This is an automatically translated article.
Diagnosis of acute malnutrition is based on arm circumference and weight for height because clinical manifestations are often difficult to recognize. If in two factors, arm circumference and weight are lower than the threshold, acute malnutrition is diagnosed.
1. Causes of acute malnutrition
Acute malnutrition is a condition in which the body does not receive enough energy and protein according to the needs. Acute malnutrition can cause stunting or edema.
Children with acute malnutrition are 5-20 times more likely to die than normal children. Causes of acute malnutrition include:
Poor nutritional intake Poor absorption of nutrients due to gastrointestinal disease or after a severe illness, the patient feels no appetite, does not want to eating There are many neuropsychiatric disorders that affect the eating habits of patients such as depression, anorexia nervosa, bulimia and other eating disorders. Infants are not exclusively breastfed for the first 6 months, do not get enough breast milk, and introduce solid foods too early.

Trầm cảm có thể ảnh hưởng đến thói quen ăn uống
2. Diagnosis of acute malnutrition
Diagnosis of acute malnutrition is based on arm circumference and weight-for-height because clinical manifestations are often difficult to recognize. If in two factors, arm circumference and weight are lower than the threshold, acute malnutrition is diagnosed. Specifically:Arm circumference: From >115mm - 125mm (applicable to children 6-59 months old); Weight/height: Weight/height from -3SD to -2SD 2.1. Edema malnourishment The main cause of edematous malnutrition in children is the lack of protein supply. Recognizing signs include:
Edema starting from 2 lower extremities, then the whole body; soft white edema, concave press. Digestive disorders or pneumonia. Based on arm circumference or weight-for-height, it may be normal. The limbs, groin, buttocks often have red spots on the skin, then turn black and peel off, easy to infect and cause patchy. Diagnosed with heart failure, enlarged liver, osteoporosis,... Tests show a decrease in hemoglobin, a decrease in sodium and potassium, an increase in non-essential or essential amino acids,...

Trẻ bị suy dinh dưỡng thể phù
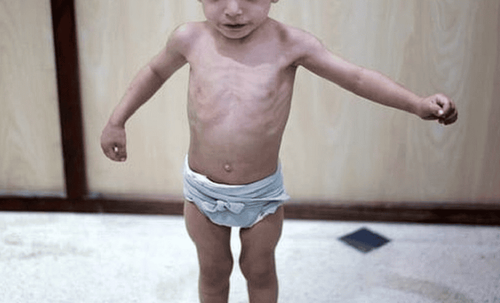
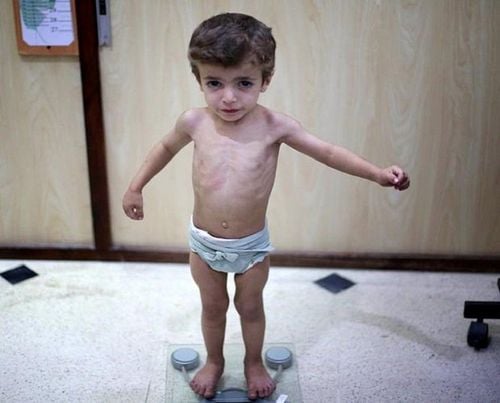
2.2. Malnutrition in stunting form Malnutrition in this form is mainly caused by lack of energy supply. Signs of recognition include:
The child has no fat layer under the skin of the face, limbs, buttocks, so the child is stunted, sunken eyes Dry, wrinkled skin Having appetite or not The child becomes moody, less flexible, fussy . Hematocrit decreased Hematocrit, blood protein decreased Blood sugar and electrolyte changes 2.3. Combined malnutrition is a combination of stunting and edematous malnutrition, caused by children's lack of energy and protein deficiency. Recognizing signs:
Baby's weight drops below 60% of normal baby weight (under - 4SD). Children have edema, but the body is thin, the cheeks are sunken, but there is swelling in the instep of the feet and there may be pigment patches. Children also have poor appetite, or have digestive disorders.
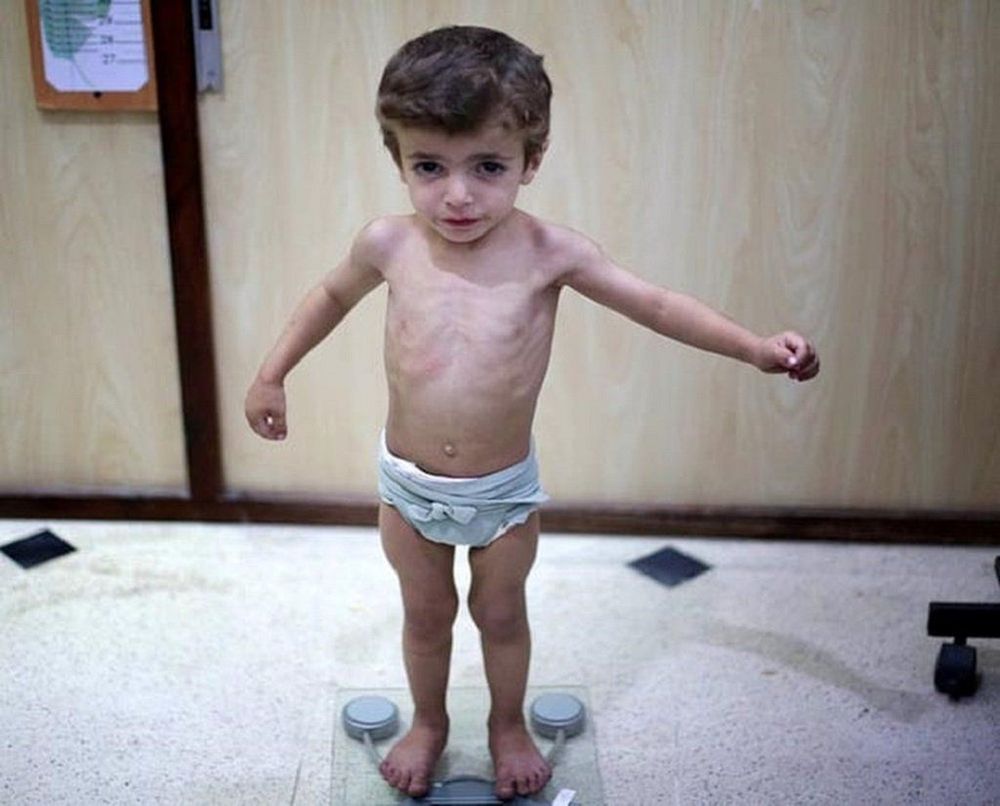
Suy dinh dưỡng phối hợp khi trẻ biếng ăn và bị rối loạn tiêu hóa