacterial properties that reduce inflammation in anal fissures after childbirth. This method should be done in the evening before bed for the best results.
- Tamanu oil: Tamanu oil is a natural oil that reduces pain, prevents inflammation, and heals wounds quickly. Use a cotton ball to absorb the solution and apply it to the wound. Doing this twice a day for a month will heal the fissure, reducing anal fissures after childbirth.
Before applying aloe vera, olive oil, coconut oil, or tamanu oil to the wound, clean the anus thoroughly and correctly. Wash the anus with warm water and dry it with a soft towel to avoid damaging the anal fissures after childbirth.
The above methods for treating anal fissures after childbirth are only applicable for mild cases. For severe cases, patients should visit reputable clinics for examination and treatment according to doctors' instructions.